Overview: Chemical Reactions & Equations - 1 | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Chemical Change |

|
| Chemical Equations |

|
| Writing a Chemical Equation |

|
| Skeletal Chemical Equations |

|
| Balanced Chemical Equations |

|
Chemical Change
A chemical change happens when any two substances interact with each other by gaining, sharing, or donating electrons.
- Whenever a chemical change occurs, we say that a chemical reaction has taken place. For example, cooking of food, respiration, digestion of food, and exposure of iron to the humid atmosphere.
- Chemical change involves the change of state, change of colour, the evolution of gas, or change of temperature.
 Examples of Chemical Change
Examples of Chemical Change
Let's do some activities to understand chemical reactions better.
Activity 1
Aim: Perform an activity to show that a chemical reaction has taken place (change in state and change in colour).
Materials Required: Magnesium ribbon, Sandpaper, Tongs, Spirit lamp or burner, Watch-glass, Suitable eyeglasses
Procedure: (i) Clean a magnesium ribbon about 3-4 cm long by rubbing it with sandpaper.
(i) Clean a magnesium ribbon about 3-4 cm long by rubbing it with sandpaper.
(ii) Hold it with a pair of tongs.
(iii) Burn it using a spirit lamp or burner and collect the ash so formed in a china dish as shown in the Figure above.
(iv) Burn the magnesium ribbon keeping it away as far as possible from your eyes.
Result:
As the magnesium ribbon burns, you will observe a dazzling white flame and the ribbon will change into a white powder, which is the magnesium oxide. This activity shows that a chemical reaction has taken place as there is a change of state of the magnesium ribbon.
Activity 2
Aim: Perform an activity to show that a chemical reaction has taken place (evolution of a gas and change of temperature).
Materials Required: Conical flask (250 mL), cork, glass tube, zinc granules, dilute sulphuric acid.
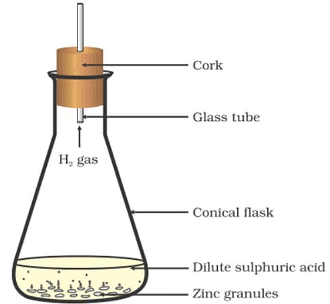
Procedure:
(i) Set up the apparatus as shown in the above figure.
(ii) Remove the cork and glass tube. Place some dilute sulphuric acid into it.
(iii) Add a few small granules of zinc and immediately close the flask with the cork.
We observe that hydrogen gas is evolved which is indicated by the bubbles.
On touching the flask, we find that it is hotter now than before.
Result:
This activity shows that a chemical reaction has taken place. Before mixing the sulphuric acid and granules of zinc there were no fumes and the flask was at room temperature. But after following all the procedures given, some changes happened and that is the hotter flask than before and bubbles of hydrogen are seen. Thus, there is the evolution of gas and a temperature change.
Chemical Equations
The description of a chemical reaction in a short form is called a chemical equation. Chemical equations make use of symbols to represent factors such as the direction of the reaction and the physical states of the reacting entities.
For example:
- In the above example, when magnesium and oxygen come into contact and undergo a chemical reaction, they are referred to as reactants. The resulting substance that is formed as a result of this reaction is called the product, specifically magnesium oxide.
- The reactants are written on the left-hand side (LHS) with a plus sign between them.
- Similarly, the products are written on the right-hand side (RHS) with a plus sign between them.
- The arrowhead points towards the product and shows the direction of the reaction.
Writing a Chemical Equation
Skeletal Chemical Equations
A chemical equation written in the form of symbols and formulae is called a skeletal chemical equation. Such an equation may not be balanced.
 Skeletal chemical equationIn the above equations, there are three carbon atoms on the LHS while there is only one carbon atom on RHS hence, this equation is not balanced, now let's see some Balanced chemical equations.
Skeletal chemical equationIn the above equations, there are three carbon atoms on the LHS while there is only one carbon atom on RHS hence, this equation is not balanced, now let's see some Balanced chemical equations.
Balanced Chemical Equations
 No. of atoms on both sides should be equal
No. of atoms on both sides should be equal
A chemical equation in which the number of atoms of each element on LHS and RHS is equal is called a balanced chemical equation.
Example: Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
This is a balanced equation because the number of atoms of Zn, H, S, and O is equal on the reactant (LHS) and product (RHS) sides.
Balancing of Chemical Equation
Let us illustrate the balancing of the chemical equations by taking an example:
Example: Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
The following steps are involved:
- Step I - First of all, we see that number of Fe and O atoms on the reactant and product sides are different. So the equation needs to be balanced.
- Step II - Select the compound which has a maximum number of atoms. It may be a reactant or product. In that compound, select the element which has the maximum number of atoms. Using these criteria, we select Fe304 as the compound and oxygen as the element. There are four 0 atoms on RHS and one O atom on the LHS. Hence, multiply H2O(containing O) by four to balance O.
 The partly balanced equation becomes:
The partly balanced equation becomes:
Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + H2 - Step III - Fe and H are still to be balanced. Take either now for balancing. Let us take H. There are eight H atoms on LHS and two H atoms on RHS. Multiply H2 by four to equalise H atoms.
 The equation would become:
The equation would become:
Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + H2 - Step IV - Fe is left to be balanced. There is one Fe atom on LHS and three Fe atoms on RHS. Multiply Fe on LHS by three to equalize
 We can write the equation now as:
We can write the equation now as:
3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + H2 - Step V - Finally, we write the equation, after removing boxes and check whether it is balanced or not.
3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
This method of balancing equations is known as the hit and trial method as we complete the balancing by making trials for different elements. - Step VI - Writing Symbols of Physical States. To make the equation more informative, we write the physical states of different substances on LHS and RHS. Thus,
3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2 (g) - Notations (s), (l) and (g) are used for solid, liquid and gaseous states respectively. In the above equation (g) after H2O means H2O is in the form of steam (gaseous), and (aq) is written for an aqueous solution.
- Sometimes the reaction conditions, such as temperature, pressure, catalysts, etc., for the reaction are indicated above and/or below the arrow in the equation. For example,

|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Overview: Chemical Reactions & Equations - 1 - Science Class 10
| 1. What is a chemical change? |  |
| 2. What are chemical equations? |  |
| 3. How do you write a chemical equation? |  |
| 4. What are skeletal chemical equations? |  |
| 5. What is a balanced chemical equation? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
 The partly balanced equation becomes:
The partly balanced equation becomes: The equation would become:
The equation would become: We can write the equation now as:
We can write the equation now as:


















