Overview: Metals & Non-Metals - 2 | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Reaction of Metals with Solutions of Other Metal Salts
Reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their compounds in solutions or when molten. As discussed earlier, not all metals share the same level of reactivity. The displacement reactions mentioned in Chapter 1 provide clear evidence regarding the reactivity of metals.
Activity 8
Aim: Experiment to compare the reactivity of metals.
Materials required: Iron nail, copper wire, copper sulphate solution, iron sulphate solution, two test tubes, test tube stand, corks, thread.
Procedure:
- Take a clean copper wire and an iron nail.
- Suspend the copper wire in one test tube and iron nail in the other tube with the help of a piece of thread.
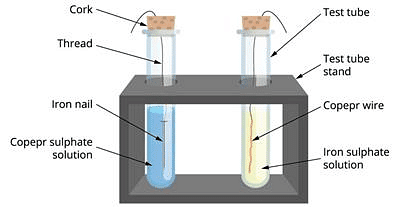
- Fill upto half the test tube containing copper wire with a solution of iron sulphate and test tube containing iron nails with a solution of copper sulphate.
- Wait for about 20 minutes.
- We find that a chemical change has occurred in test tube containing iron nail and copper sulphate solution while there is no change in the tube containing copper wire and iron sulphate solution.
- We say that a displacement reaction has taken place in the test tube containing Fe + CuSO4 solution.
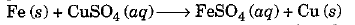 Due to this reaction, the blue colour of copper sulphate has disappeared and reddish brown deposit of copper is observed. Actually more reactive metal iron has displaced less reactive metal copper from its solution.
Due to this reaction, the blue colour of copper sulphate has disappeared and reddish brown deposit of copper is observed. Actually more reactive metal iron has displaced less reactive metal copper from its solution.
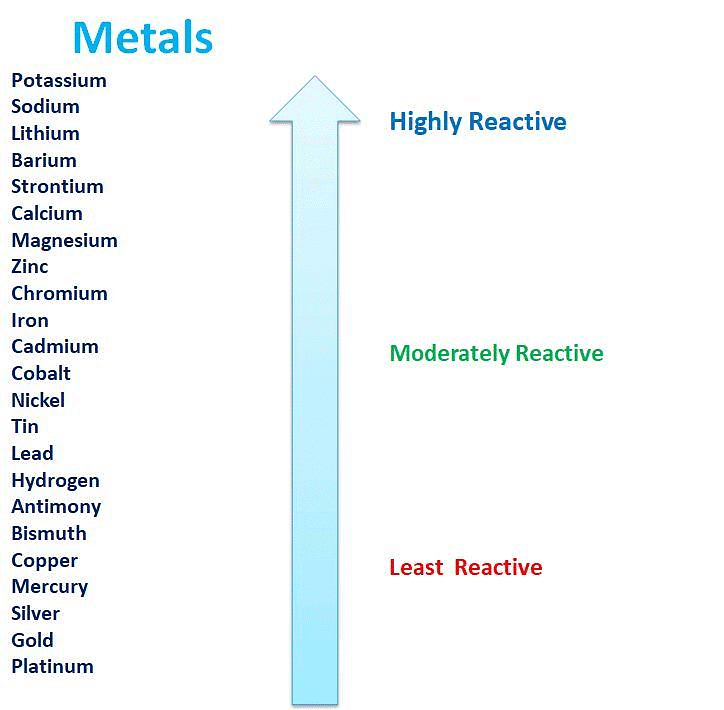
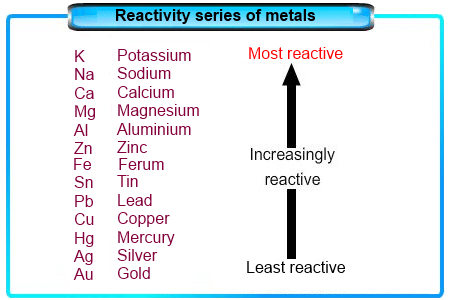
The Reactivity Series
- The reactivity series is a list of metals sorted by how reactive they are, from most to least reactive.
- This series is based on observations and experiments, including how metals react in displacement reactions.
- Metals that are higher in the series are very reactive and cannot be extracted from their compounds just by heating with carbon.
