PIB Summary- 10th May, 2021 | PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary - UPSC PDF Download
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH)
Context:
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare has provided an enhanced allocation of Rs. 2250 Crore for the year 2021-22 for ‘Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture’ (MIDH).
What is the MIDH Scheme?
The Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture or MIDH is a scheme for the holistic growth and development of the Indian horticulture sector.
- This Centrally Sponsored scheme covers vegetables, fruits, roots and tuber crops, aromatic plants, flowers, spices, bamboo, coconut, cashew and cocoa.
- MIDH also provides technical support and advice to state horticultural missions, Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY), Saffron Mission and the National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA).
- MIDH is under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, GOI.
- The strategies to improve the horticulture segment employed by the scheme include technology promotion, research, post-harvest management, extension, processing and marketing. The scheme emphasises using differentiated strategies for different states based on the region’s agro-climatic features.
MIDH Objectives:
The major goal under this scheme is to promote the growth of the horticulture sector in India.
- The scheme envisages the aggregation of farmers into farmers’ groups like FIGs/FPOs and FPCs to:
(i) Achieve economies of scale
(ii) Augment horticulture production
(iii) Enhance farmers’ incomes
(iv) Boost nutritional security
(v) Improve productivity by way of quality germ-plasm, planting material and water use efficiency through micro-irrigation
(vi) Support skill development
(vii) Generate employment for rural youth in horticulture, post-harvest management and also in the cold chain sector. - The scheme also envisages the capacity building of farmers in adopting improved technology through existing institutions such as Krishi Vigyan Kendras, state agriculture universities and Institutes with the Department of Horticulture in the States.
MIDH Sub-Schemes
The Mission includes the following sub-schemes:
- National Horticulture Mission (NHM): It is implemented by the State Horticulture Missions and is aimed at increasing production in the horticulture sector. Know more about the National Horticulture Mission and the Golden Revolution in the link.
- National Horticulture Board (NHB): It implements the various schemes under the MIDH at the state and UT levels.
- Horticulture Mission for North East & Himalayan States (HMNEH): It is implemented by the State Horticulture Missions of the Northeastern and Himalayan states.
- Coconut Development Board (CDB): It implements the schemes of the MIDH in all the coconut-growing states in the country.
- Central Institute for Horticulture (CIH), Nagaland: The institute was established in Medizipehima, Nagaland in 2006-07 for providing technical backstopping through capacity building and training of farmers and Field functionaries in the North Eastern Region.
- National Bamboo Mission (NBM)
The following image shows the areas of operation of the MIDH sub-schemes: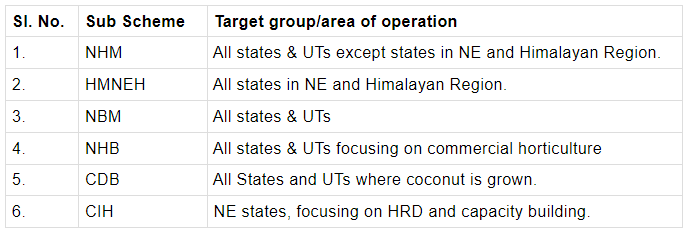
MIDH Strategies
The strategies adopted by the mission for achieving its stated objectives are discussed below.
- Adopt an end-to-end comprehensive approach covering pre-production, production, post-harvest management, processing and marketing to ensure appropriate returns to farmers/producers.
- Promote R&D technologies for cultivation, production, post-harvest management and processing with particular emphasis on cold chain infrastructure for increasing the shelf life of perishable products.
- Augment productivity through:
(i) Diversification from traditional crops to plantations, vineyards, orchards, flowers, vegetable gardens as well as bamboo plantations.
(ii) Extension of suitable technology to farmers for high-tech horticulture including protected cultivation and precision farming.
(iii) Raise the acreage of orchards and plantation crops including bamboo and coconut, particularly in states where the total area under horticulture is less than 50% of the agricultural area. - Better post-harvest management, processing for value addition and marketing infrastructure.
- Adopt a coordinated approach and encourage partnership, synergy and convergence among R&D, processing and marketing agencies in public as well as private sectors, at the national, regional, state and sub-state levels.
