Overview: Tribunals in India | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction

Tribunals are not originally a part of the Constitution of India. They were introduced in 1985.
- Tribunals were constituted with the objective of delivering speedy, inexpensive and decentralised adjudication of disputes in various matters.
- Tribunals are created to avoid the regular courts’ route for dispensation of disputes.
- Some tribunals are specialised government agencies like boards and they also have decision-making powers conferred upon them by law.
- The provision for tribunals was not present in the Constitution originally.
Types of Tribunals

- The 42nd Amendment Act introduced these provisions in accordance with the recommendations of the Swaran Singh Committee.
- The Amendment introduced Part XIV-A to the Constitution.
- This Part is called ‘Tribunals’. It contains two articles.
(i) Article 323A: Administrative Tribunals. Administrative tribunals are quasi-judicial institutions that resolve disputes related to the recruitment and service conditions of persons engaged in public service. Article 323A provides for this and the Central Administrative Tribunal was created under this Section.
(ii) Article 323B: Tribunals for other subjects such as:
(a) Taxation
(b) Industrial and labour
(c) Foreign exchange, import and export
(d) Land reforms
(e) Food
(f) The ceiling on urban property
(g) Elections to Parliament and state legislatures
(h) Rent and tenancy rights - While 323A deals with administrative tribunals, 323B deals with other types of tribunals (like National Green Tribunal, Competition Appellate Tribunal (COMPAT), Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT), etc.
- Tribunals under 323A can be established only by the Parliament. However, tribunals under 323B can be established by both the Parliament and the State Legislature.
- Under 323A, there can be only one tribunal at the centre and one for each state (or two or more states), but under 323B, there can be a hierarchy of tribunals.
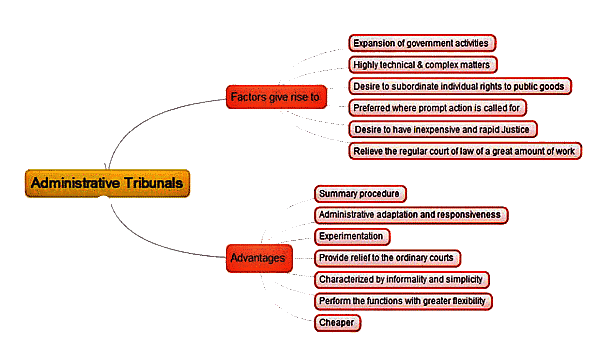
Need of Tribunal
- To overcome the situation that arose due to the pendency of cases in various Courts, domestic tribunals and other Tribunals have been established under different Statutes, hereinafter referred to as the Tribunals.
- The Tribunals were set up to reduce the workload of courts, to expedite decisions and to provide a forum that would be manned by lawyers and experts in the areas falling under the jurisdiction of the Tribunal.
- The tribunals perform an important and specialised role in the justice mechanism. They take a load off the already overburdened courts. They hear disputes related to the environment, armed forces, tax and administrative issues.
Constitutional Provisions
- Tribunals were not part of the original constitution, it was incorporated in the Indian Constitution by 42nd Amendment Act, 1976.
(i) Article 323-A deals with Administrative Tribunals.
(ii) Article 323-B deals with tribunals for other matters. - Under Article 323 B, the Parliament and the state legislatures are authorised to provide for the establishment of tribunals for the adjudication of disputes relating to the following matters:
(i) Taxation
(ii) Foreign exchange, import and export
(iii) Industrial and labour
(iv) Land reforms
(v) Ceiling on urban property
(vi) Elections to Parliament and state legislatures
(vii) Foodstuff
(viii) Rent and tenancy rights - Articles 323 A and 323 B differ in the following three aspects:
(i) While Article 323 A contemplates the establishment of tribunals for public service matters only, Article 323 B contemplates the establishment of tribunals for certain other matters (mentioned above).
(ii) While tribunals under Article 323 A can be established only by Parliament, tribunals under Article 323 B can be established both by Parliament and state legislatures with respect to matters falling within their legislative competence.
(iii) Under Article 323 A, only one tribunal for the Centre and one for each state or two or more states may be established. There is no question of the hierarchy of tribunals, whereas under Article 323 B a hierarchy of tribunals may be created. - Article 262: The Indian Constitution provides a role for the Central government in adjudicating conflicts surrounding inter-state rivers that arise among the state/regional governments.
