Old NCERT Summary (Satish Chandra): India & the World | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Europe |

|
| Growth of Feudalism |

|
| The Arab World |

|
| East and South East Asia |

|
Introduction
Between the eighth and eighteenth centuries, significant transformations occurred in both India and the broader global context. Europe and Asia witnessed the emergence of novel social and political structures, influencing the perspectives and lifestyles of their respective populations. These developments also left a lasting imprint on India due to its extensive trade and cultural ties with regions surrounding the Mediterranean Sea, including interactions with influential empires like the Romans and Persians.
Europe
I. Roman empire broken into two by 6th century:
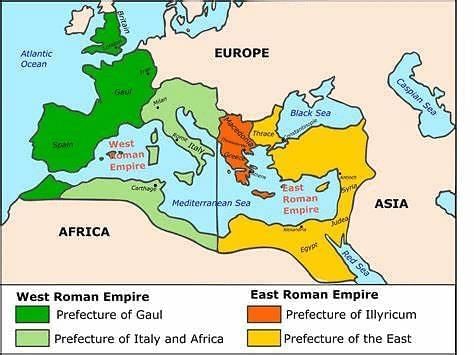
- By the 6th century, the Western Roman Empire, centered around Rome, faced invasions and pressure from various Germanic and Slavic tribes, leading to its eventual collapse.
- The Western Roman Empire primarily followed Catholicism and struggled to maintain its unity amidst external threats.
- In contrast, the Eastern Roman Empire, known as the Byzantine Empire, thrived with its capital in Constantinople.
- The Byzantine Empire encompassed territories in Eastern Europe, Turkey, Syria, and North Africa, serving as a cultural and religious bridge between Greco-Roman civilization and the Arab world.
- The Greek Orthodox Church was predominant in the Byzantine Empire, influencing its cultural and religious landscape.
II. Byzantine Influence and Decline
Role of Byzantium:
- The Byzantine Empire played a significant role in mediating between Greco-Roman traditions and emerging Arab civilizations.
- Its strategic location facilitated trade and cultural exchange between East and West.
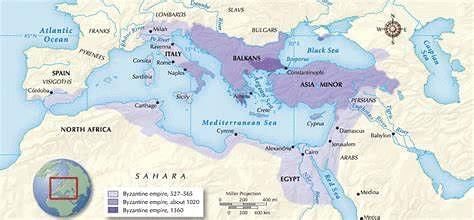
Fall of Byzantium:
- Despite its cultural and military achievements, the Byzantine Empire faced internal strife and external pressures.
- Constantinople fell to the Ottoman Turks in the mid-15th century, marking the end of Byzantine rule and the beginning of Ottoman dominance in the region.
III. Transition into the Dark Ages and Revival
Collapse of the Western Roman Empire:
- Following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, Europe entered a period often referred to as the "Dark Ages."
- Urban centers declined, trade networks faltered, and there was a general disruption in governance and social order.
Revival and Rebuilding:
- Despite the challenges, pockets of civilization continued to thrive, particularly in the Byzantine and Islamic worlds.
- By the 10th century, Europe began to experience a revival characterized by the rebuilding of urban centers, the revitalization of trade routes, and the emergence of new centers of learning and innovation.
IV. The High Middle Ages and the Prelude to the Renaissance
Rapid Progress and Prosperity:
- From the 12th to the 14th century, Europe witnessed a period of rapid progress and prosperity known as the "High Middle Ages."
- Advancements in agriculture, technology, and commerce fueled economic growth and social development.
Establishment of Universities:
- The establishment of universities across Europe, such as the University of Paris and the University of Bologna, facilitated the dissemination of knowledge and the exchange of ideas.
- Scholars from diverse backgrounds congregated in these centers of learning, laying the foundation for intellectual inquiry and innovation.
Transition to the Renaissance:
- The intellectual ferment of the High Middle Ages paved the way for the Renaissance, a transformative period that spanned from the 14th to the 17th century.
- The Renaissance was characterized by a renewed interest in classical learning, art, and literature, marking a cultural and intellectual rebirth that reshaped European society and laid the groundwork for the modern world.
Growth of Feudalism

