Life Processes- 1 Chapter Notes | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Earth is the only known planet to support life. There are beings who live, die and become part of nature again. The living organism can be differentiated from the inanimate entities on various parameters of life processes.
Life Processes
- The maintenance of living organisms is essential even if they are moving, resting, or even sleeping. The processes that together maintain life are known as life processes.
- The various life processes which take place in living organisms are called metabolic activities or metabolism. These life processes can either be anabolic or catabolic in nature.
- Nutrition, respiration, transportation, and excretion are some of the life processes that are essential for the functioning as well as maintenance of living organisms.
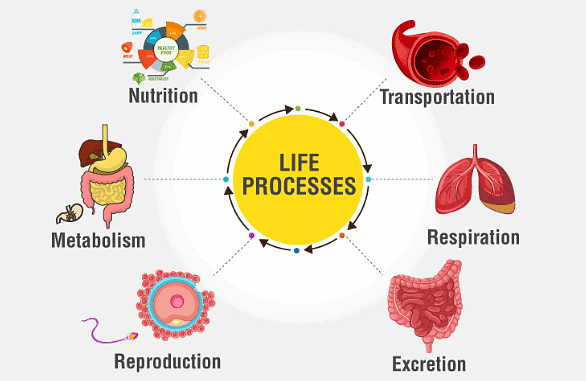 Life Processes
Life Processes
Nutrition
- Nutrition is defined as a process by which living organisms procure food or synthesize it and convert it into simple absorbable form by a series of biochemical processes.
- Nutrient can be defined as a substance that an organism obtains from its surroundings and use as a source of energy as well as providing raw materials for the biosynthesis of body constituents.
- There are two basic modes of nutrition: autotrophic and heterotrophic.

Autotrophic Nutrition
- Autotrophic organisms meet their carbon and energy needs through photosynthesis. This process involves the conversion of external substances into stored energy.
- During photosynthesis, autotrophs absorb carbon dioxide and water, converting them into carbohydrates with the help of sunlight and chlorophyll.
- Carbohydrates produced are used as an energy source for the plant's activities.
- Excess carbohydrates are stored as starch, acting as an internal energy reserve for the plant's future needs.

- In a similar manner, humans store energy from food as glycogen.

Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis can be defined as the synthesis of organic compounds (carbohydrates) from CO2 and H2O using radiant energy or solar energy by chlorophyll molecules.
The process of photosynthesis involves two phases: Light Reaction and Dark Reaction.
The following events occur during the process of photosynthesis:
- Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
- Conversion of light energy to chemical energy as well as splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
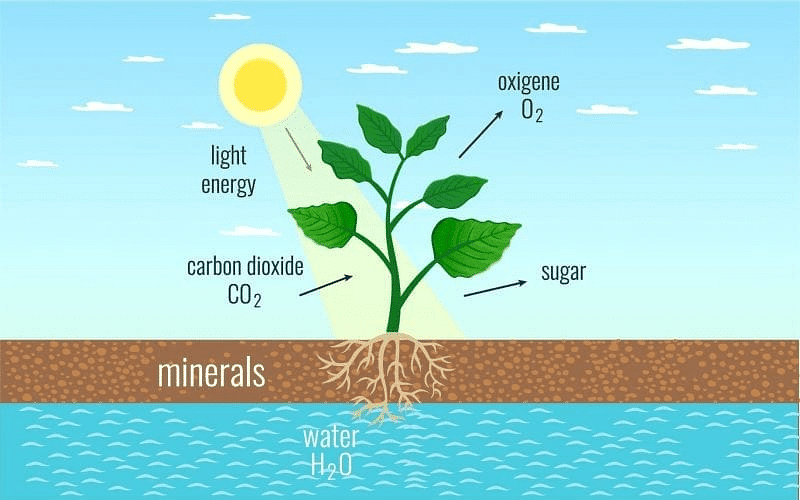 Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Experiment Activity:
- Take a potted plant with variegated leaves, such as a money plant or crotons.
- Place the plant in a dark room for three days to deplete starch reserves.
- Expose the plant to sunlight for about six hours.
- Pluck a leaf, mark the green areas, and trace them on a sheet of paper.
- Boil the leaf in water and then immerse it in alcohol.
- Heat the alcohol in a water-bath until it boils.
- Observe color changes in the leaf and solution.
- Dip the leaf in a dilute iodine solution and compare colors with the initial tracing.
- Draw conclusions about starch presence in different leaf areas.
Heterotrophic Nutrition
Heterotrophic organisms cannot prepare their food. They are dependent on plants, animals or on dead decaying organic materials for their food. Saprophytes derive their nourishment from dead decaying matter.