Administrative Tribunals

The characteristics of administrative tribunals are mentioned below:
- They are of statutory origin, and so must be created by a statute by Parliament/Legislatures.
- They are quasi-judicial in nature, which means, they have some, not all the features of a court.
- They function on the principles of natural justice and are not bound by the Civil Procedure Code.
- They have the power to summon witnesses, administer oaths and compel the submission of documents, etc. like other courts.
- The writs of prohibition and certiorari are available against decisions of such tribunals.
- They are independent bodies and are not subject to administrative interference.
➤ Administrative Tribunals Advantages
- Tribunals offer flexibility when compared to ordinary courts that have to adhere to strict procedures.
- They are cheaper and offer speedy justice.
- The procedure followed by the tribunals is simple and easy to understand even for the layman.
- They also offer relief to the ordinary courts that are already over-burdened with suits.
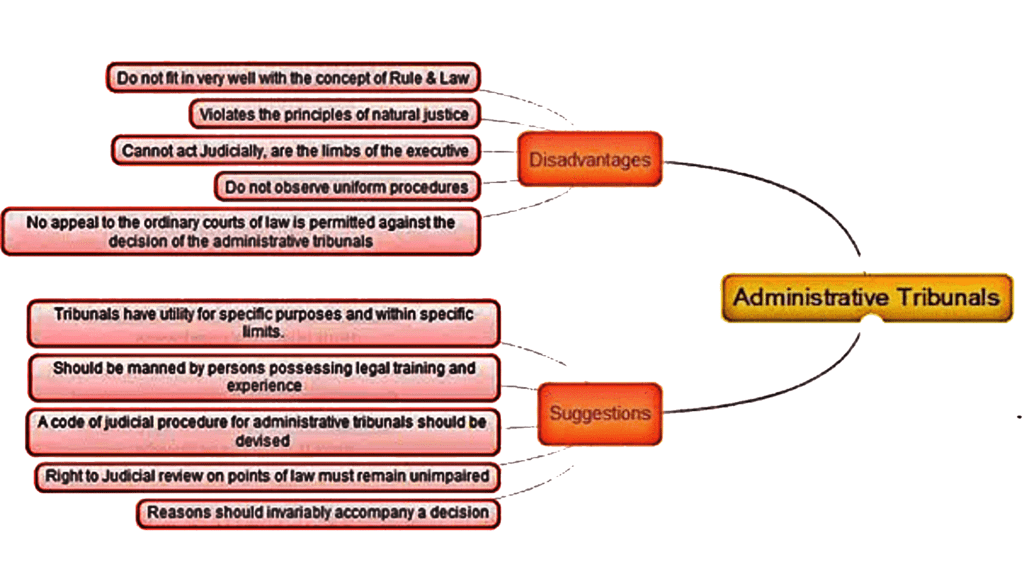
➤ Administrative Tribunals Disadvantages
- They go against the spirit of the “Rule of Law”.
(i) Rule of Law ensures that arbitrary power is not exercised by institutions or individuals.
(ii) It is the principle that everybody is subject to and accountable to the law (which is fair). - Ordinary courts have a uniform code of procedure for civil and criminal cases. But, administrative tribunals have no uniform code of procedure.
- Such tribunals are sometimes handled by subject matter experts who have no experience in dealing with judicial proceedings. Hence, they end up adopting summary procedures as well.
➤ Challenges of Administrative Tribunals
Although tribunals were constituted to deliver speedy and quick justice to people, there are some challenges in their functioning.
- There is a lack of autonomy in the appointment and funding of tribunals.
- In the Chandra Kumar case (1997), the Supreme Court had held that appeals against the orders of a tribunal could be made in the High Court. This defeats the purpose of reducing the burden of the normal courts.
- Currently, there is a lack of infrastructure for the tribunals to function efficiently.
- Generally, the government appoints retired judges as chairpersons to tribunals. Because of this, current judges could show favouritism towards certain things so that they may be appointed post-retirement.
- The autonomy of the tribunals should be maintained and there is a need for structural and functional reforms of tribunals so that they are removed from the influence of the executive.
