Olympiad Notes: Metals and Non-Metals | Olympiad Preparation for Class 10 PDF Download
Introduction
Elements can be classified as metals and non-metals on the basis of their properties.
- Examples of some metals are: Iron (Fe), Aluminium (Al), Silver (Ag), Copper (Cu)
- Examples of some non-metals are: Hydrogen (H), Nitrogen (N), Sulphur (S), Oxygen (O)
Chemical Properties of Metals
The reaction of metals with air
Metals combine with oxygen to form metal oxide.
Metal + O2 → Metal oxide
examples:
(i) 2Cu + O2 → 2CuO
Copper oxide (black)
(ii) 4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3
Aluminium oxide
(iii) 2Mg + O 2 → 2MgO
The reactivity of different metals is different from O2.
Na and K react so vigorously that they catch fire if kept open so they are kept immersed in kerosene.
- Surfaces of Mg, Al, Zn, Pb are covered with a thin layer of oxide which prevents them from further oxidation.
- Fe does not burn on heating but iron fillings burn vigorously.
- Cu does not burn but is coated with black copper oxide.
- Au and Ag do not react with oxygen.
Amphoteric Oxides: Metal oxides that react with both acids as well as bases to produce salts and water are called amphoteric oxides.
Examples:
(i) Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + H2O
(ii) Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
Sodium Aluminate
Reaction of Metals with Water
- Metal + Water → Metal oxide + Hydrogen
- Metal oxide + Water → Metal hydroxide
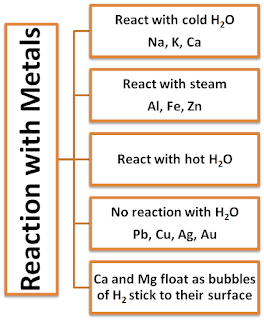
Examples:
(i) 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 + Heat
(ii) Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
Reaction of metals with acids (Dilute)
Metal + Dilute acid → Salt + H2
Cu, Ag, Hg do not react with dil. acids.
Examples: Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2
Reaction of Metals with Solutions of other Metal Salts
- Metal A + Salt solution B → Salt solution A + Metal B
- Reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their compounds in solution form.
Fe + CuSO4→ FeSO4 + Cu
Reactivity Series
The reactivity series is a list of metals arranged in the order of their decreasing activities.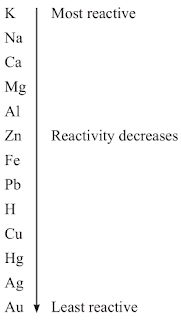
The reaction of Metals with Non-metals
- The reactivity of elements is the tendency to attain a completely filled valence shell.
- Atoms of the metals lose electrons from their valence shell to form a cation. An atom of the non-metals gains electrons in the valence shell to form an anion.
Ionic Compounds
The compounds formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal are called ionic compounds or electrovalent compounds.
- Physical nature: They are solid and hard, generally brittle.
- Melting and Boiling Point: They have high melting and boiling point.
- Solubility: Generally soluble in water and insoluble in solvents such as kerosene, petrol etc.
- Conduction of electricity: Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten and solution form but not in the solid state.
Occurrence of Metals
- Minerals: The elements or compounds which occur naturally in the earth’s crust are called minerals.
- Ores: Minerals that contain a very high percentage of particular metal and the metal can be profitably extracted from it, such minerals are called ores.
Extraction of Metals from Ores
- Step 1. Enrichment of ores.
- Step 2. Extraction of metals.
- Step 3. Refining of metals.