- For instance, carbon cannot reduce the oxides of metals like sodium, magnesium, calcium, and aluminium to their elemental forms, as these metals are more eager to bond with oxygen than with carbon.
- Instead, these metals are extracted using electrolytic reduction.
- For example, sodium, magnesium, and calcium are produced by electrolysis of their molten chlorides:
- At cathode: Na+ + e- → Na
- At anode: 2Cl- → Cl2 + 2e-
- Aluminium is also extracted through the electrolytic reduction of aluminium oxide.
 Activity Series: Relative reactivities of metals
Activity Series: Relative reactivities of metals
How do Metals and Non-Metals React?
Before we discuss the reaction between metals and non-metals, let us look at the electronic configuration of some noble gases, metals and non-metals as given in the table.
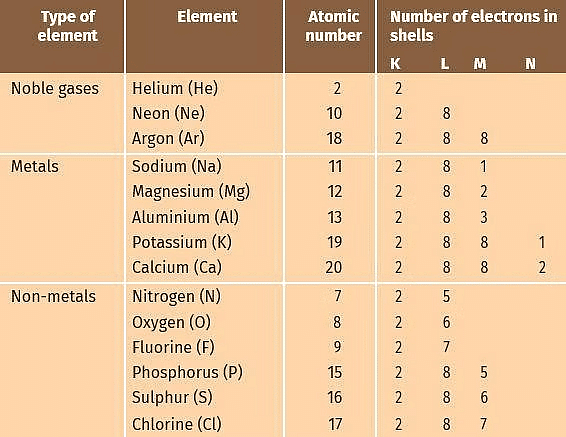 Electronic Configurations of Some Elements
Electronic Configurations of Some Elements
- Noble gases which have a completely filled valence shell (outermost shell) have no tendency to take part in the reaction.
- Eight electrons (2 electrons in case of helium) in the outermost shell is considered to be a stable configuration.
- Other elements react because they also want to attain stable configuration or we can say that chemical reactions take place because of the tendency of elements to attain noble gas configuration (eight electrons in the valence shell).
- Let us consider why sodium reacts with chlorine to form sodium chloride.
- From the table we find that sodium has 1 electron in the outermost M shell. If it loses the electron in the M shell then L shell will become the outermost shell, which shall have 8 electrons i.e., inert gas configuration.
- Thus, it has a tendency to lose 1 electron. Chlorine has 7 electrons in M shell which is the outermost shell. If it gains 1 electron, then the number of electrons will become 8, i.e., it will acquire noble gas configuration. Thus, it will have a tendency to gain one electron.
- Now, sodium loses one electron and gives it to chlorine to form sodium chloride. In this way, both the elements aquire stability by possessing noble gas configuration.
Formation of sodium chloride can be represented as under:
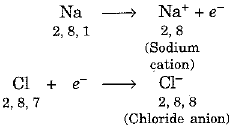
The transfer of electron from sodium to chlorine can be represented as under:

Sodium and chloride ions being oppositely charged attract each other and are held by strong electrostatic forces of attraction.
Formation of magnesium chloride can be represented as under: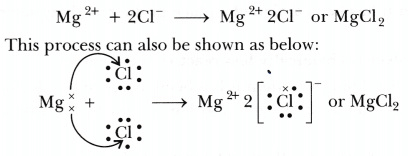
Properties of Ionic Substances
Ionic substances have several key properties:
- Physical nature: Ionic compounds are solid and quite hard due to the strong attraction between positive and negative ions. They tend to be brittle and can break when pressure is applied.
- Melting and boiling points: These compounds have high melting and boiling points because a lot of energy is needed to break the strong forces between the ions.
- Solubility: Ionic compounds usually dissolve well in water but do not dissolve in organic solvents like kerosene or petrol.
- Conduction of electricity: Electricity can pass through a solution of an ionic compound because the ions move towards opposite electrodes. In solid form, ionic compounds do not conduct electricity because their ions cannot move due to the rigid structure. However, when melted, they can conduct electricity since heat overcomes the forces holding the ions in place, allowing them to move freely.
Activity 9
Aim: Experiment to prove that salts impart colour to the flame.
Materials required: Burner, spatula, sodium chloride, potassium chloride and barium chloride.
Procedure:
- Take a metal spatula and clean it well.