I. Feudal System in Europe
Dominance of Chiefs and the King:
- The most powerful elements were the chiefs who dominated large tracts of land with military power and played an important part in governance.
- The king was effectively the most powerful feudal chief, controlling other chiefs by making them take an oath of loyalty as vassals.
- Tensions arose from time to time between the king and the vassals (fiefs). Government was thus dominated by a landed aristocracy, which was hereditary.
Key Features of Feudalism:
- Landed aristocracy held significant influence, with power often inherited within noble families.
- Serfdom and the Manor system were integral components, where peasants (serfs) were obliged to work the land and provide a portion of their produce to the landlord.
- Military organization was structured around feudal obligations, with lords responsible for raising and maintaining armed forces.
II. Serfdom and Manor System
Definition of Serfs and Manor:
- Serfs = peasants who had to compulsorily work on the land.
- Manor = the house where the landlord lived. Serfs had to cultivate the lands surrounding the manor and give a part of the produce to the landlord.
- Landlords held authority over the manor, administering justice and enforcing law and order.
III. Evolution of Warfare and Military Organization
Impact of Cavalry and Technological Advancements:
- Cavalry gained popularity in warfare because of the iron stirrup and a new harness, which allowed the horse to pull twice the weight it could earlier.
- These inventions came to the West from East Asia and were introduced in India from the 10th century.
Decentralization of Military Power:
- As armies grew in size, kings found it increasingly challenging to manage them centrally.
- Consequently, military responsibilities were decentralized, with feudal lords assuming command over their own armed forces.
- In many cases, lords collected taxes from the peasantry, remitted tributes to the king, maintained armies, and utilized the remaining resources for personal consumption.
IV. Feudalism in India
Local Fiefs (Samantas):
- In India, local fiefs (Samantas) exercised similar powers, with the peasantry dependent upon them.
V. Role of the Catholic Church in Europe
Political and Moral Authority:
- The Catholic Church played pivotal roles in shaping both political structures and cultural life in medieval Europe.
- Through its moral authority, the Church influenced societal norms and values, guiding the conduct of rulers and subjects alike.
Social Welfare and Educational Institutions:
- Many monastic orders and denominations were established from revenue obtained from tax-free land grants by feudal chiefs and kings.
- Churches served the poor and needy, provided medical aid and shelter to travellers, and served as centres for education and learning.
The Arab World
Islam united warring Arab tribes into a powerful empire.
I. Rise of Islam and Early Conquests
Prophet Muhammad (570-632 A.D):
(a) He is the founder of Islam.
(b) He grew up in the deserts of Arabia.
(c) His first converts were the Arabs.
(d) Sind and Multan were conquered by the Arabs by 712 A.D.
II. Abbasid Empire and Its Influence
Abbasids in Baghdad:
- Abbasids came to power as Caliphs at Baghdad in middle of 8th century. Claimed to belong to same tribe as prophet Muhammad. Most powerful empire for ~150 yrs.
- Controlled parts of North Africa, Egypt, Syria, Iran and Iraq and important trade routes connecting India and China with the Mediterranean.
- Region attained prosperity by levying taxes on trade and due to enterprising Arab merchants.
Assimilation of Knowledge:
- Arabs assimilated scientific knowledge and administrative skills of empires they had overrun.
- Many Chinese inventions like compass, paper, printing, gun powder reached Europe from China through Arabs
House of Wisdom (Bait-ul-hikmat):
Established in Baghdad, translated works from various civilizations into Arabic, fostering intellectual exchange and advancement.
India did not enjoy close cultural contact with Arabs until Sindh was conquered in 8th century.
- Decimal system reached Arabs from India after this and was popularized by Al-Khwarizmi.
- Suryasiddhanta (Astronomy - Aryabhatta) and Charaksamhita,Sushrutsamhita were also translated.
III. Arab Invasion in India: Muhammad bin Qasim
Conquest of Sind:
- Al-Hajjajj, the Governor of Iraq sent Muhammad-bin-Qasim to India
