Olympiad Notes: Sources of Energy | Olympiad Preparation for Class 10 PDF Download
Introduction
Energy is the ability or the capacity to do work and make all movements. Just as we gain energy in our body from the food that we eat, the same way various sources of energy like coal, petroleum solar energy, hydel, biogas, etc. are used to generate electricity which is the most common form of energy widely used in households and industry.
Sources of Energy
- Energy is the capacity of doing work.
- The truth about energy is that energy can neither be created nor be destroyed, it can only be converted from one form to another.
- The energy present in the matter is invisible. The energy present in nature is primary energy.
- Further, in this article, we will read more about sources of energy.
Good Sources of Energy
- The sources of energy which is needed to obtain energy in the usable form are said to be good sources of energy.
- Also, it must provide an adequate amount of energy in a convenient form over a long period of time.
Need of Energy
We need energy in every aspect of our life, even every life process requires energy. However, some common places where energy is required are:
- In keeping us alive
- To do physical work
- In making food
- Transport
- In machines
Fuels
The sources of energy that burning provides energy to do work are fuels. Some fuels are diesel, petrol, LPG, wood, etc.
Characteristics of Good Fuel
- Have a high calorific value. i.e. releases more heat per unit mass.
- Burns with a little or no smoke.
- Leaves less residue.
- Easily available and accessible
- Inexpensive
- Easy to store and transport
- Burn smoothly
Classification of Sources of Energy
Energy sources are mainly classified as conventional and non-conventional sources of energy.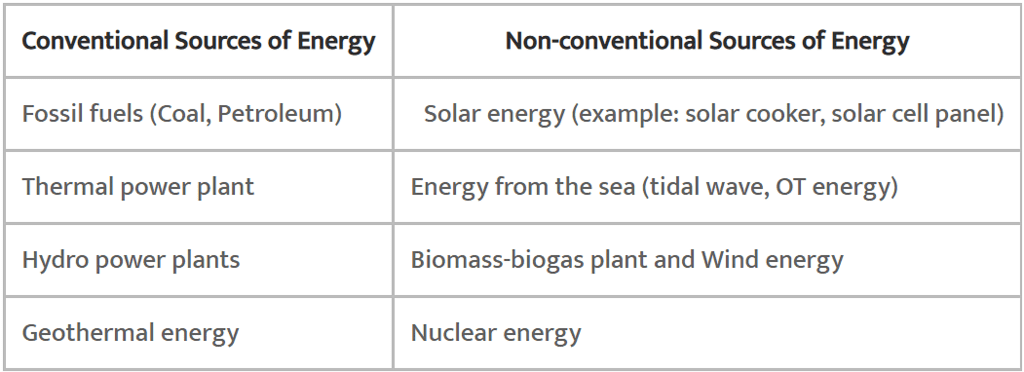 Conventional Source of Energy
Conventional Source of Energy
- Energy source which is fixed in nature like fossil fuels, biomass, etc. is conventional sources of energy.
- Consumption of conventional sources of energy causes greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental damage.
Fossil Fuels
- Fossil fuels are formed from dead and decayed organic matters (plants and animals) after exposure to heat and pressure in the earth’s crust over hundreds of millions of years.
- Coal forms due to the subjection of plant tissues under high pressure and temperature whereas petroleum are obtained from the remains of animals between sedimentary rocks.
- Those buried substances get converted to crude oil, coal, natural gas.
- These are available in limited amounts on this earth.
- These are non-renewable sources of energy.
Disadvantages of Using Fossil Fuels
- Fossil fuel burning releases oxides of Carbon, Nitrogen which damages trees and plants also reduces the fertility of the soil.
- It also releases oxides of Sulphur which is responsible for acid rain.
- The main emission after burning fossil fuels is carbon dioxide which is a greenhouse gas, thus causing a greenhouse effect. (Responsible for melting of glaciers).
Note: We can control the pollution caused by fossil fuels. To control the same we have to increase the efficiency of the combustion process and also by using various techniques to reduce the escape of harmful gases and ashes to surroundings.
Thermal Power Plant
A thermal power plant is a setup in which heat generates electricity by burning coal. Water is heated, turns into steam which spins a steam turbine. The kinetic energy of rotation is converted into electrical energy through the electric generator. The steam produced is sent back to the plants are set up near coal fields in order to make transmission of electric power more economical.