- There should be some form of judicial control over tribunals so that the Rule of Law is maintained.
➤ Other Tribunals
A few examples of other tribunals are briefly described below.
Armed Forces Tribunal
- This is a military tribunal established under the Armed Forces Tribunal Act, 2007.
- It settles disputes with respect to the commission, emoluments, appointments and service conditions of personnel in the armed forces.
- Its Principal Bench is in New Delhi. It also has ten Regional Benches.
National Green Tribunal


- It was formed in 2010 for effective and expeditious disposal of cases that are related to the protection and conservation of the environment, forests and other natural resources.
- Read more on the National Green Tribunal (NGT) in the linked article.
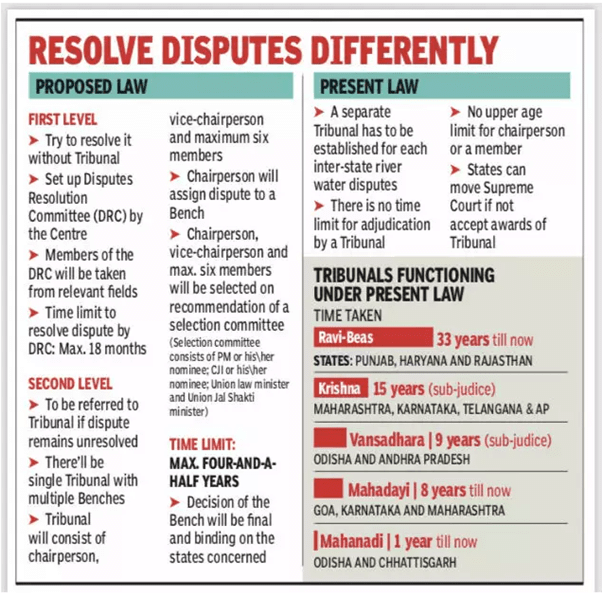
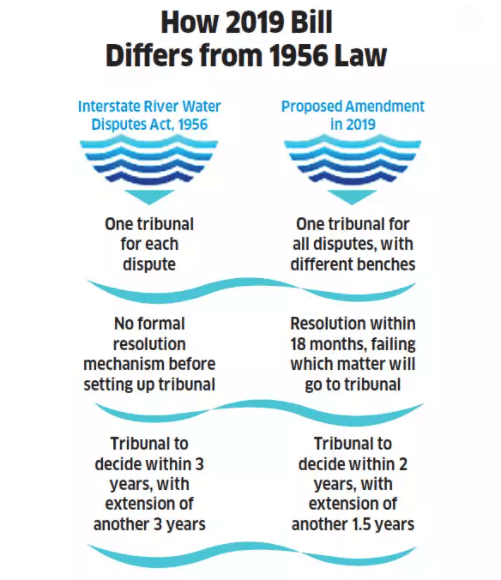
Water Disputes Tribunal
- These are constituted for the purpose of settling disputes between Indian states on the question of water-sharing between rivers that flow through multiple states.
- For more on the Inter-State river water disputes tribunal, check the linked article.
Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT)
- Established in 1941, the ITAT deals with appeals under the direct taxes acts.
- The orders passed by this tribunal are final and an appeal lies to the High Court only if a substantial question of law arises for determination.
- Currently, the tribunal has 63 Benches.
