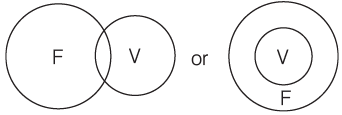Overview: Syllogism | CSAT Preparation - UPSC PDF Download
What is Syllogism?
Syllogism questions consist of a major and a minor premise, leading up to a conclusion. These questions ask you to derive the conclusion on the basis of the relationship existing between different elements of premises.
Let us see an example of syllogism:
Statements:
(a) All cats are dogs.
(b) All dogs are birds.
Conclusion: All cats are birds.
This conclusion is quite visible. But to solve complex problems we have some standard methods.
Various Patterns of Premises
A premise is something assumed or taken for granted.
Type 1: All As are Bs
Premise is:
Reactions:
Some Bs are As- This is a definite conclusion.
Some Bs are not As- This is a probable conclusion.
Type 2: Some As are Bs
The premise is: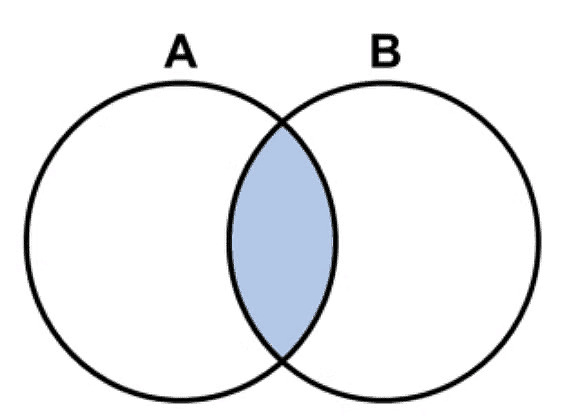
Valid Reactions: Some As are Bs - This is a definite conclusion (Although the above image also shows that some Bs are not As, this cannot be taken as a definite conclusion.)
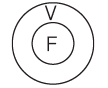
Type 3: No A is B
The premise is as follows: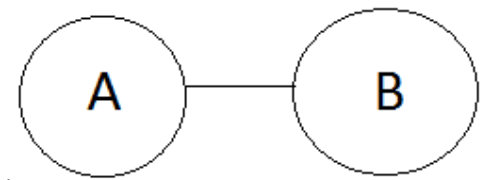 The conclusion No B is A is a valid conclusion.
The conclusion No B is A is a valid conclusion.
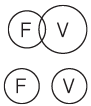
Type 4: Some As are not Bs
Premise: 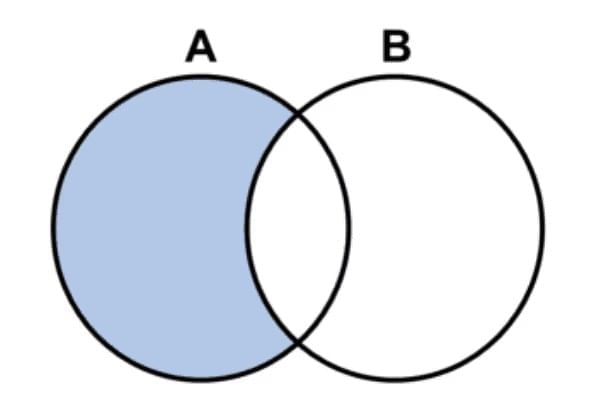
The first component has similarities with the second component.
Type 5: Only a Few
Premise: 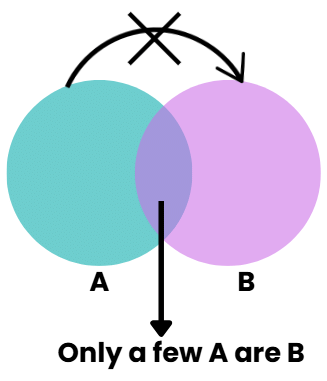
only a small portion of a group possesses a particular characteristic, not all of them.
Important Keywords to note:
1. Each, Every, Only, 100% → All
2. Almost, Little, Few, At most, At least, Many, Mostly, 1-99% → Some
3. None, 0% → No
Method of Solving Syllogism Questions
Method 1: Analytical Method
Following are the four major types of statements generally asked:
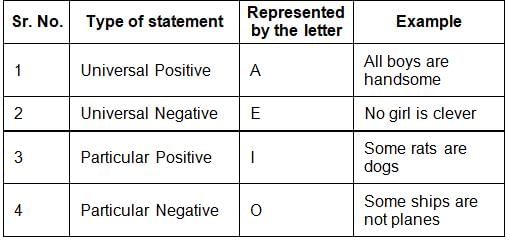
While deriving conclusions, the following points should be kept in mind:
- With two particular statements, no universal conclusion is possible.
- With two positive statements, no negative conclusion is possible.
- With two negative statements, no positive conclusion is possible.