Hydropower plant

- In a Hydropower plant, the kinetic energy of water is used to produce electric energy.
- In this power, plant water is blocked or kept at a height (with stored potential energy) which falls on the turbine connected to the dynamo from a large height thus turbine gets rotated and electricity is produced.
- Hydropower plants are situated near dams.
Advantages of hydropower plants
- No environmental pollution is caused.
- Flowing water is a renewable source of energy.
- Dam construction prevents flooding of rivers and also provides water for irrigation purposes.
Disadvantages of hydropower plant
- A large amount of agricultural land, a wide variety of flora, and fauna gets submerged in the water of the reservoir of the dam.
- Large ecosystems are destroyed.
- Natural vegetation when submerged underwater in anaerobic conditions they produce methane which causes the greenhouse effect.
- People face many social and environmental problems. Also, a dam is much more expensive to construct.
Non-conventional sources of energy
- The energy which is generated by using wind, tides, solar, geothermal heat, and biomass including farm and animal waste as well as human excreta is known as non-conventional energy.
- All these sources are renewable or inexhaustible and do not cause environmental pollution.
- Non-conventional sources of energy are inexpensive.
Biomass
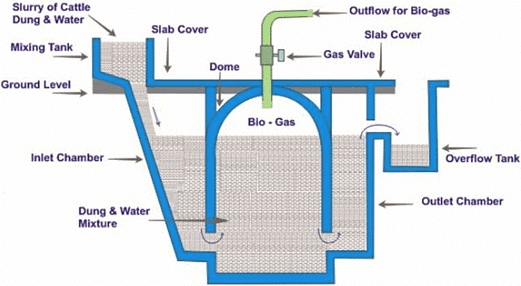
- One must be aware of the use of cow dung as the fuel, but burning dung cakes gives less heat but a lot of smoke. So Advanced technology is needed to increase the efficiency of these fuels.
- When wood is burnt in a limited supply of oxygen and water then charcoal is produced. It burns smokeless and has a higher heat generation efficiency.
- Cow dung, residue after harvesting the crops, vegetable waste, and sewage, when decomposed in the absence of oxygen, produce biogas.
- When the gas is produced by the input material of cow dung, then it is said as ‘gobar gas’.
- Biogas contains up to 75% methane, so it is regarded as an excellent fuel.
- The left slurry in the biogas plant is used as manure which is reached with nitrogen and phosphorous.
Wind Energy

- The blow of wind is caused by unequal heating of landmass and water bodies by solar radiation.
- Blowing wind possesses kinetic energy which can be used by us to obtain a different source of energy.
Uses of wind energy
- We can generate electricity by rotating the turbine of the dynamo with the help of windmills.
- It is also used to lift underground water for irrigation and another purpose.
- Flour and other mills also use the kinetic energy of wind.
- To get a larger amount of energy a large number of windmills are installed infield, this large area of field is called a wind energy farm.
Solar Energy

- The sun is regarded as the ultimate source of energy. It releases an enormous amount of energy and it will continuously release its energy for more than 5 billion years.
- Photovoltaic cells convert solar radiations directly into electricity through silicon solar cells. These photovoltaic cells when arranged on flat sheets are said to be solar panels.
- There are various devices that use solar energy, they are solar cookers, solar cells, solar water heaters, etc.
Energy from the sea
- Sea is said to be a treasure of minerals and resources. Apart from it, Sea is also regarded as a good natural source of energy.
- The several energy consequences related to the sea are given below:
Tidal Energy
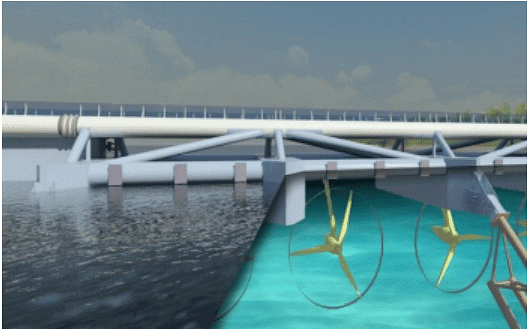
- The water level in the sea rises and falls periodically due to the gravitational pull of the moon and the spinning of the earth.