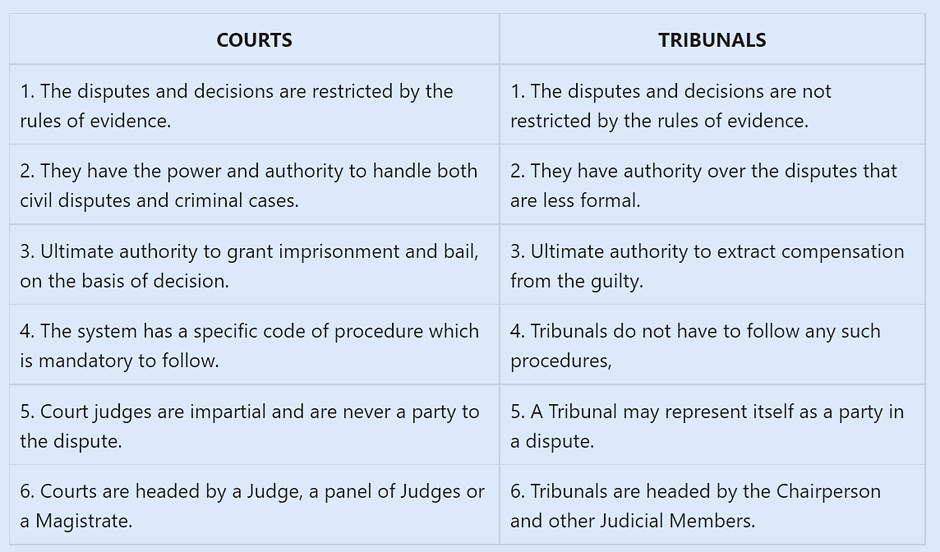
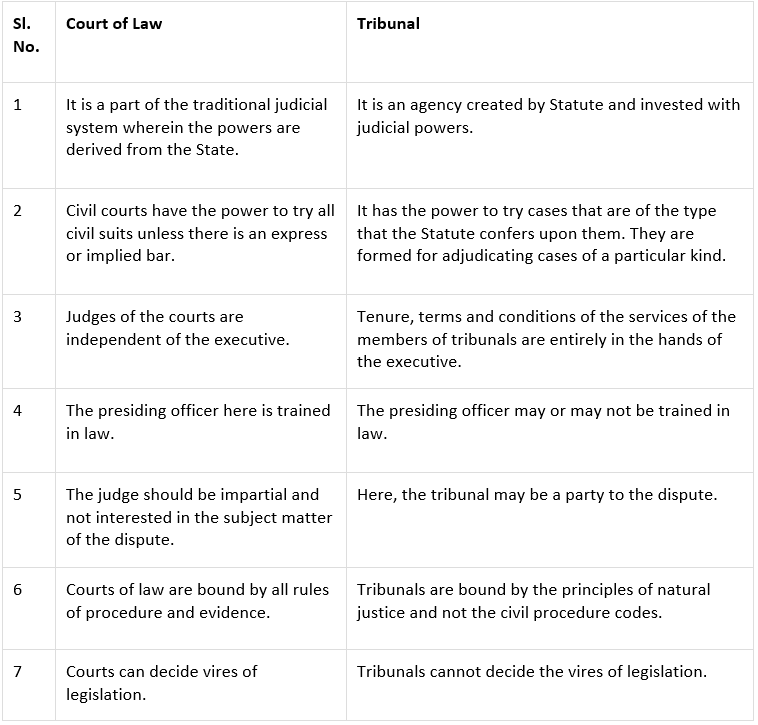
➤ Tribunal vs Court Both tribunals and courts deal with settling disputes between parties that affect the subjects’ rights. Tribunals are like courts in many respects but there are differences between the two. The following table summarises the difference between tribunals and courts.
Both tribunals and courts deal with settling disputes between parties that affect the subjects’ rights. Tribunals are like courts in many respects but there are differences between the two. The following table summarises the difference between tribunals and courts.
Merging of Tribunals
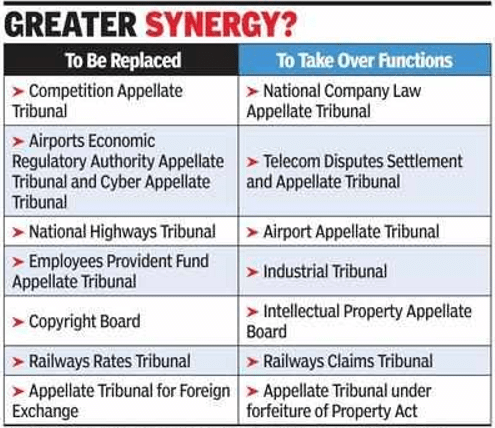
- The Finance Act of 2017 merged eight tribunals according to functional similarity.
The list of the tribunals that have been merged are given below:
(i) The Employees Provident Fund Appellate Tribunal with The Industrial Tribunal.
(ii) The Copyright Board with The Intellectual Property Appellate Board.
(iii) The Railways Rates Tribunal with The Railways Claims Tribunal.
(iv) The Appellate Tribunal for Foreign Exchange with The Appellate Tribunal (Smugglers and Foreign Exchange Manipulators (Forfeiture of Property) Act, 1976.