- Heat some sodium chloride directly over the burner flame. You will see a golden-yellow flame.
- Next, use a clean spatula to heat potassium chloride. This will produce a violet flame.
- Finally, heat barium chloride on another clean spatula. This will create a green flame.
CAUTION: This activity needs a teacher's help. It is advisable for students to wear eye protection.
Many salts create colours when burnt. None of the salts melted during heating, which shows that ionic salts have high melting and boiling points.
We observe that a golden-yellow flame is produced.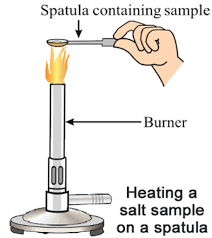
Thus, many salts produce flame when ignited with a flame. We also observed that none of the salts melted during heating proving that ionic salts have high melting and boiling points.
Activity 10
Aim: Experiment to prove that salt solutions conduct electricity.
Materials required: A beaker, battery, bulb, switch, graphite rods, sodium chloride solution.
Procedure: 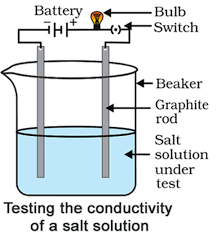
- Set up the apparatus as shown in the figure.
- Fill the beaker with sodium chloride solution. The bulb will glow, showing that the sodium chloride solution has ions that conduct electricity. This experiment helps us see that ionic compounds dissolve in water and break apart into ions that can carry an electric current. You may repeat the experiment with other ionic compounds to observe similar conductivity.
Occurrence of Metals
Elements or compounds which occur naturally in the earth’s crust are known as minerals. Minerals from which metals can be extracted profitably are called ores. Seawater also contains some soluble salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, etc.
Extraction of Metals
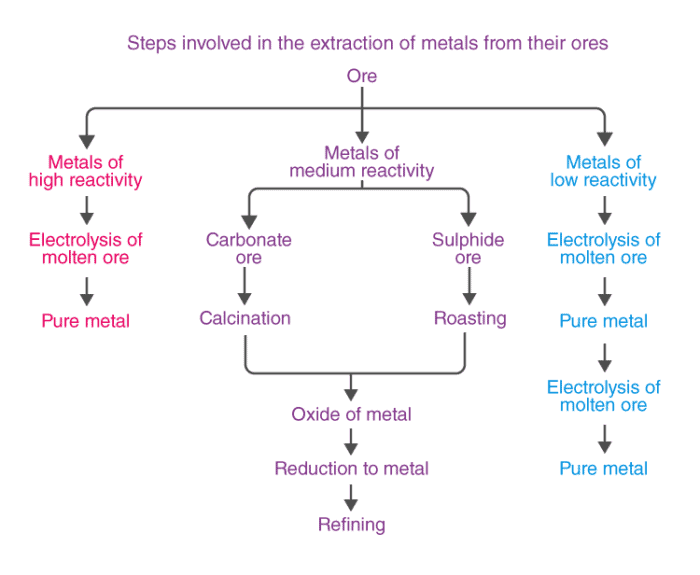
On the basis of reactivity, we can group the metals into three categories :
(i) Metals of low reactivity. For example, gold, silver, platinum and copper.
(ii) Metals of medium reactivity. For example, zinc, iron, lead, etc.
(iii) Metals of high reactivity. For example, potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium and aluminium.
- Ores of many metals are oxides. This is because oxygen is a very reactive element and is very abundant.
- Different techniques are to be used for obtaining the metals falling in each category Several steps are involved, in the extraction of pure metal from the ores.
Enrichment of ores
- Ores are generally contaminated with impurities, such as soil, sand, etc., called gangue.
- These impurities must be removed from the ores before proceeding to extraction.
- The method used for removing gangue depends upon the physical and chemical properties of the gangue and the ore.
Extracting metals low in the activity series
- Such metals are very unreactive. For example, cinnabar (HgS) is an ore of mercury.
- When heated, it is first converted to mercury oxide which on further heating changes to metallic mercury.
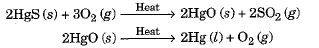
- Similarly, copper which occurs in nature as Cu2S can be obtained by just heating in air.
