Organizational Theory and Design: Managing Cultural Diversity | NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Dimensions of Diversity |

|
| Different strategies of managing diversity |

|
| Cultural Diversity Management Program |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
- Understanding Diversity in the Workplace:
- Diversity in an organization refers to the major differences among people, including less obvious aspects like thoughts, beliefs, and values.
- Researchers like Nkomo and Taylor describe diversity as a mix of individuals with various group identities within the same social system.
- Globalization's Impact on Diversity:
- Due to globalization, people from diverse cultures and backgrounds now communicate more, making it crucial for companies to adapt to a changing environment.
- Companies need diversity to be creative and competitive on a global scale.
- Challenges and Skills for Managers:
- Managers in a multicultural work environment must learn skills to navigate diversity challenges.
- This involves valuing differences in both employees and customers to ensure everyone is treated with dignity.
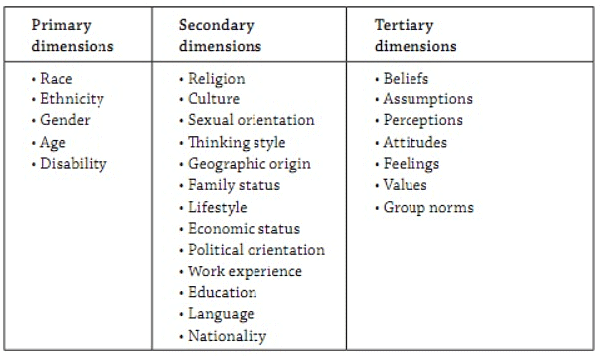
- Primary and Secondary Dimensions of Diversity:
- Primary dimensions, such as gender, ethnicity, race, age, and abilities, strongly influence a person's identity and worldview.
- Secondary dimensions, like education, geographic location, religion, and work experience, add subtle richness to diversity.
- Expanding Diversity Dimensions:
- Culture, social class, and language are considered primary dimensions by some experts.
- Additional secondary dimensions include religion, culture, and political orientation.
- Tertiary Dimensions and Individual Identity:
- Some experts introduce tertiary dimensions, such as historical experiences, which form the core of individual identity.
- Understanding and appreciating these dimensions contribute to a more inclusive workplace.
Dimensions of Diversity
- Definition of Cultural Diversity: Cultural diversity is when a group has people from different cultural backgrounds, making it a more varied and interesting social system.
- Benefits of Homogeneous Groups: In groups with cultural harmony, people tend to communicate more and in diverse ways because they share common views and a shared culture.
- Social Identity Theory: According to social identity theory, having a similar culture in management groups can increase satisfaction and cooperation while reducing emotional conflict.
- Challenges of Managing Cultural Diversity: Managing cultural diversity at work can be challenging, but effective policies can help companies navigate and embrace differences.
- Essence of Diversity in the Workplace: Diversity in the workplace means bringing together individuals of different ethnicities, religions, and ages to form a united and productive team.
- Globalization's Impact: Advancements in communication technology, like the Internet and cell phones, have led businesses to expand globally, requiring them to manage diverse teams.
- Changing Perspective on Diversity: Managing diversity goes beyond recognizing differences; it involves valuing individual talents and differences in the workplace.
- Building Inclusive Organizations: Companies with diverse cultures should incorporate the values of their employees into all aspects of the organization to create a welcoming environment.
- Recognizing Diversity as an Asset: Organizations that embrace cultural diversity see it as an asset and use it for the growth of the company, its employees, and to meet customer needs.
- Competitive Advantage: To stay competitive, companies must effectively manage and utilize their diverse workforce.
- Significance of Managing Diversity: Managing diversity in the workplace is crucial for the overall culture of an organization, as explained by Johnson and Johnson (2006).
- Increasing Interdependence: The growing interdependence among people and the globalization of business have led to a more diverse workforce, making diversity management increasingly important (Johnson and Johnson, 2006).
- Organizational Culture Defined: Triandis and Wasti (2008) define organizational culture as shared behaviors, human-made aspects, practices, and values within a society.
