Operation Management in International companies | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
International Operations Management
Global Perspective of Operations Management:
- Operations Management is now more global.
- Even if a company sells only in its home country, it can still have international operations.
International Business Operations:
- This means a company might get its materials or products from other countries.
- It might also produce its goods in other countries.
Adapting to Favorable Conditions:
- Smart companies use good conditions anywhere in the world to benefit their business.
Dynamic Business Approach:
- A lively or dynamic company grabs opportunities worldwide.
Defining International Operations Management:
- This term means the activities that change things in a company that works internationally.
Benefits of Going International
- Going global has several advantages compared to staying within one country.
Cost of Production Advantage:
- Companies operating internationally can benefit from cost advantages in different locations.
- For example, a multinational company (MNC) can set up a branch anywhere with the lowest production costs. In China, for instance, wages are much lower than in Mexico, and only a small fraction compared to the US or Japan.
Scale of Economies Advantage:
- MNCs can make use of scale of economies, meaning they benefit from producing goods or services on a large scale.
- An example is Coca-Cola, which sells the same soft drink in over 160 countries worldwide.
- This approach also takes advantage of the experience curve, where the more you produce, the more efficient and cost-effective you become.
- Two important considerations for this strategy are: a) the product must meet customer needs, and b) there must be a big enough demand to support large-scale production.
Creating Value through International Business:
- International businesses aim to make new values through their operations.
- For example, they might group manufacturing for nearby countries to save money on production and shipping costs.
- Multinational companies (MNCs) can choose cheaper suppliers abroad, reducing transportation costs.
- They can also sell the same products in multiple countries and move production between plants in different countries based on currency exchange rates.
Significance of Operations Management:
- Operations management is crucial for a company, especially in the international market.
- It helps a company compete successfully globally.
- Other important areas include Total Quality Management (TQM), Business Process Re-engineering, New Product Development, Lead Time, Greater Flexibility, Business Process Outsourcing, Six Sigma, and Reduced Cost of Production.
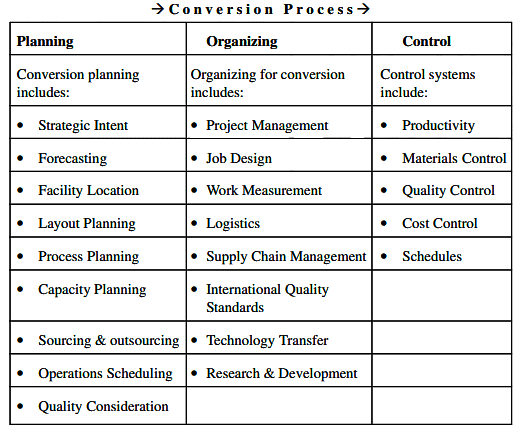
Model of International Operations Management:
- A model of international operations management is like a plan for how companies can operate on a global scale.
- It involves managing the conversion process efficiently.
Model for International Operations Management
Strategic Issues In International Operations Management
The effective coordination of Operations Management in an international business is crucially tied to the overall corporate strategy. In essence, the firm's corporate strategy should establish the framework for planning and executing activities related to operations management. For instance, in the case of a company adopting a differentiation strategy, the focus of international operations management should be on developing distinctive goods and services to establish a unique position distinct from others or competitors.
International Production Strategies
Manufacturing Compatibility:
- Compatibility means how well foreign investment matches the company's competitive strategies.
- Strategies include:
- Cost minimization: Focus on achieving economies of scale and utilizing low-cost labor markets in regions like Asia, Mexico, and Eastern Europe.
- Dependability: Ensuring trust in the company's products, delivery, and pricing promises.
- Quality: Consistently meeting or exceeding customer expectations; essential for competitive advantage.
- Flexibility: Ability to produce different products and adjust output volume, linked to agile manufacturing.
- Research & Development (R&D): Directed efforts towards scientific knowledge and product/process innovations.
Production Configuration:
- Involves determining the layout of production facilities, considering:
- Centralized production: One manufacturing facility serves multiple markets.
- Regional production: Facilities cater to specific regional markets.
- Multi-domestic approach: Establishing production facilities in various countries to meet local demands.
- Factors influencing facility location include country resources, technology, product characteristics, government policies, and organizational considerations.
- Involves determining the layout of production facilities, considering:
Production Coordination:
- Involves integrating activities across the international supply chain, including purchasing, warehousing, shipment, and inbound logistics.
- Outbound logistics must also be coordinated effectively to reach customers competitively.
Control of Production:
- Involves measuring performance to respond to changing conditions.
- Organizational structure should coordinate activities according to the plan.
- Strategies should be flexible to accommodate deviations from the plan due to uncontrollable factors while minimizing time and cost variations.
International Logistics Management
Logistics Management
Definition:
- Logistics Management involves planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient and cost-effective flow and storage of raw materials, in-process inventory, finished goods, and related information.
- It ensures conformity to customer requirements and is a crucial part of materials management.
Relation to Supply Chain Management:
- Logistics is a key dimension of supply chain management.
- While logistics focuses more on transportation and storage, supply chain management extends to managing relationships with suppliers and customers.
International Business Focus on Logistics:
- International business managers need to consider the flow of materials, parts, and supplies both from vendors to the firm and within different units of the firm.
- Major issues include dealing with long distances, using multiple transport modes, and navigating complex regulatory contexts in international materials management.
Challenges in Managing Logistics:
- For organizations involved in international operations, managing logistics involves dealing with various aspects such as cost-effective purchasing, currency exchange, transportation, inventory, communication, duties and tariffs, as well as environmental and regulatory issues.
Components of Logistics
Fixed Facilities:
- Includes production facilities, warehousing, and inventory storage.
Inventory Management:
- Aims to minimize inventory costs.
Order Processing:
- The efficiency of order processing has implications for inventory costs and other logistics aspects.
Material Handling and Transportation:
- Vital components of logistics involving the movement of goods.
Third Party and Fourth Party Logistics (3PL and 4PL)
Outsourcing in Logistics:
- Many firms outsource tasks not considered core to their operations, including transportation and warehousing.
- Logistics is an emerging business area in India.
Third Party Logistics (3PL):
- Firms providing multiple logistics services, including transportation, warehousing, cross-docking, inventory management, packaging, and freight forwarding.
- May own and operate transportation equipment and warehousing facilities.
Fourth Party Logistics (4PL):
- Integrators that assemble resources, capabilities, and technology to design, build, and operate comprehensive supply chain solutions.
- Non-asset based organizations providing logistics consultancy services.
Benefits and Disadvantages of Outsourcing:
- Benefits include overall cost reduction, specialist expertise, flexibility, and efficient customer service.
- Disadvantages may include reduced control and complicated communication.
International Logistics Outsourcing
Definition:
- Logistics outsourcing involves fully delegating some or all activities to a third party.
Global Trends:
- Globalization, integrated logistics, and communication technology shape the world trade pattern.
- Core activities are focused on, while non-core activities are outsourced for sustainable competitive advantage.
Reasons for Outsourcing:
- Increasing IT requirements, global competition, cost-cutting pressure, and the need for flexibility drive organizations to outsource non-core activities.
- In China, drivers include cost reduction, reengineering benefits, focus on core competencies, and market penetration for improved customer satisfaction.
FAQs on Operation Management in International companies - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is international operations management? |  |
| 2. What is the role of international logistics management in global operations? |  |
| 3. How does international operations management differ from domestic operations management? |  |
| 4. What are the key challenges in international operations management? |  |
| 5. What skills and competencies are required for international operations management? |  |