- He Conquered Sind with the permission of Caliph Walid
Battle of Rewar
- Fought between Muhammad-bin-Qasim and Dahir the ruler of Sind
- Dahir was defeated. Sind and Multan was captured.
- Muhammad-bin-Qasim called Multan as "City of Gold".
Administrative System
- Sind and Multan were divided into number of Iqtas or districts by Muhammad-bin-Qasim and Arab military officers headed the Iqtas.
- The sub-divisions of the districts were administered by the local Hindu Officers.
- Jizya was imposed on non-Muslims.
Muhammad bin Qasim's Army
- 25,000 troops with 6000 Camels, 6000 Syrian horses, 3000 Bactrian Camels and an artillery force with 2000 men, advanced guards, and five catapults.
(v) End of Muhammad-bin-Qasim
- Caliph Walid was succeeded by Caliph Sulaiman.
- He was an enemy of Al-Hajjaj, the Governor of Iraq.
- Muhammad-bin Qasim was the son-in-law of Al-Hajjaj, so he dismissed him and sent to Mesopotamia as a prisoner where he was tortured to death.
- For more than 150 years, Sind and Multan continued to remain as the part of the Caliph's Empire.
(vi) Rani Bai's heroic defense against Muhammad bin Qasim
- The wife of Dahir and the other women of Sind put up a heroic defense within the Fort of Rewar.
IV. Legacy and Impact
Spread of Islam in India:- Arab conquest paved the way for Islam's penetration into India.
Effects of Arab Conquest
- The subjugation of Sind made way for Islam into India.
- The art of administration, astronomy, music, painting, medicine and architecture were learnt by Arabs from our land and they spread astronomy, Indian Philosophy, and numerals to Europe.
Indian Impact
- Brahma Siddhanta- a Sanskrit work of Brahmagupta was translated into Arabic in which the names of Indian Scientists like Sindbad, Bhala, Manaka are mentioned.
In a hospital at Baghdad, Dhana was appointed as a chief Medical officer. - A serious disease of Caliph Harun-al-Rashid was cured by physician Manaka.
- Europe stagnated due to rigid Catholic Church doctrines. India also did not progress much. Arab science declined after the 14th century due to growing orthodoxy and political changes.
East and South East Asia
I. Tang and Mongol Dynasties in China
- Reached its zenith during this period, fostering a prosperous era marked by cultural and economic growth.
- Facilitated extensive trade with the West along the Silk Route, exporting a plethora of goods.
- Mongol invasion in the 13th century capitalized on the Tang dynasty's weakening state, ultimately leading to its demise.
- Unified North and South China through disciplined and mobile cavalry tactics.
- Mongol rule extended to Vietnam and Korea, with famous encounters with figures like Marco Polo, who visited the court of Kublai Khan.
II. Sailendra Dynasty in Southeast Asia
Territorial Influence:
- Dominated Palembang (Sumatra), Java, Malay Peninsula, and parts of Thailand.
Cultural and Religious Centers:
- Sanskrit and Buddhist centres of learning
- Famous for Borobudur Temple – a mountain carved into nine terraces, surmounted by a stupa
III. Kambuja Dynasty in Cambodia and Annam
Temple Complexes:
- Located in Cambodia and Annam (South Vietnam)
- Angkor Thom complex (~200 temples in 3.2 sq. km); the largest is Angkor Wat
- Temples have statues of gods, goddesses, and nymphs.
Cultural Influence:
- Temples served as inspiration for literature, folk dances, songs, puppets, and statues, contributing to the region's rich cultural heritage.
- Flourishing of Buddhism, coinciding with its decline in India, with the incorporation of Hindu deities into Buddhist practices.
Traders from various parts of the world visited Southeast Asia, leading to cultural mingling.
- Religious tolerance existed. Indonesia and Malaya were converted to Islam only after its consolidation in India.
- Elsewhere, Buddhism continued to flourish.
- Commercial and cultural contacts were eventually snapped after the arrival of the British and Dutch in the 17th century.
|
228 videos|855 docs|219 tests
|
FAQs on Old NCERT Summary (Satish Chandra): India & the World - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. How did feudalism develop in Europe? |  |
| 2. What was the role of the Arab World during this time period? |  |
| 3. How did feudalism differ in East and South East Asia compared to Europe? |  |
| 4. What impact did the growth of feudalism have on society in Europe? |  |
| 5. How did India interact with the rest of the world during this time period? |  |





