- Reasons for Managing Cultural Diversity: Managing diversity is necessary due to factors like the increasing number of females, growing workforce mobility, and the influx of young employees in global organizations.
- Protection of Minority Groups: Managing diversity involves ensuring the inclusion and protection of minority groups, such as ethnic, gender, aged, and disabled workers.
- Challenges in the Workplace: Despite projections that minority groups and women will dominate the workforce in the next decade, they often face disqualification in organizations, raising concerns expressed by governments and business executives (Rubaii-Barrett & Beck, 1993).
- Broad Understanding of Diversity: Theorists like Kandola et al. (1995) state that diversity includes virtually all ways in which people differ, not just gender, ethnicity, and disability.
- Focus on Diverse Employee Needs: Managing diversity, according to Jenner (1994), involves addressing the diverse needs of employees and managing human resources effectively.
- Inclusive Workplace Concept: Barak (2000) emphasizes the need for an 'inclusive workplace,' holding diversity not only within the organization but also in the larger community it operates in.
- Importance of Training and Orientation: Multicultural organizations with employees from different cultures need to provide various training methods, proper orientation, and motivation to manage cultural differences successfully.
- Staffing Approaches for Global Organizations: Global organizations use different staffing approaches like ethnocentric, polycentric, geocentric, and region-centric to manage cultural diversity.
- Key Strategies for Success: Human resource managers play a crucial role in implementing successful strategies, such as hiring culturally adaptable resources for international projects.
- Selection Process for Global Employees: HR managers are responsible for selecting global employees through a diverse selection board with members from different nations and at least three to five years of expatriate experience (Uma et al., 2009).
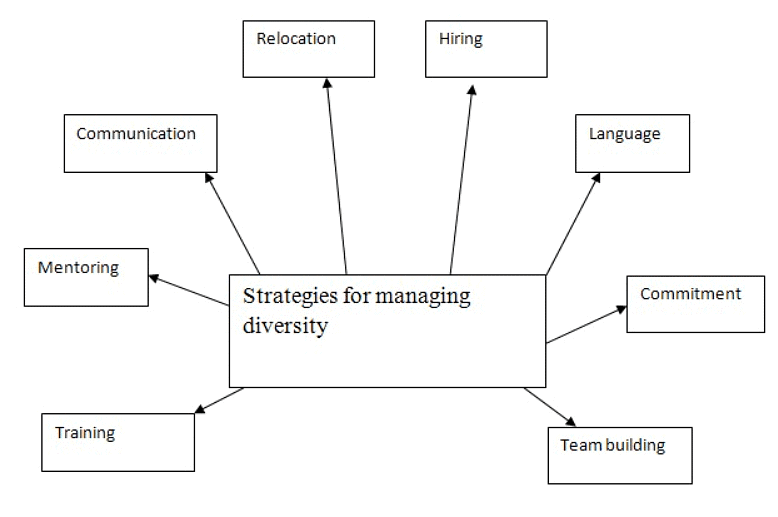
- Essential Skills for Organizational Success: Multilingualism, effective communication, team building, and mentoring are crucial skills for the success of global organizations.
- Employee Retention and Motivation: Retaining employees, providing the right motivation, and ensuring proper replacement after expatriation and repatriation are essential for the long-term success of multinational companies (MNCs).
Different strategies of managing diversity
- Advantages of Homogeneous Work Structure:
- Having a similar and cohesive work structure brings significant benefits to organizations.
- Organizations that can attract and retain competent members from diverse backgrounds tend to succeed in the marketplace.
- Equitable Career Progression:
- Organizations ensuring fair and impartial career progression for minority group members experience high-quality human resource dividends.
- Multicultural Organizations for Global Markets:
- Multicultural organizations are well-suited to cater to diverse external customers in a global market.
- They possess a good understanding of the legal, political, social, economic, and cultural environments of foreign nations (Adler, 1991).
- Different Views on Managing Cultural Diversity:
- In management literature, various perspectives exist on how to handle cultural diversity within an organization.