- Organisms adapt to their environment, and their nutrition methods vary based on food type, availability, and how it's acquired.
- For instance, the nature of the food source (stationary like grass or mobile like a deer) influences how it's accessed.
- Differences exist in the nutritive apparatus used by animals like cows and lions.
- Organisms employ various strategies to acquire and utilize food.
- Some organisms externally break down food before absorption, for example, fungi such as bread molds, yeast, and mushrooms.
- Others ingest whole material and break it down internally, based on body design and function.
- Some organisms obtain nutrition from plants or animals without causing harm, employing parasitic strategies.
- Parasitic nutrition is observed in organisms like cuscuta, ticks, lice, leeches, and tapeworms which depend on a host for nutrition.
Holozoic nutrition is a mode of nutrition that involves swallowing solid food material. Ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion are the various steps involved in holozoic nutrition.
Nutrition in Humans & Other Organisms
- In animals, procurement of food is highly variable. The process of nutrition becomes more complex in multicellular organisms as compared to unicellular organisms. In single-celled organisms like Amoeba, the food is taken in through the general body surface.
- In humans, the digestive system consists of a long alimentary canal and digestive glands. Various parts of the alimentary canal in sequence are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
- In the mouth, food is crushed by teeth and mixed with saliva, secreted by salivary glands. Saliva contains an enzyme called salivary amylase that breaks down starch into simple sugar.
- When we swallow the food (bolus), it is further pushed forward by rhythmic contraction and relaxation of muscles present inlining of the alimentary canal. These movements are called peristaltic movements. Thus, the food is carried to the stomach through the food pipe or esophagus.
- The stomach is a large C-shaped hollow organ that expands when food enters it. The muscular walls of the stomach help in mixing the food thoroughly, with the gastric secretions.
- The gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach secrete hydrochloric acid, a protein-digesting enzyme called pepsin and mucus.
- Hydrochloric acid facilitates the action of the enzyme pepsin as this enzyme works in an acidic medium. Apart from it, hydrochloric acid prevents the fermentation of food and also kills harmful microorganisms present in the food. Mucus protects the inner wall of the stomach from excoriation by highly acidic HCl.
- From the stomach, the partially digested food (chyme) enters the small intestine. The exit of food from the stomach is regulated by a sphincter muscle which releases it in small amounts into the small intestine.
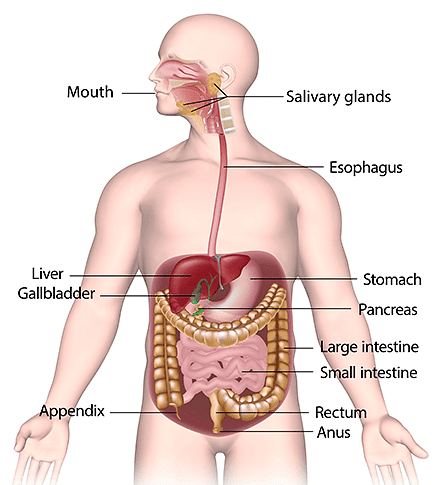 Digestive System
Digestive System
- The length of the small intestine differs in various animals depending on the feeding habit. Herbivores have a longer small intestine (due to the high bulk of vegetal matter and cellulose) as compared to carnivores (due to the smaller bulk of animal food).
- The small intestine is the site of the complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. The proximal part of the small intestine referred to as the duodenum receives partially digested acidified food from the stomach. Duodenal glands secrete an alkaline mucus-containing juice that helps in neutralising the chyme and protects the duodenal wall from corrosion.
- A common hepatopancreatic duct opens into the duodenum. It is formed of the common bile duct from the liver and gall bladder as well as a pancreatic duct from the pancreas.
- Fats are present in the form of large globules in the small intestine which makes it difficult for enzymes to act on them. Bile juice from the liver contains bile pigments and bile salts. Bile salts break fats into small globules by a process called emulsification and thus increase the efficiency of enzyme action (lipase).
- The pancreas secretes slightly alkaline pancreatic juice which contains three major following enzymes:

(i) Trypsin which digests proteins.
(ii) Lipase which digests fats.
(iii) Amylase which digests carbohydrates. - The walls of the small intestine contain glands that secrete intestinal juice. The enzymes present in it, finally convert the proteins into amino acids, complex carbohydrates into glucose and fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
- The inner lining of the small intestine has numerous finger-like projections called villi which increase the surface area for absorption of digested food. The villi are richly supplied with blood vessels that take the absorbed food to every cell of the body, where it is utilised for obtaining energy, building up new tissues and the repair of old ones.
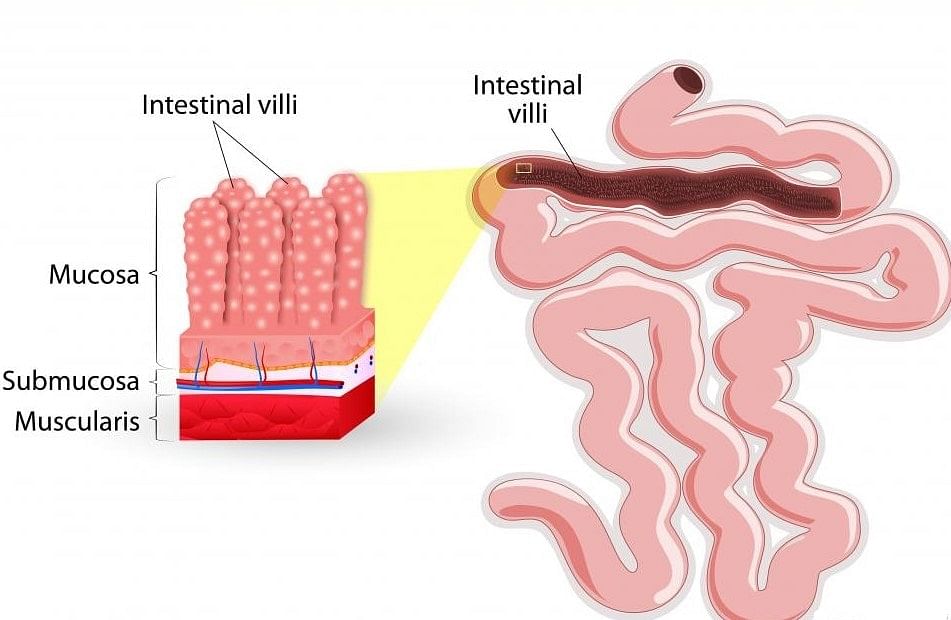 Small Intestine
Small Intestine
- The undigested food is sent into the large intestine where more water is reabsorbed from undigested food. The rest of the undigested food material is removed from the body via the anus. The anal sphincter regulates the exit of this waste material.
- The food material taken in during the process of nutrition is used by cells to provide energy for various life processes.
- Some organisms use oxygen to bring about the complete breakdown of glucose in cells into carbon dioxide and water (aerobic respiration).
Respiration is a biochemical catabolic process that involves:
(i) Intake of molecular oxygen from the environment
(ii) Stepwise oxidation of food with incoming oxygen
(iii) Elimination of carbon dioxide produced during oxidation and
(iv) Release of energy.Question for Chapter Notes: Life Processes- 1Try yourself:What is the primary function of villi in the small intestine?View Solution
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Life Processes- 1 Chapter Notes - Science Class 10
| 1. What is photosynthesis and why is it important for life on Earth? |  |
| 2. What are the main components required for photosynthesis to occur? |  |
| 3. How do plants absorb carbon dioxide and water for photosynthesis? |  |
| 4. What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis? |  |
| 5. What are the end products of photosynthesis and how do they benefit living organisms? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|




