- With two particular statements, no conclusion is possible, except when an 'I' type of statement is given and then by reversing it, an 'I' type of conclusion is given.
Important points related to conclusions drawn from single statements:
- A statement of type 'E' when reversed, gives a conclusion of type 'E & O'.
- A statement of type 'A' when reversed, gives a conclusion of type 'I'.
- A statement of type 'I' when reversed, gives a conclusion of type 'I.'
- A statement of type 'O' when reversed, does not give a conclusion of any type.
Method 2: Venn Diagrams
- Another method of solving such types of questions is by drawing a Venn diagram representing the statements.
- However, it is important that all possible Venn diagrams be drawn.
- If a conclusion can be deduced from all the possible solutions, then that conclusion is true.
- If the conclusion can be concluded from one of the possible Venn diagrams and not from the other possible Venn diagram, then that conclusion is taken as false.
Types of Premises and Their Trivial Conclusions
The types of premises seen in syllogisms and their trivial (immediate) conclusions are as summarised in the table below
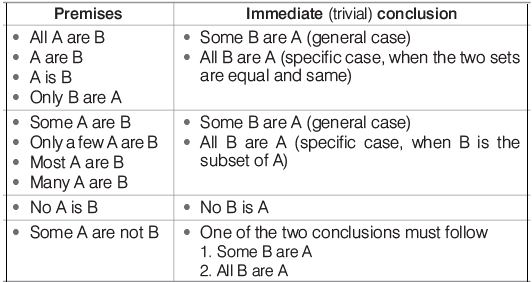 Following types of questions are asked under syllogism:
Following types of questions are asked under syllogism:
Type I Statement and Conclusions Based Questions
In these types of questions a set of statements (two, three or four) is given followed by a set of conclusions (two, three or four) on the basis of statements given the correctness of conclusion is checked or conclusions follow from the statement or not.
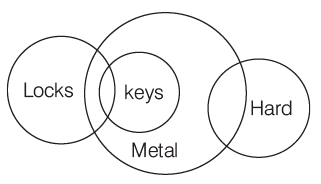
Example: Consider the following statements
1. Some locks are keys.
2. All keys are made from metal.
3. Some metals are hard.
Which of the following conclusion can be drawn from the above statement?
(a) All locks are keys
(b) All keys are hard
(c) Some locks are hard
(d) None of these
Ans: (d)
Sol: Here, we make a Venn diagram from the statement.
So, from the above diagram, it can be concluded that none of the conclusion is correct.
Type II Correctness of the Statements
Following questions consists of four statements, of these four statements, we have to check for the two statements which cannot be true but both can be false. Study the statements carefully and identify the two that satisfy the above condition.
Example: Examine the following statements
1. All fruits are vegetables.
2. Some fruits are not vegetables.
3. Fruits are not vegetables.
4. Some fruits are vegetables.
Which of the following two statements cannot both be true?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Sol: The statement can be understood as follows
1. All fruits are vegetables.
2. Some fruits are not vegetables or atleast one of the fruits is a vegetable
3. Fruits are not vegetables.
4. Some fruits are vegetables.
So, from above four statements only Statements 1 and 3 cannot be true.
Type III Choosing Logically Related Statements
In these types of questions a set of six statements is given, out of which four combinations of three statements can be made, from these six statements we have to choose a set of statements or a combination in which third statement will logically follow the first two statements.
Example: The following question contains six statements followed by four sets of combinations of three. Choose the set in which the third statement is a logical conclusion of the first two.
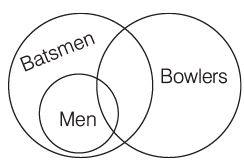
1. Men are batsmen.
2. Boys are fielders.
3. Boys are not batsmen.
4. Some batsmen are bowlers.
5. Boys are not bowlers.
6. Some men are bowlers.
(a) 123
(b) 143
(c) 231
(d) 164
Ans: (d)
Sol: Here, note that a given statement can be looked at as a premise as well as conclusion. In such questions, consider each answer option at a time and verify where the third statement given in the option logically follows from the first two. Based on the outcome, mark or eliminate the answer options. Taking each answer option at a time, observe that only in option (d) the third statement follows the first two.
All men are batsmen and some men are bowlers. Hence, the men who are bowlers are also batsmen. So, there are some batsmen who are also bowlers. The Venn diagram for option (d) is shown is figure. Hence, the correct answer is option (d).
Type IV Checking Correctness of Set of Statements
In these type of questions, few set of statements are given from which we have to choose the correct set in which the third statement can be inferred from the first two statements.
Example: In this question, there are three sets of statements given. Select the set that is most logical i.e., the third statement can be concluded from the first two statements.
