Overview: Metals & Non-Metals - 1 | Science Class 10 PDF Download
An overview of the chapter Metals & Non-metals is provided in this document, which will help you quickly review the topic and get a good grasp of it with the help of all the activities explained in this document.
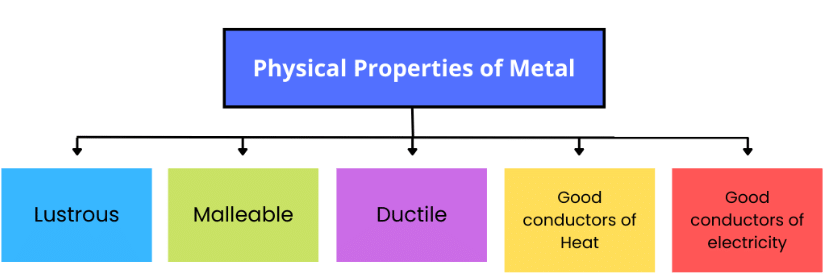
Properties of Metals
Metals show metallic lustre, and are generally hard, malleable and ductile. They are good conductors of heat and electricity.
The following activities prove the above points:
Activity-1: Metals Possess Lustre
Aim:
Perform an activity to show that metals possess lustre.Materials required:
Copper strip, blade, piece of cloth.Procedure:
- Take a copper strip that has remained exposed to moisture and atmosphere for a long time. It will have a greenish coating of copper oxide and copper carbonate.
- Rub the strip with a blade patiently for about five minutes.
- Clean the surface with a clean cloth piece.
Results:
- We shall find that the surface which was dull earlier become shining red-brown which is the colour of copper.
- The activity proves that metals have lustre.
- All metals have lustre, but the colours might be different.
Activity-2: Metals are malleable & ductile
Aim:
Perform an activity to prove that metals are malleable (can be beaten into sheets) and ductile (can be drawn into wires).Materials required:
Metals such as iron, copper, aluminium, hammer.Procedure:
- Take a small piece of iron metal. Place it on an iron block.
- Strike the iron piece with a hammer about ten times.
Result:
- We observe that the iron piece is flattened into a thin sheet. This property is known as malleability.
- Most of the metals are malleable. Gold and silver are the most malleable metals.

Note:
- Similarly, we find that most metals are ductile, i.e., they can be drawn into wares, using a suitable mechanical device.
Surprisingly, one gram of gold can be drawn into thin wire measuring two kilometres.

Activity-3: Metals- Effective Heat Conductors
Aim:
Perform an activity to show that metals are good conductors of heat.Materials required:
Iron stand, clamp, iron wire, pin, wax, burner.Procedure:
- Take long straight ironware about 30 cm long.
- Clamp it to an iron stand as shown.
- Fix a pin to the free end of the wire using wax.
- Heat the wire using a burner near the place where it is clamped.
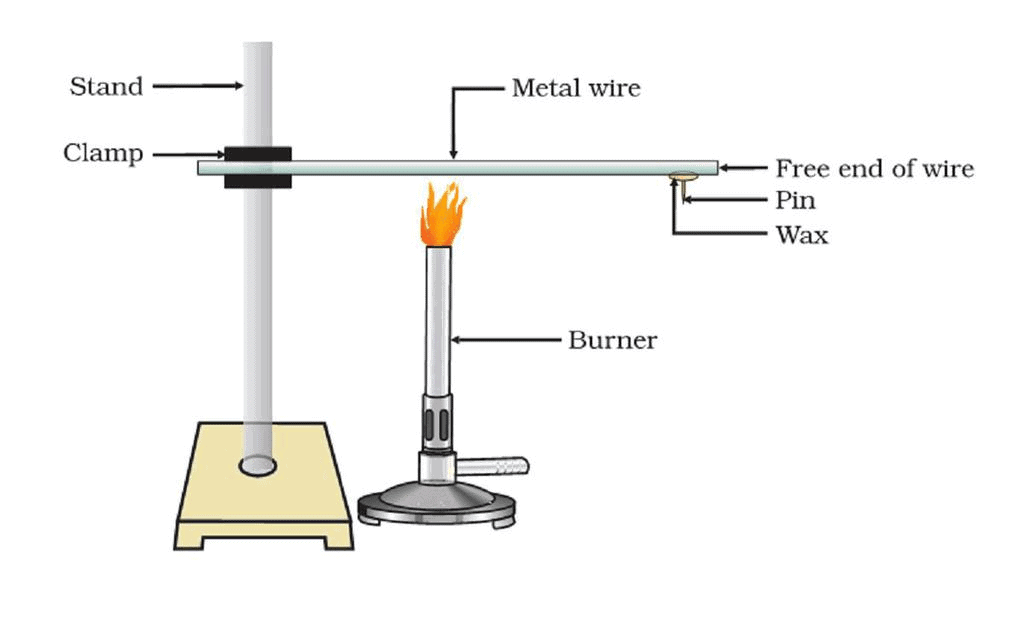 Experiment Setup Result:
Experiment Setup Result:
- We observe that after some time, the pin that was fixed to the free end of the wire with wax falls down.