- Positive Aspects of Cultural Diversity:
- Cultural diversity is seen as a boost to creativity, thorough problem analysis, improved decision-making, flexibility, and innovation in business practices (Adler and Gundersen, 2008).
- Challenges of Cultural Diversity:
- Despite its advantages, cultural diversity can lead to conflicts, miscommunication, misunderstanding, increased tension, and a lack of cohesion and commitment, negatively affecting organizational performance (Glick et al., 1993).
- Diverse Views on Managing Diversity:
- Different writers have identified five contrasting views on cultural diversity management in organizations (Seymen, 2006).
- Competitive Advantage: Some authors view cultural diversity as a tool for gaining a competitive advantage in the market.
- Different writers have identified five contrasting views on cultural diversity management in organizations (Seymen, 2006).
- Balancing Advantages and Disadvantages:
- Others suggest enhancing the benefits of cultural diversity while minimizing the drawbacks.
- Homogeneous Organizational Culture:
- Some propose integrating diversity into a homogeneous organizational culture.
- Universalism vs. Multiculturalism:
- Another perspective suggests favoring universalism over multiculturalism.
- Cultural Diversity as a Human Resource Function:
- Lastly, some believe that managing cultural diversity is a crucial aspect of human resource functions within the organization.
- Cultural Diversity as a Competitive Advantage:
- Cultural diversity is seen as a competitive advantage, meaning that a diverse workforce can contribute to the organization's success (Seymen, 2006).
- Performance in Heterogeneous Environments:
- Research suggests that organizations perform better in a diverse, heterogeneous environment compared to a homogeneous one (Seymen, 2006).
- Objectives of Creating Cultural Diversity:
- Creating a culturally diverse organization aims to promote pluralism over single-culture and ethno-relativity over ethno-centralism (Daft, 2003).
- Long-Term Corporate Benefits:
- Having a culturally diverse workforce is recognized as bringing long-term benefits to the organization (Herbig and Genestre, 1997).
- Organizational Culture and Diversity:
- Cultural diversity is managed within the framework of organizational culture, emphasizing the establishment of a common culture that focuses on a shared cultural identity to achieve organizational goals (Kidger, 2002).
- Effective Management of Diversity:
- Effective management of cultural diversity improves staff retention, attracts and recruits top talent, enhances problem-solving, creativity, and innovation among employees.
- Wide Talent Pool and Recruitment Success:
- A diverse workforce allows companies to recruit from a broad talent pool, increasing the chances of finding the best employee for each position, especially when traditional labor pools lack the required skills and numbers.
- Influencing Organizational Culture:
- According to Person (1999), cultures can be influenced to create a dominant culture that is coherent and influential over other subcultures, making it the organizational culture.
- Cultural Diversity as a Human Resource Program:
- Cultural diversity is considered a human resource program and strategy, with the responsibility of management placed on human resource departments and their modern management techniques (Seymen, 2006).
- Importance of In-Service Training:
- The focus is on providing multicultural workforce with in-service training programs to manage cultural diversity effectively (Peppas, 2001).
- Execution of Variable Management:
- Managers of a culturally diverse workforce need to implement variable management and organizational behavior systems to harmonize differences and achieve common objectives (Wright and Noe, 1996).
- Perception of Cultural Diversity by Managers:
- Managers often see cultural diversity in the workplace as a challenge, but it can either be a disadvantage or a valuable resource for market competition.
- Potential Problems Due to Unmanaged Cultural Diversity:
- Failure to manage cultural diversity can lead to various problems that hinder organizational performance.
- Financial Costs of Unmanaged Diversity:
- The first problem is financial, with high turnover, absenteeism, and lawsuits leading to significant costs. Losing dissatisfied employees results in a loss of invested recruiting and training funds (Daft 1997; Robinson and Dechant 1997).
- Reduced Individual and Organizational Output:
- Unmanaged diversity can result in reduced individual and organizational output due to prejudice and non-acceptance. Unrewarded individuals are less innovative and less likely to contribute ideas or take on leadership roles.
- Tarnished Corporate Image:
- Another issue is the tarnishing of the corporate image, which develops around employee unhappiness. This can negatively impact the company's reputation.