1. All watermelons are green. All greens are healthy. All watermelons are healthy.
2. All men have a business. Mohan has a business. Mohan is a man.
3. All roses are fragrant. All flowers are fragrant. All flowers are roses.
(a) Only 2 follows
(b) 1 and 3 follow
(c) 1 and 2 follow
(d) Only 1 follows
Ans: (d)
Sol: Here, consider the first set and verify it. Based on the outcome, eliminate answer options. Now, based on the options left, verify the remaining sets.
Consider Set 1 Since, all watermelons are green, the set of watermelons is a subset of the set of green objects. Similarly, since all greens are healthy, the set of green objects is a subset of the set of the healthy objects. Thus, the set of watermelons is a subset of the set of healthy objects.Therefore, all watermelons are healthy. So, set 1 is logical. Hence, option (a) can be eliminated.
Consider Set 2 All men have a business. Mohan also has a business. Thus, the set of men as well as the set of Mohan are subsets of the set of people having a business. Now, there can be a set of people who are not men but have a business. Mohan can clearly belong to this set. So, the Mohan may or may be a part of the set of men.Thus, the conclusion does not follow. Therefore, set 2 is not logical. Hence, option (c) can be eliminated.
Consider Set 3 Using the same logic as for set 2, the set of flowers and roses may or may not overlap. Thus, the conclusion does not follow. Therefore, set 3 is not logical. Hence, option (b) can be eliminated.Hence, the correct answer is option (d).
Solved Examples
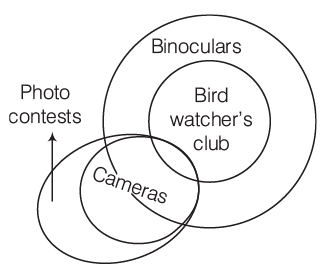
Example1: Examine the following statements
1. Only those who have a pair of binoculars can become the members of the birdwatcher’s club.
2. Some members of the birdwatcher’s club have cameras.
3. Those members who have cameras can take part in photo contests.
Which of the following conclusions can be drawn from the above statements?
(a) All those who have a pair of binoculars are members of the birdwatcher’s club
(b) All members of the birdwatcher’s club have a pair of binoculars
(c) All those who take part, in photo contests are members of the birdwatcher’s club
(d) No conclusion can be drawn
Ans: (b)
Sol: Here, make the consolidated Venn diagram and see which of the conclusion followsIt can be seen from the diagram that all the members of the birdwatcher’s club have a pair of binoculars. Hence, the right answer is option (b).
Example2: Statements:
All dogs are mammals.
Some mammals are carnivores.
Conclusion:
I. Some dogs are carnivores.
II. All carnivores are dogs.
Select the correct conclusion(s):
(a) Only conclusion I
(b) Only conclusion II
(c) Both conclusions I and II
(d) Neither conclusion I nor II
Ans: (d)
Sol: Neither conclusion I nor II is valid based on the given statements. The first statement only establishes a relation between dogs and mammals, and the second statement establishes a relation between mammals and carnivores. We cannot directly relate dogs to carnivores based on the given information.
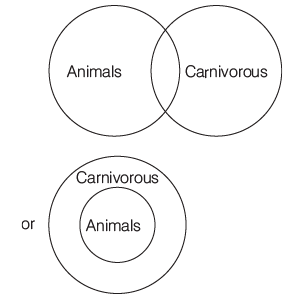
Example3: Examine the following statements
1. All animals are carnivorous.
2. Some animals are not carnivorous.
3. Animals are not carnivorous.
4. Some animals are carnivorous.
Which of the following two statements cannot both be true?
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Sol: The statements can be understood as follows
1. All animals are carnivorous.
This statement can be represented using a Venn diagram as2. Some animals are not carnivorous.
This means that there is atleast one animal which is not carnivorous.3. Animals are not carnivorous.
4. Some animals are carnivorous.
The Venn diagram for this is
Now, consider options
(a) 1 and 3 These statements are contradictory and hence cannot both be true. However, if Statement 2 is true, they can both be false. Hence, option (a) is correct.
(b) 1 and 2 These statements contradict each other and hence cannot both be true. However, both cannot be false, if Statement 1 implies then Statement 2 will be be false. Hence, option (b) is not correct.
(c) 2 and 3 Both statements are complementary and hence can both be true but they both cannot be false at the same time. Hence, option (c) is not correct.
(d) 3 and 4 These statements are contradictory and hence cannot both be true. However, one of these has to be true and hence they both cannot be false at the same time.
Hence, option (d) is not correct.
|
205 videos|264 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Overview: Syllogism - CSAT Preparation - UPSC
| 1. What is the difference between Venn Diagrams and Euler’s Circles in syllogism? |  |
| 2. How can Type I statements lead to trivial conclusions in syllogism? |  |
| 3. What are the criteria for checking the correctness of statements in Type II syllogism questions? |  |
| 4. How do Type III questions involve choosing logically related statements? |  |
| 5. What is the process for checking the correctness of a set of statements in Type IV questions? |  |