- We observe the same with other metals. This is because the wax gets melted because of heat.
- This proves that metals are good conductors of heat. The best conductors of heat are silver and copper. Lead and mercury are comparatively poor conductors of heat.
Activity-4: Metals- Effective electricity conductors
Aim:
Perform an activity to show that metals are good conductors of electricity.Materials required:
Battery, bulb, switch, clips, samples of metals.Procedure:
- Set up an electric circuit as shown.
- Place a piece of copper metal between terminals A and B.
- We find that the bulb in the circuit glows. This is because the copper metal passes on the current from clip A to clip B.
Result:
- Copper metal is a good conductor of electricity.
- We observe the same phenomenon with other metals also.
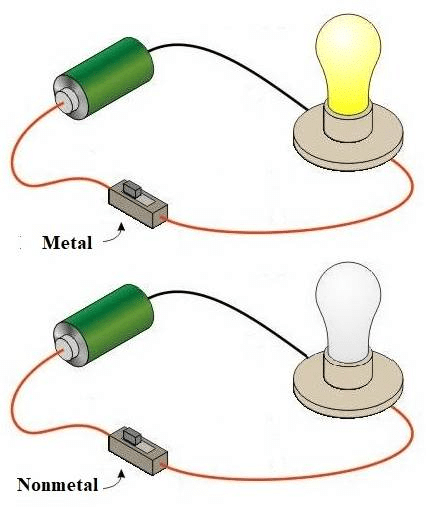 Metals conduct Heat and Electricity easily
Metals conduct Heat and Electricity easilyMetals are Sonorous
- Metals produce a sound when they strike a hard surface. We express it by saying that metals are sonorous.
- That is why school bells are made of metals.

Properties of Non-metals
- Substances like carbon, sulphur and iodine are non-metals.

- They are either solids or gas with the exception of bromine which is a liquid.
- Non-metals, in general, do not possess metallic lustre, do not conduct heat and electricity and are not sonorous.
- They are comparatively softer substances.
Exceptions
- Metals, in general, have high melting points. But mercury, gallium and caesium have low melting points and are liquids at room temperature.
- Iodine, a non-metal, shows lustre.
- Diamond, an allotrope of carbon, is the hardest natural substance known. Graphite, another allotrope of carbon, is a conductor of electricity.
- Alkali metals like sodium and potassium (metals) are soft and can be cut with a knife. They have low densities and low melting points.
Activity-5: Distinguishing Metals and Non-Metals
Aim:
Perform an experiment to decide whether the given substance is a metal or a non-metal.Materials required:
A piece of magnesium ribbon, sulphur powder, pair of tongs, an iron sheet, burner, test tube, blue and red litmus papers.Procedure:
- Hold the Mg ribbon with a pair of tongs. It burns and forms a white residue.
- Collect the white residue and dissolve it in water in a test tube.
- Dip red litmus paper into it. It turns blue showing that the solution was alkaline. It means metals on burning form basic oxides.
- Now bum sulphur powder on a thick sheet of iron. Collect the fumes produced (SO2) into an inverted test tube over it.
- Immediately add water to the test tube and shake.
- Now dip a blue litmus paper into the solution. It turns red.
- That means the solution in the test tube was acidic.
- That means sulphur, a non-metal on burning forms oxide which is acidic.
Result:
- Thus metals form basic oxides, and non-metals form acidic oxides.
