Old NCERT Summary (RS Sharma): The Mauryan Empire | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Chandragupta Maurya |

|
| Imperial Organization |

|
| Ashoka (273-232 B.C.) |

|
| Ashokan Edicts |

|
| Impact of the Kalinga War |

|
| Internal Policy and Buddhism |

|
| Asoka’s Place in History |

|
Delve into the captivating epoch of the Mauryan Empire, a pivotal era in Indian history orchestrated by visionary leaders. Uncover the saga of Chandragupta, Ashoka, and their illustrious successors, witnessing how their rule reshaped India's cultural, political, and philosophical landscapes, imprinting an enduring legacy on civilization.
 Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya
- Chandragupta Maurya founded the Maurya dynasty, potentially coming from an ordinary family or the Maurya clan in the Gorakhpur region.
- With the help of Chanakya, he overthrew the weakening Nanda rulers to establish Maurya rule.
- Chandragupta is said to have conquered a large part of India with an army of 600,000, although the accuracy of this claim is debated.
- He liberated north-western India from Seleucus' rule through a victorious war and obtained territories like eastern Afghanistan, Baluchistan, and regions west of the Indus River through a peace deal.
- Chandragupta's reign saw the establishment of a vast empire covering Bihar, Orissa, Bengal, western and northwestern India, and the Deccan, with the Mauryas ruling most of the subcontinent, except for Kerala, Tamil Nadu, parts of north-eastern India, and certain areas in the north-west that were beyond the British Empire's control.
Imperial Organization
Mauryan Administration Overview:
- Detailed system known from Megasthenes' account and Kautilya's Arthasastra.
- Megasthenes, a Greek ambassador, wrote about Pataliputra and the entire Maurya empire.
- Arthasastra, compiled later, still contains genuine information about Mauryan rule
Chandragupta Maurya's Rule:
- Absolute power centralized in the king.
- Council of wise members advised the king, but his adherence to their advice remains unclear.
- Provinces governed by royal family members, further divided into smaller units.
Administration Focus:
- Special attention given to towns like Pataliputra, Kausambi, Ujjain, and Taxila.
- Pataliputra had six committees overseeing various functions, e.g., sanitation, foreign affairs, and record-keeping.
Government Structure:
- Central government managed around two dozen state departments controlling social and economic activities.
Mauryan Military Strength:
- Chandragupta had a large army of 600,000 foot-soldiers, 30,000 cavalry, 9000 elephants, and 8,000 chariots, possibly including a navy.
- Military affairs overseen by a board of officers through six committees, each dedicated to different branches of the armed forces.
Financing the Army:
- State-controlled economic activities to meet army expenses.
- Revenue collected from cultivated land, taxes imposed on peasants, tolls on goods, and state monopolies on mining, liquor, and arms production contributed to the treasury.
Chandragupta Maurya's Legacy:
- Established a well-organized administration and a stable financial base through these measures.
Ashoka (273-232 B.C.)
 Ashoka Chandragupta Maurya passed the baton to Bindusara, whose rule fostered strong ties with Greek princes. But the spotlight truly shines on Asoka, the standout among Mauryan rulers. There's a gripping legend suggesting he was incredibly ruthless, allegedly eliminating 99 brothers to claim the throne. Yet, tales are tales—his biography penned by Buddhist authors is a captivating mix of fact and fiction, making it a fascinating read but not entirely reliable.
Ashoka Chandragupta Maurya passed the baton to Bindusara, whose rule fostered strong ties with Greek princes. But the spotlight truly shines on Asoka, the standout among Mauryan rulers. There's a gripping legend suggesting he was incredibly ruthless, allegedly eliminating 99 brothers to claim the throne. Yet, tales are tales—his biography penned by Buddhist authors is a captivating mix of fact and fiction, making it a fascinating read but not entirely reliable.
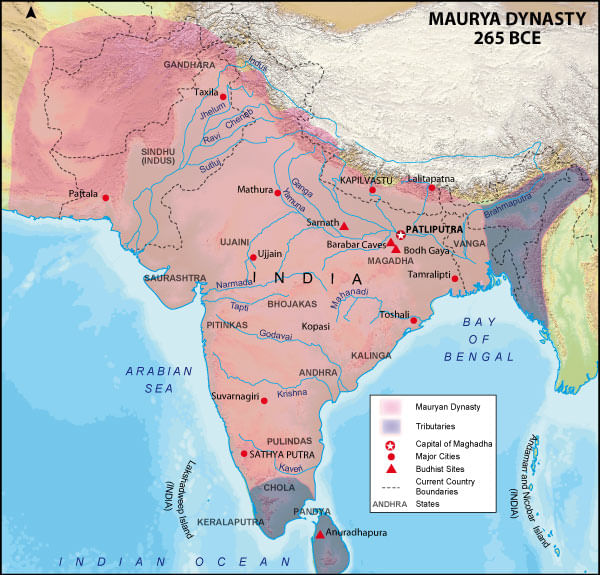 Mauryan Empire
Mauryan Empire
Ashokan Edicts
 Edicts
Edicts
Asoka's Historical Insights from Inscriptions
- Asoka pioneered direct communication with people through inscriptions.
- Inscriptions found on rocks, polished stone pillars with capitals, and caves.
- Spread across the Indian subcontinent and extended to Kandahar in Afghanistan.
- Comprised 44 royal orders, each with multiple copies.
Language and Scripts Used