- Increased Training Costs:
- Managing cultural diversity may require additional training costs, such as language and cultural awareness training to facilitate integration into the workplace and local society.
- Rise in Conflicts:
- Diverse workplaces may experience increased conflicts arising from feelings of dominance, unawareness, or fear. If not addressed, these conflicts can lead to derogatory comments or gestures, impacting productivity.
- Worker Disappointment and Efficiency:
- Mismanaged diversity can cause worker disappointment and negatively affect efficiency. It is crucial for management to address and effectively manage cultural diversity to avoid these challenges.
- Effective Approaches to Manage Cultural Diversity:
- Overcoming stereotypes and promoting fairness is a key approach to managing cultural diversity in global organizations.
- Blending with Dominant Organizational Culture:
- Integrating cultural diversity with a dominant organizational culture is another effective strategy.
- Human Resource Program or Strategy:
- Implementing a human resource program or strategy is a practical way to handle cultural diversity in organizations.
- Adopting an Employee Relationship System:
- Establishing an employee relationship system is a valuable approach to effectively manage cultural diversity.
- Diversity Management Training Program:
- Providing diversity management training programs helps employees and managers understand and navigate cultural differences in the workplace.
Cultural Diversity Management Program
- Creating a Supportive Environment for All Groups: To successfully manage cultural diversity, it's crucial to establish a supportive environment where everyone feels respected regardless of their background.
- Positive Outcomes of a Respectful Environment: A respectful environment leads to increased commitment, efficiency, and improved work relationships, as well as attracting and retaining the best employees (Daft 1997).
- Utilizing Diverse Workforce for Business Growth: Companies can enhance business growth and customer service by leveraging the skills of their diverse workforce, including language abilities, cultural sensitivity, knowledge of home country business networks, and market insights.
- Competitive Advantages in Marketing: By incorporating these techniques, organizations gain a competitive edge in marketing goods and services, both to an increasingly diverse local community and the global market (Karpin 1995).
- Manager's Role in Changing Organizational Culture: A good manager plays a crucial role in changing organizational culture to better reflect the values of a diverse workforce.
- Managerial Abilities for Diversity Management: Managerial abilities for effective diversity management include understanding and accepting diversity concepts, recognizing that diversity permeates every aspect of management, and being self-aware about culture, identity, biases, prejudices, and stereotypes.
- Readiness to Challenge Institutional Practices: Managers should be ready to challenge and change institutional practices that create barriers for different groups within the organization.
- Benefits of Successful Diversity Management: Successfully managing diversity enhances good management practices by preventing discrimination and promoting inclusiveness, ensuring all employees can contribute to organizational goals.
- Focus on Maximizing Employee Capability: Managing diversity emphasizes maximizing the capabilities of all employees to contribute effectively to organizational objectives.
- Affirmative Action and Legal Responsibility: Affirmative action targets specific groups, addressing historical biases, such as people of different colors and women, focusing on legal necessity and social responsibility.
Conclusion
In summary, a diverse workforce reflects the evolving global landscape and open market. Managing cultural diversity requires managers to treat all ethnic and minority groups impartially, fostering a fair and secure environment with equal opportunities and challenges for everyone. Using management tools is essential in training the workforce about diversity, including relevant laws and regulations. As workplaces often comprise diverse cultures, organizations must adapt to the changing business environment to achieve success. The significance of managing diversity lies in recognizing its value and responding to the growing need for racial impartiality (Prabhu, 2009).
|
847 videos|1297 docs|420 tests
|
FAQs on Organizational Theory and Design: Managing Cultural Diversity - NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams
| 1. What is the importance of managing cultural diversity in organizational theory and design? |  |
| 2. What are the dimensions of diversity that should be considered in a cultural diversity management program? |  |
| 3. What are some strategies for managing cultural diversity in organizations? |  |
| 4. How can a cultural diversity management program benefit an organization's bottom line? |  |
| 5. How can organizations ensure the successful implementation of a cultural diversity management program? |  |