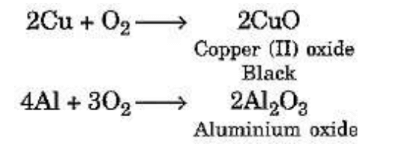
Reaction of Metals with Oxygen
Magnesium burns in the air easily to produce magnesium oxide. However, not all metals combine
with oxygen easily. Some metals require heating in combination with oxygen.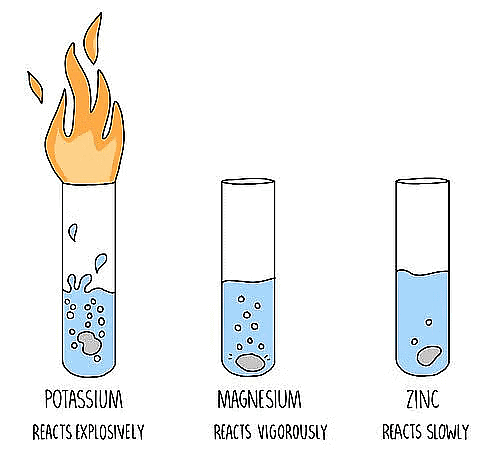 For example :
For example :
Amphoteric oxides
Some metal oxides such as aluminium oxide and zinc oxide show both acidic as well as basic
behaviour. Such metal oxides react with both acids as well as bases to produce salt and
water. Such oxides are known as amphoteric oxides. This is illustrated by taking the example
of aluminium oxide.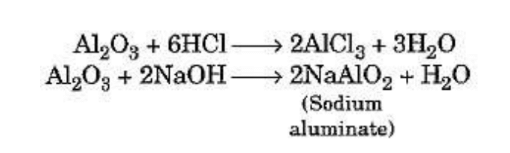
Solubility of Metal Oxides
Most metal oxides are insoluble in water. Oxides of sodium and potassium dissolve in water
to form alkalis.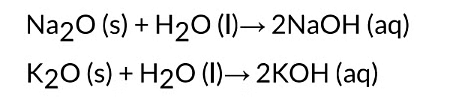
Reactivity of Different Metals with Oxygen
(i) Sodium and potassium metals react so vigorously with oxygen that they catch fire when
kept in the open. They are kept immersed in kerosene oil.
(ii) Surface of metals like Mg, Al, Zn and Pb is covered with oxide layer, when kept at ordinary
temperature.
(iii) Iron does not burn on heating but iron filings bum vigorously when sprinkled on the
flame.
(iv) Copper does not bum but forms a black layer of copper (II) oxide.
(v) Silver and gold do not react with oxygen even at high temperature.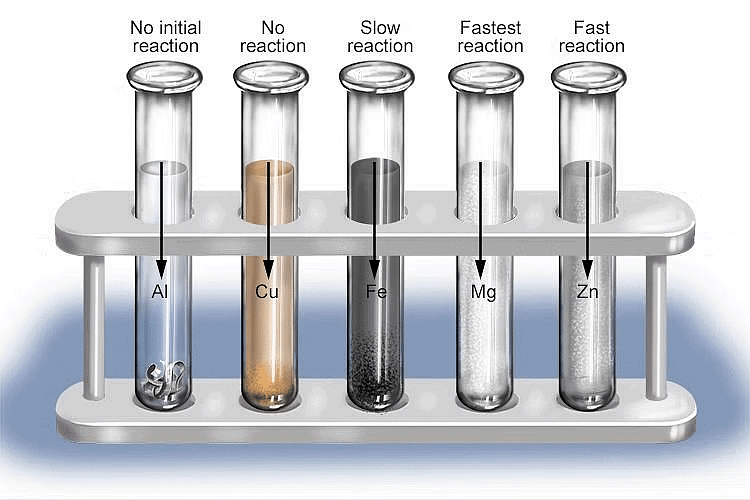
Anodising
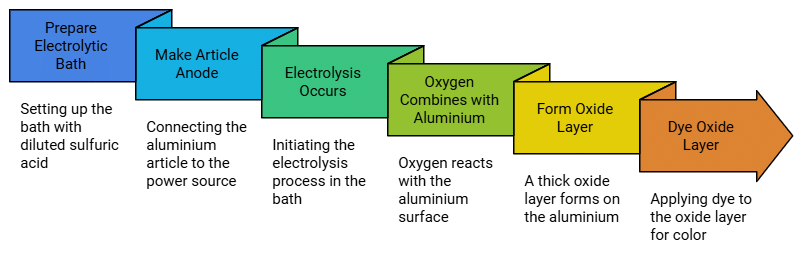
The process of forming thick oxide layer on aluminium is called anodising. This oxide layer
makes it resistant to further oxidation. Anodising is carried out by electrolysis of a solution
of dil sulphuric acid. The article to be anodised is made the anode in the electrolytic bath:
oxygen liberated at the anode combines with the aluminium article and an oxide layer is
formed on the metal. The oxide layer can be dyed easily to give aluminium article an
attractive look.
Reaction of Metals with Water
Different metals show different reactivity with water.
(i) Metals like Na, K and Ca react with cold water instantly. Na and K metals react so
violently that hydrogen produced in the reaction catches fire.
2K (s) + 2H20(I) → 2KOH (aq) + H2 (g) + Energy
(ii) Reaction with Ca is less violent. Heat evolved is not sufficient for hydrogen to catch fire.
Ca (s) + 2H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
Calcium floats on water because bubbles of hydrogen formed sticks to the metal (hydrogen
is lighter than air).
(iii) Magnesium does not react with cold water. It reacts with hot water to form magnesium
hydroxide and hydrogen. It also starts floating like calcium.
Mg + 2H20 (hot) → Mg(OH)2 + H2
(iv) Metals like AI, Fe and Zn do not react either with cold or hot water. They react with
steam to form metal oxide and hydrogen.