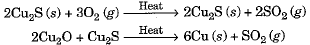
Extracting metals in the middle of the activity series
- Such metals iron, zinc, lead, and copper (Fe, Zn, Pb, Cu, etc.) are usually present in the form of sulphides and carbonates, which are both converted into oxide first.
- The sulphide ore is converted into oxide ore by heating strongly in the presence of excess air. This process is known as roasting.
- The carbonate ore is changed into oxide by heating strongly in limited supply of air.
Calcination
The metal oxides are then subjected to reduction with carbon.

- Reduction can also be brought about by reactive metals like sodium, calcium, aluminium etc. When manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium, the following reaction takes place:
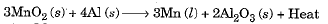
- In the above reaction, Mn is getting reduced while Al is getting oxidised. Al is higher on the activity series than Mn.
- The amount of heat evolved is so large that the metal is obtained in the molten state.
Thermit Process
- The reaction of iron (III) oxide (Fe2O3) with aluminium is an exothermic process. Iron is obtained in molten state which is used to join railway tracks or cracked machine parts.
- This reaction is known as thermit reaction and the process is known as thermit process.
Extraction of Metals towards the top of Activity Series
- Metals that are high in the reactivity series are very reactive.
- Their oxides cannot be reduced with carbon because these metals have a stronger attraction to oxygen than to carbon.
- Such metals are extracted through electrolytic reduction. Sodium, magnesium, and calcium are obtained by electrolytic reduction of their molten chlorides, with the metals forming at the cathode and chlorine gas being released at the anode.
- The reactions can be represented as:
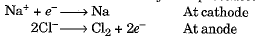
Aluminium is produced by electrolytic reduction of aluminium oxide, which is part of the overall process of extracting metals from their ores.
Refining of Metals
Electrolytic Refining
- The most common method for purifying impure metals is through electrolytic refining.
- This method is used for various metals, including copper, zinc, tin, nickel, silver, and gold.
- In this process, the impure metal acts as the anode, while a thin strip of pure metal serves as the cathode.
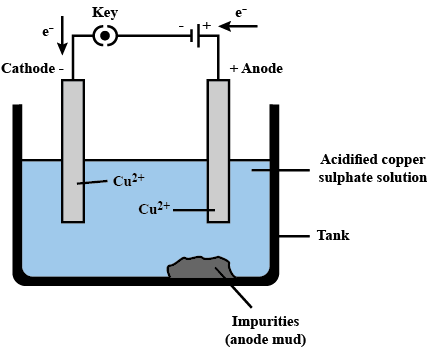
- A solution of metal salt, such as acidified copper sulphate, is used as the electrolyte for copper refining.
- The anode consists of impure copper, and the cathode is made of pure copper.
- When electric current flows through the electrolyte, the pure metal from the anode dissolves into the solution.
- Simultaneously, an equivalent amount of pure metal is deposited on the cathode.
- Soluble impurities dissolve in the solution, while insoluble impurities settle at the base of the anode, forming what is known as anode mud.
Corrosion
- Silver items turn black when they are in contact with air due to a reaction with hydrogen sulphide, forming silver sulphide, which is black.
- Copper reacts with humid carbon dioxide in the air, losing its shiny brown surface and developing a green layer. This green layer is known as basic copper carbonate.
- Iron, when exposed to moist air for an extended period, develops a brown flaky substance called rust. Rust is formed when iron reacts with moisture in the air, resulting in brown iron oxide. These instances illustrate rusting.
Activity 11
Aim: Perform an experiment to find out conditions which cause rusting of iron.
Materials required: Three test tubes with corks, iron nails, anhydrous calcium chloride, oil.
Procedure:
- Take three test tubes. Place iron nails in each of them.