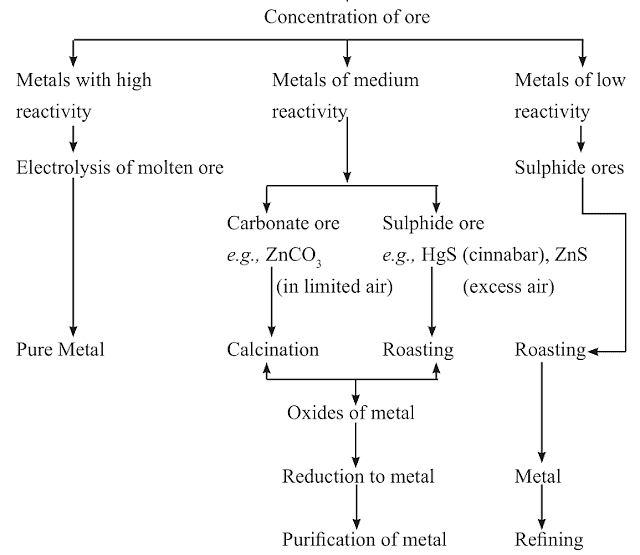
Steps Involved in Extraction of Metals from Ores
Gangue → Roasting → Calcination → Reduction
Important terms
(a) Gangue: Ores are usually contaminated with large amount of impurities such as soil, sand etc. called gangue.
(b) Roasting: The sulphide ores are converted into oxides by heating strongly in the presence of excess air. This process is called roasting.
2ZnS + 3O2 →(Heast) 2ZnO + 2SO2
(c) Calcination: The carbonate ores are changed into oxides by heating strongly in limited air. This process is called calcination.
ZnCO3 →(Heat) ZnO + CO2
(d) Reduction: Metal oxides are reduced to corresponding metals by using reducing agent like carbon.
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
Refining of Metals
The most widely used method for refining impure metal is electrolytic refining.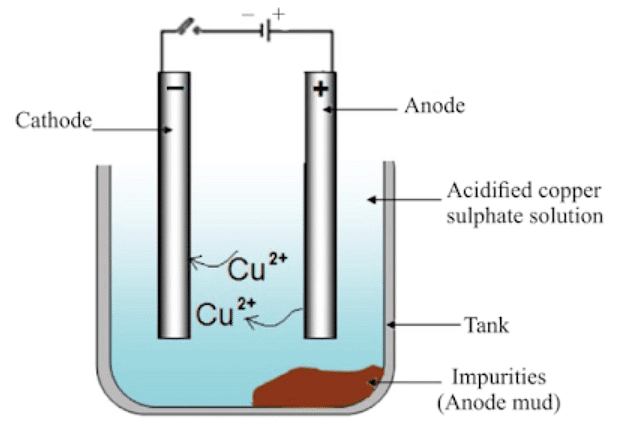
- Anode: Impure copper
- Cathode: Strip of pure copper
- Electrolyte: Solution of acidified copper sulphate
(i) On passing the current through the electrolyte, the impure metal from the anode dissolves into the electrolyte.
(ii) An equivalent amount of pure metal from the electrolyte is deposited at the cathode.
(iii) The insoluble impurities settle down at the bottom of the anode and is called anode mud.
Corrosion
The surface of some metals gets corroded when they are exposed to moist air for a long period of time. This is called corrosion.
Examples:
(i) Silver becomes black when exposed to air as it reacts with air to form a coating of silver sulphide.
(ii) Copper reacts with moist carbon dioxide in the air and gains a green coat of copper carbonate.
Prevention of Corrosion
- The rusting of iron can be prevented by painting, oiling, greasing, galvanizing, chrome plating, anodizing or making alloys.
- Galvanization: It is a method of protecting steel and iron from rusting by coating them with a thin layer of zinc.
- Alloy: An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals or a metal and a non-metal.
Examples of alloy: Iron: Mixed with a small amount of carbon becomes hard and strong.
|
70 videos|242 docs|187 tests
|
FAQs on Olympiad Notes: Metals and Non-Metals - Olympiad Preparation for Class 10
| 1. What are the main properties that differentiate metals from non-metals? |  |
| 2. Can you give examples of common metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. How do metals and non-metals react with oxygen? |  |
| 4. What are some common uses of metals and non-metals in daily life? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of knowing the properties of metals and non-metals in science? |  |
