Activity-6: AI, Fe and Zn react with Steam
Aim:
Perform an activity to show that AI, Fe, and Zn react with steam to form a metaloxide and hydrogen.
Materials required:
Hard glass test tube, glass wool, samples of AI, Fe, and Zn metals, burner, stand, cork, delivery tube, trough, another glass tube to collect water.Procedure:
(1) Set up the apparatus as shown in the figure.
(2) Place the sample of Al metal and glass-wool soaked in water as shown in the figure.
(3) Fill the trough with water and invert a test tube filled with water over the other end of the delivery tube.
(4) Place a burner below the glass-wool soaked in water.
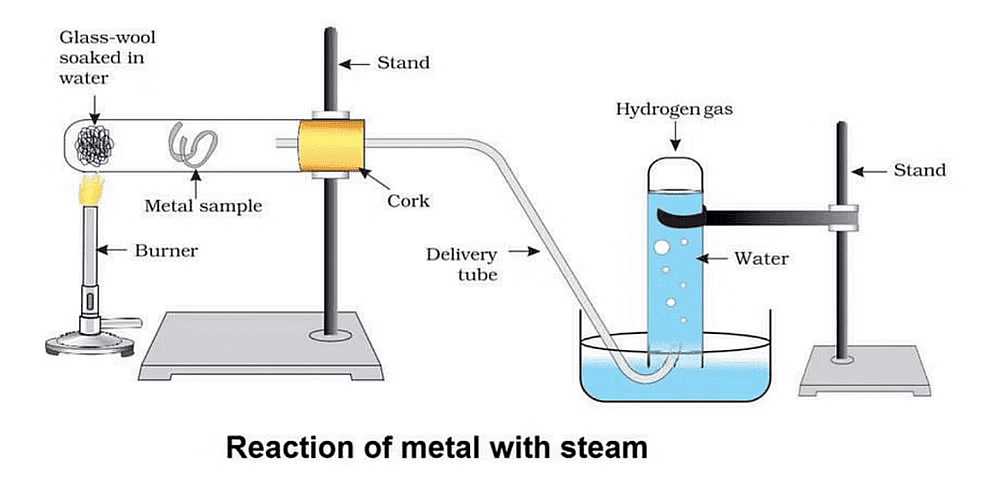
The action of steam on a metal
We find that hydrogen gas is evolved which is collected in the glass test tube.
The reactions taking place are represented as under :
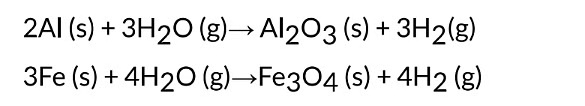
It is observed that lead, copper, silver and gold do not react with cold water or hot water or steam.
The Reaction of Metals with Acids
Different metals react with acid with different rate of reaction. Some metals do not react at all.
Activity 7: Rates of Reactions of Metals with Acids
Aim:
Perform an activity to study the rates of reactions of metals with acids.Materials required:
Mg, AI, Zn, Cu, Mn metals, test tubes, dilute HCl, dilute HN03.Procedure:
(1) Take dilute hydrochloric acid in different test tubes.
(2) Add a small amount of different metals in the test tubes separately.
It is observed that different metals react at different speeds. It is found that the rate of reaction is fastest with Mg. It decreases in the order: Mg > AI > Zn > Fe. There is no reaction at all with copper. The reactions with metals can be written as:
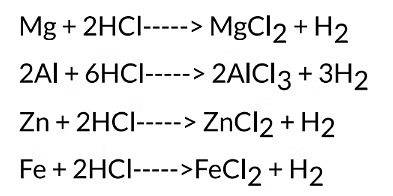
(3) Copper does not react at all with dilute hydrochloric acid.
(4) Now take dilute HN03 in different test tubes. Add the above metals separately in different test tubes. It is observed that hydrogen gas is not evolved with any metal. This isbecause hydrogen gas gets oxidised to water by nitric acid and some oxide of nitrogen isproduced.
(5) Take very dilute nitric acid in two test tubes. In one test-tube add a small piece of magnesium and in the other, a small piece of manganese. We observe that hydrogen gas isevolved in the two test tubes.
Aqua regia
It is the only reagent that is capable of dissolving metals like gold and platinum. It is obtained by mixing concentrated hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid in a ratio of 3:I. Aqua regia is a Latin word meaning 'royal water'. Aqua regia is highly corrosive and fuming.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Overview: Metals & Non-Metals - 1 - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the main properties of metals? |  |
| 2. How can we distinguish between metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. What happens when metals react with oxygen? |  |
| 4. How do metals react with water? |  |
| 5. Why are metals considered effective conductors of heat and electricity? |  |






















