Overview: Biological Classification | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
Introduction
Biological classification is the scientific procedure of arranging the organisms in a hierarchical series of groups and sub-groups on the basis of their similarities and dissimilarities. Many biologists have contributed to this method of classification, which took years for researchers to decide the most fundamental characteristics for the classification.
Need for Classification
Right from archaic times, several attempts have been made to classify living organisms. The first man to attempt a scientific basis of classification was Aristotle. He used simple morphological characters to classify plants as trees, shrubs, and herbs.
He classified the animals into two groups:
1. Enaima (with red blood)
2. Anaima (without red blood)
However, a need for a proper system of biological classification was always felt.
➢ Need for Classification of Living Organisms
- The study of one or two organisms is not sufficient to know the essential features of the group.
- All kinds of organisms do not occur in one locality.
- Classification helps in knowing the relationship between the different groups of organisms.
- It helps in knowing the evolutionary relationship between organisms.
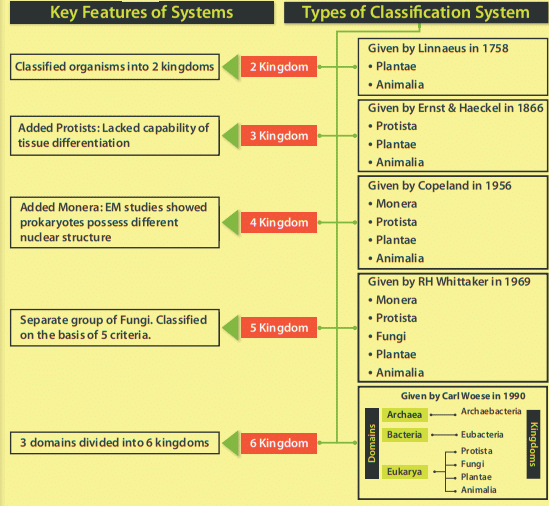
Types of Classification System
1. Two Kingdom Classification System
In the year 1758m Linnaeus (the father of the taxonomy system) divided all the living organisms into two kingdoms. These are Plantae and Animalia.
(i) Features of Kingdom Plantae
- They have a cell wall.
- An autotrophic mode of nutrition is followed. The reserve food is starch.
- A big central vacuole is present.
- There aren’t any excretory organs, nervous system, sense organs and muscular system.
- No locomotion is seen except in some lower algae.
- Plantae absorbs inorganic nutrients from the outside.
- They experience unlimited growth but have well-defined growing points.
- The response to external stimuli is slow.
(ii) Features of Kingdom Animalia
- The cell wall is absent.
- There are no inorganic crystals present in their cells.
- Central vacuole is absent.
- Growth is limited and well-defined growing points are not present.
- A heterotrophic mode of nutrition is used.
- Show quick response to external stimuli.
- The muscular system is present.
- Locomotion is present.
- Excretory organs, nervous system and sense organs are present.
- Reserve food as glycogen.
2. Three Kingdom Classification System
- In the year 1866, Ernst Haeckel, classified living organisms into three kingdoms i.e. Plantae, Protista, and Animalia.
- The new kingdom Protista included all those organisms, which lack the capability of tissue differentiation.
- This group included algae, fungi, and Protozoa. Later, kingdom Protista was reserved only for the unicellular organism.
Limitations of the Three Kingdom Classification System:
- No separation of Prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
- Both unicellular and multicellular organisms are classified under Protista.
3. Four Kingdom Classification System
- In addition to Protista, Plantae and Animalia, the four kingdom classification system included Monera.
- The studies with electron microscope made it clear that bacteria and related organisms have a different nuclear structure as compared to others. These are prokaryotes.
- As a result of this, Copeland in the year 1956, introduced the kingdom-Monera. Fungi continued to remain with Plantae in this system.
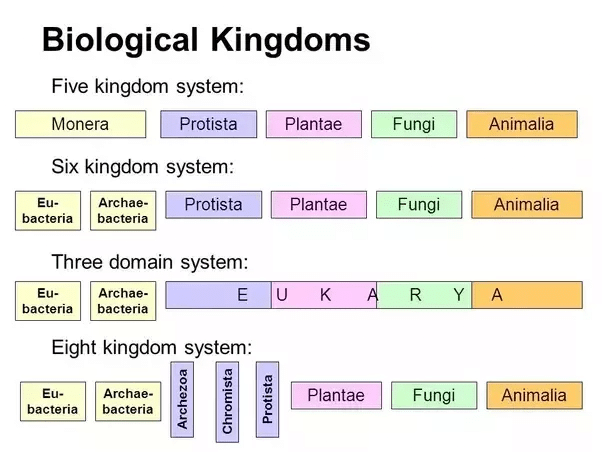
4. Five Kingdom Classification System
In the year 1969, this classification came into existence. RH Whittaker proposed this system. He created a separate group for fungi.
The primary criterion for classification here were:
- Cell structure
- Modes of nutrition
- Reproduction
- Thallus organisation
- Phylogenetic relationships
5. Six Kingdom Classification System
- Carl Woese a Professor in the Department of Microbiology, University of Illinois, came up with the Six Kingdom Classification System in the year 1990.
- It was also known as the three-domain system as in it organism classification was done in three domains, i.e., Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya.
- It majorly used the basic principles of the five-kingdom system but divides the Monera into two domains Archaebacteria, Eubacteria and other eukaryotes in the third kingdom.
(i) Archaea
Archaea domain includes prokaryotic organisms. These have a monolayer core of lipids in the cell membrane and distinct nucleotides in their 16S RNA. It contains a single kingdom called Archaebacteria. This kingdom includes early prokaryotes. These are methanogens, halophiles and thermoacidophiles.
(ii) Bacteria
The bacteria domain consists of typical prokaryotes that lack membrane-covered cell organelles. These do not have microchambers for separating various metabolic activities. It also has a single kingdom-Eubacteria.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Kingdom-Eubacteria: The members of this kingdom have a peptidoglycan cell wall, naked DNA in coiled form, glycogen food reserves. There is no sap vacuole and 70S ribosomes are present. The members of this kingdom are bacteria, mycoplasma, Actinomycetes, rickettsiae, spirochaetes, cyanobacteria, Firmicutes.
(iii) Eukarya
The domain eukarya contain all the eukaryotes.
The four kingdoms of this domain are:
(a) Protista
(b) Animalia
(c) Plantae
(d) Fungi
|
26 videos|312 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Overview: Biological Classification - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What is biological classification? |  |
| 2. Why is classification important in biology? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of classification systems? |  |
| 4. How is biological classification useful in scientific research? |  |
| 5. How does biological classification help in conservation efforts? |  |