- Inscriptions primarily in Prakrit language and Brahmi script across most of the empire.
- In the north-western regions, inscriptions appeared in the Kharosthi script.
- In Kandahar, Afghanistan, inscriptions in Aramaic using Greek script and language.
Placement of Inscriptions
- Generally positioned along ancient highways.
Information Revealed
- Insights into Asoka's life, his domestic and foreign policies, and the expanse of his empire.
Impact of the Kalinga War
 Destruction from Kalinga war
Destruction from Kalinga war
- Asoka, influenced by Buddhism, altered policies after the remorseful Kalinga war, shifting from physical conquest to cultural influence.
- Despite this shift, he didn't entirely abandon militaristic actions but aimed to expand his empire through ideological means.
- The Kalinga conflict deeply affected Asoka, prompting a strong embrace of Dhamma and remorse for the suffering caused.
- He prioritized propagating Dhamma among his people, extending welfare measures to new territories, including care for animals.
- Asoka emphasized obedience and trust in his rule, sending peaceful envoys to Greek kingdoms as part of his diplomatic efforts.
- While advocating peace and Dhamma, Asoka didn't become an extreme pacifist, retaining conquered lands and maintaining a substantial military force.
- He appointed officials to enforce social norms and righteousness, rewarding or punishing as necessary within his empire.
- Asoka's approach proved successful, with inscriptions highlighting the positive impact of his policies on nomadic groups, leading them to adopt settled agricultural lives and abandon hunting.
Internal Policy and Buddhism
- Asoka turned to Buddhism after the Kalinga war, reportedly becoming a monk and supporting Buddhist causes generously.
- He undertook pilgrimages to Buddhist shrines, as hinted by inscriptions mentioning his 'dharma yatras'.
- Tradition claims a Buddhist council was chaired by Asoka's brother, sending missionaries to South India, Sri Lanka, and Burma, supported by Brahmi inscriptions found in Sri Lanka.
- Asoka upheld a paternal kingship ideal, urging officials to care for citizens as his own children and appointing officials to promote Dhamma among various societal groups, including women.
- He prohibited certain rituals, especially those involving women, and banned animal slaughter in the capital while discouraging extravagant social gatherings.
- Asoka's Dhamma aimed at preserving social order, advocating respect for parents, Brahmins, and Buddhist monks, and compassion for slaves and servants.
- His teachings focused on tolerance, compassion for animals, proper conduct with relatives, and upheld existing social structures without promoting any particular sectarian faith.
- While stressing the rewards of heaven through good behaviour, Asoka's teachings didn't emphasize attaining nirvana, aligning with broader societal harmony over specific religious goals.
Asoka’s Place in History
Asoka's Achievements
- Political Unity: Unified India politically, promoting a single dharma, language (Sanskrit), and script (Brahmi) through inscriptions.
- Tolerance and Inclusivity: Respected various languages and religious sects, including non-Buddhist ones, fostering a tolerant religious policy.
- Missionary Zeal: Sent officials across the empire to administer and promote cultural exchanges between regions.
- Cultural Spread: Extended the central Gangetic basin's material culture to regions like Kalinga, lower Deccan, and northern Bengal.
Pacifist Policy
- Peace and Non-Aggression: Advocated a policy of peace, non-aggression, and cultural expansion, unprecedented in his time.
- Unique Stance: Unlike predecessors and apart from Egypt's Akhnaton, Asoka was exceptional in pursuing peaceful strategies despite possessing a significant army.
- Counsel to Successors: Advised successors to abandon aggressive policies, a progressive move for his era.
Impact and Limitations
- Limited Endurance: Asoka's peaceful approach didn't endure beyond his rule, as viceroys and vassals asserted independence after his reign.
- Neighbouring States: Failed to influence neighbouring states, leading to incursions within 25 years of his departure from power in 232 B.C.
|
110 videos|652 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Old NCERT Summary (RS Sharma): The Mauryan Empire - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. Who was Chandragupta Maurya? |  |
| 2. What was the administration like under Chandragupta Maurya? |  |
| 3. Who was Bindusara? |  |
| 4. What were the policies of Ashoka? |  |
| 5. How was Ashoka's administration different from his predecessors? |  |
