- There are mainly two types of tides one is high tide and the other is low tide. The difference in sea levels is called tidal energy.
- Across a narrow opening to the sea, a dam is constructed to harness tidal energy.
- The turbine is fixed at the opening which converts tidal energy to electricity.
Wave Energy
- Strong winds across the sea generate sea waves.
- The kinetic energy of these waves can be trapped to generate electricity.
Ocean thermal energy
- Sun heats the upper layer of the sea while the lower layer of the sea is relatively cold.
- This difference in temperature of the water level is used to obtain electricity in ocean thermal conversion plants.
- The condition to obtain the energy from these plants is that it can only operate if the temperature difference between the water at the surface and water at depths up to 2 km is 293 K (20°C) or more.
- A volatile liquid like ammonia boils on the warm surface water. The vapors of the liquid are then used to run the turbine of the generator.
Geothermal Energy
- When we divide the word ‘Geothermal’ which geo means earth and thermal means heat. Thus, It is clear that the energy is obtained from the heat of the earth is said to be geothermal energy.
- The molten rocks which are formed deep inside the earth get pushed upwards due to geological changes.
- These rocks get trapped in a certain region of the earth's crust which is called
- When underground water comes in contact with hotspots, steam generates. If this underground water finds outlets then these outlets are called hot springs.
- The steam trapped in rocks is routed through a pipe to a turbine and used to generate electricity.
Nuclear Energy

- The energy released during the nuclear reaction is said to be nuclear energy.
- It is used for heat generation and also as fuel for marine vessels.
- Nuclear energy can be obtained by two processes, they are:
(i) Nuclear Fission
(ii) Nuclear Fusion - Nuclear Fission:
- Fission itself means ‘split up’.
- The nucleus of a heavy atom (such as uranium, plutonium, or thorium), when bombarded with low-energy neutrons, splits into lighter nuclei.
- This process releases a tremendous amount of energy, which is used to heat water and produce steam which further is used to rotate the turbine and obtain electricity.
- Nuclear Fusion:
- Fusion means ‘add up’.
- Two lighter nuclei (hydrogen) combine to form a heavy nucleus (like helium) and a tremendous amount of energy is released.
- There is needed a very high temperature and pressure for fusion.
- A hydrogen bomb is based on this principle.
- Sun and stars obtain energy by nuclear fusion.
Advantages of nuclear energy:
- It is the alternative source of energy with the decrement of fossil fuels.
- From a little nuclear fuel, a large amount of energy is released.
- Do not produce greenhouse gas like CO2.
Disadvantages of nuclear energy
- Due to improper nuclear waste storage and storage, there is environmental contamination.
- There is always a risk of accidental leakage of harmful radiations.
- The cost of installation is much high.
- There is limited availability of nuclear fuel.
Environmental Consequences
- There are always two faces of any resources present to us. One is a good part and the other one is evil.
- The sources of energy that give us relief, on the other hand, it also cause a great damage to nature and natural resources.
- The energy source we choose depends upon many factors, it can be easily and economically extracted from the source and we have that efficient technology to extract energy.
- Also profoundly we see the environmental issues related to the extraction.
- No any source of energy is pollution free. We only compare that either one is cleaner than the other. Let’s see in case of solar energy, it is pollution free but the devices used in it is made in the industry which caused damage to the environment.
Classification of sources of energy on the basis of availability with respect to time
There are two types of sources of energy on the basis of availability with respect to time. They are renewable and non-renewable sources of energy.
Renewable Sources of Energy
- Sources that are being used continuously and will be depleted over time and end one day are said to be renewable sources of energy. Example: Fossil fuels
Non-Renewable Sources of Energy
- The source which can be regenerated and can be reused again and again and will last forever is said to be non-renewable sources of energy. Example: Solar energy, Water energy, wind energy, etc.
|
70 videos|242 docs|187 tests
|
FAQs on Olympiad Notes: Sources of Energy - Olympiad Preparation for Class 10
| 1. What are the main sources of energy used in our daily lives? |  |
| 2. How do renewable sources of energy benefit the environment? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy sources? |  |
| 4. What role does nuclear energy play in the current energy scenario? |  |
| 5. What are some challenges associated with the use of renewable energy sources? |  |




