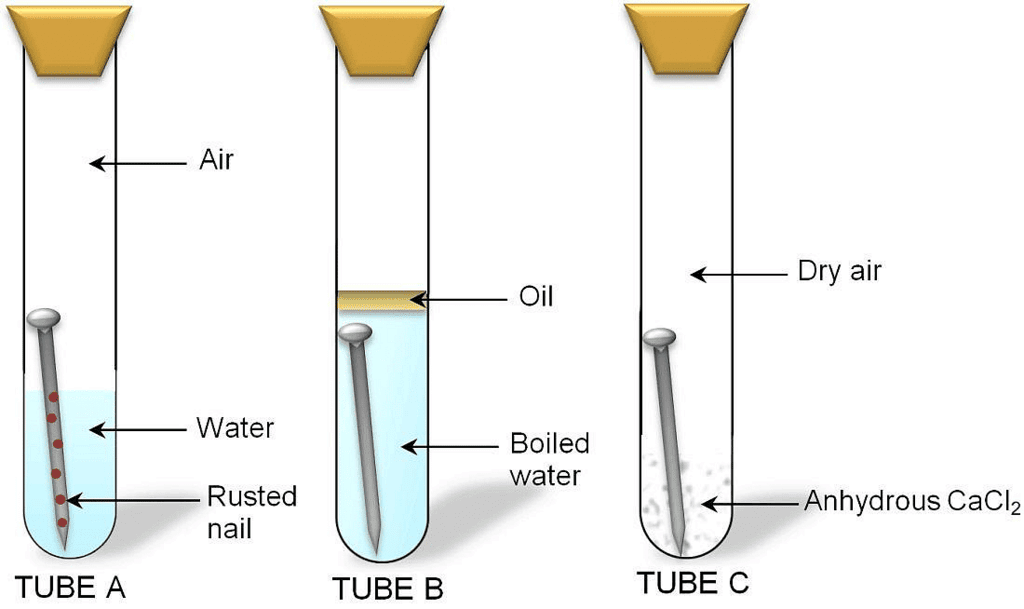 Investigating the condition under which iron rusts
Investigating the condition under which iron rusts - Label these tubes A, B and C.
- Pour some water in test tube A and cork it.
- Pour boiled water in test tube B. Add 1 mL of oil and cork it. The oil will form the upper layer and prevent the air from dissolving in water.
- Put some anhydrous calcium chloride in test tube C and cork it. Anhydrous calcium chloride will absorb the moisture from the air.
- Leave these test tubes for a few days.
It is observed that iron nails rust in test tube A but they do not rust in test tubes B and C. This is because iron nails are exposed to both water and air in test tube A. In test tube B, the nails are exposed to only water and in test tube C, the nails are exposed to only air. This means presence of both water and air necessary for rusting to take place.
Prevention of Corrosion
Rusting of iron can be prevented by the following methods:
- By painting the surface.
- By oiling or greasing the surface.
- Galvanizing, chrome plating, anodising or making alloys.
Galvanisation
It is a method of protecting steel and iron from rusting. The article is coated with a thin layer of zinc. The galvanised article is protected against rusting even if zinc coating is broken.
Alloying
Alloying enhances the properties of metals. For instance, iron is widely used, but pure iron is soft and stretches easily when heated. However, mixing it with a small amount of carbon (around 0.05%) makes it hard and strong.
- When iron is combined with nickel and chromium, it forms stainless steel, which is durable and rust-resistant.
- An alloy is a blend of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal. It is made by melting the main metal and dissolving other elements in a specific ratio, then cooling it at room temperature.
22-carat gold
- Pure gold which is 24-carat gold is very soft and is not suitable for making ornaments.
- It is alloyed with either copper or silver to make it hard.
- Generally, in India, 22-carat gold is used for making jewellery, it means 22 parts of gold is alloyed with 2 parts of copper or silver.
Properties of Alloys
- Alloy of a metal with mercury is known as amalgam. It has been observed that melting point and electrical conductivity of an alloy are lower than those of the constituent metals.
- For example, brass which is an alloy of copper and zinc, and bronze which is an alloy of copper and tin are not as good conductors of electricity as copper.
Solder which is an alloy of lead and tin has a low melting point and is used for welding electrical wires. - The iron pillar near the Qutab Minar was build more than 1600 years ago. The iron workers of India at that time had developed a technique which prevented rusting of iron.
- Scientists from all parts of the world have checked the quality and found that the technique used is really rust resistant i.e., it resists the formation of rust. The pillar has a height of 8 m and weight 6 tonnes or 6,000 kg.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Overview: Metals & Non-Metals - 2 - Science Class 10
| 1. How do metals react with solutions of other metal salts? |  |
| 2. What is the reactivity series of metals? |  |
| 3. How do metals and non-metals react with each other? |  |
| 4. What are the properties of ionic substances? |  |
| 5. How do metals occur in nature? |  |





