- Promote Farmer Producer Organisations and their tie-up with Market Aggregators (MAs) and Financial Institutions (FIs) to support and provide sufficient returns to farmers.
- Support capacity-building and human resource development at all levels, including, change in syllabus and curriculum of graduate courses at Colleges, Universities, ITIs, Polytechnics, as appropriate.
MIDH Activities
Some of the activities for which financial support is provided under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture are as under:
- Establishing nurseries, tissue culture units for producing quality seeds & planting material.
- Area expansion i.e. setting up new orchards and gardens for flowers, vegetables, and flowers; and also the rejuvenation of unproductive and old orchards.
- Protected cultivation, i.e. poly-house, green-house, etc. to better the productivity & grow off-season high-value vegetables & flowers.
- Organic farming and certification.
- Creation of water resources structures and watershed management.
- Bee-keeping for pollination.
- Horticulture mechanisation.
- Creation of post-harvest management & marketing infrastructure.
MIDH Funding
The scheme is a centrally-sponsored scheme which means it is partially funded by the Central Government
.
- The GOI provides 85% of the total outlay for the programmes under the mission in all states except NE and Himalayan states. The rest 15% is from the state governments.
- In NE and Himalayan states, the GOI provides 100% contribution.
Samudra Setu II
Context:
Indian Naval Ships Airavat, Kolkata and Trikand reach India with Liquid Medical Oxygen and Critical Medical equipment/supplies from Singapore, Kuwait and Qatar.
About Operation Samudra Setu II:
- Samudra Setu II is the COVID relief operation carried out by the Indian Navy.
- The Navy has deployed nine warships as part of the operation to supplement the oxygen requirement in the country.
- They are sailing in the Persian Gulf, in the Indian Ocean Region carrying back the most critical O2 supplies for COVID-19 patients.
- For the shipment of Liquid Medical Oxygen (LMO) and related medical equipment from friendly foreign countries in Persian Gulf and South East Asia, ships from all the three naval commands have been deployed.
(i) The three naval commands are located in Mumbai, Visakhapatnam and Kochi.
NITI Aayog Report
Context:
NITI Aayog and Mastercard Release Report on ‘Connected Commerce: Creating a Roadmap for a Digitally Inclusive Bharat’.
Details:
- The report identifies challenges in accelerating digital financial inclusion in India and provides recommendations for making digital services accessible to its 1.3 billion citizens.
- Based on five roundtable discussions held in October and November 2020, the report highlights key issues and opportunities, with inferences and recommendations on policy and capacity building across agriculture, small business (MSMEs), urban mobility and cyber security.
- Experts from the government, banking sector, the financial regulator, fintech enterprises, and various ecosystem innovators participated in the discussions led by NITI Aayog and supported by Mastercard.
- Key issues addressed in the report and previous rounds of discussions:
(i) Acceleration of digital financial inclusion for underserved sections of Indian society.
(ii) Enabling SMEs to ‘get paid, get capital and get digital’ and access customers, and ensure their continued resilience.
(iii) Policy and technological interventions to foster trust and increase cyber resilience.
(iv) Unlocking the promise of digitization in India’s agriculture sector.
(v) The essential elements of a digital roadmap to make transit accessible for all citizens. - Key recommendations in the report include:
(i) Strengthening the payment infrastructure to promote a level playing field for NBFCs and banks.
(ii) Digitizing registration and compliance processes and diversifying credit sources to enable growth opportunities for MSMEs.
(iii) Building information sharing systems, including a ‘fraud repository’, and ensuring that online digital commerce platforms carry warnings to alert consumers to the risk of frauds.
(iv) Enabling agricultural NBFCs to access low-cost capital and deploy a ‘phygital’ (physical + digital) model for achieving better long-term digital outcomes. Digitizing land records will also provide a major boost to the sector.
(v) To make city transit seamlessly accessible to all with minimal crowding and queues, leveraging existing smartphones and contactless cards, and aim for an inclusive, interoperable, and fully open system such as that of the London ‘Tube’.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