(v) The National Highways Tribunal with The Airport Appellate Tribunal.
(vi) The Cyber Appellate Tribunal and The Airports Economic Regulatory Authority Appellate Tribunal with The Settlement and Appellate Tribunal (TDSAT).
(vii) The Competition Appellate Tribunal with the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal.
Tribunals Reforms Ordinance 2021
- The government, through the Tribunals Reforms Ordinance 2021, is seeking to dissolve some existing tribunals and transfer their functions to the existing judicial bodies.
- Through the Ordinance, the government seeks to amend the Finance Act 2017 to include provisions related to the composition of search-cum-selection committees and the term of office of members for 19 tribunals (such as Customs, Excise, and Service Tax Appellate Tribunal) in the Act itself.
- The list of appellate bodies that the Tribunals Reform Ordinance 2021 is mentioned below along with the list of the proposed entities to which the functions of the discussed tribunals will be transferred:
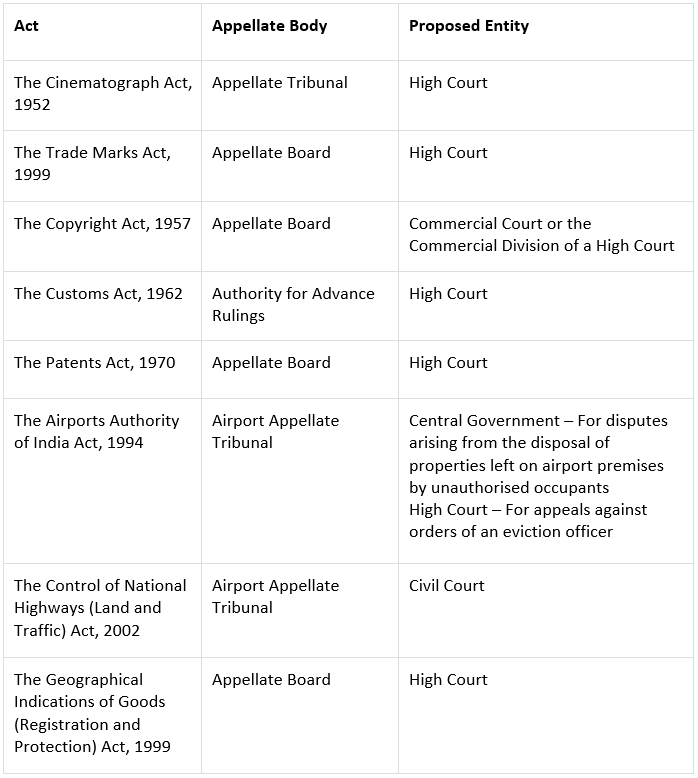
Provisions Proposed in the Tribunals Reform Ordinance 2021:
➤ Search-cum-selection committee
The committee that is responsible to recommend the names of the chairpersons and the members for the appointment by the central government in the Tribunal is called the search-cum-selection committee.
The composition of the committee as mentioned in the Tribunals Ordinance 2021 is:
- Chairperson – The Chief Justice of India, or a Supreme Court Judge nominated by him. He/She has the casting vote
- Two secretaries – Central Government nominates them
- The sitting or outgoing Chairperson, or a retired Supreme Court Judge, or a retired Chief Justice of a High Court
- The Secretary of the Ministry under which the Tribunal is constituted. He/She has no voting right.
(i) Term of Office for the Tribunals Members
The Tribunals Reform Ordinance states the following term of office:
- Chairperson – 4 years or till he attains the age of 70 years [Whichever is earlier]
- Remaining Members - 4 years or till they attain the age of 67 years [Whichever is earlier]
- National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC)
The ordinance seeks to include the NCDRC within the purview of the Finance Act 2017. The NCDRC has been set up under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
|
150 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Overview: Tribunals in India - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the purpose of tribunals in India? |  |
| 2. How are tribunals different from regular courts in India? |  |
| 3. Which areas of law do tribunals in India cover? |  |
| 4. How are tribunal decisions enforced in India? |  |
| 5. Can tribunal decisions be appealed in India? |  |





















