Participative Management (R. Likert, C.Argyris, D.McGregor) | Public Administration Optional for UPSC (Notes) PDF Download
Rensis Likert: Introduction
Rensis Likert was an influential American social psychologist who played a crucial role in developing Participative Management Theory. Unlike classical thinkers like Max Weber and F.W. Taylor, who focused on organizational structure and efficiency, Likert's work was centered around people and their interactions within organizations. He was interested in topics such as conflict management, diversity, leadership, motivation, and organizational culture.

- He believed that understanding and improving the way people work together is essential for effective management.
- Likert's background in various fields, including sociology, psychology, and engineering, shaped his perspective on organizations and management. He was known for his curiosity about how things function and his practical approach to solving social problems through research and measurement.
- One of his significant contributions was the development of the Likert Scale, a psychometric tool used to gauge people's attitudes and beliefs about certain topics. This scale is widely used in surveys to assess public opinion and social attitudes.
- Likert also helped establish the Institute for Social Research at the University of Michigan, which is renowned for its social science research and survey methodology.
Overall, Rensis Likert's work laid the foundation for understanding the importance of participative management and the role of individuals in organizational success. His emphasis on people-oriented management practices continues to influence modern management theories and practices.
Organisational Humanism: Setting the Context
The period between the post-industrial revolution and the 20th century saw the emergence of various industrial reforms aimed at achieving maximum productivity. The focus during this time was primarily on quantity, efficiency, and machinery for production. The early 1900s to the early 1950s were significantly influenced by Taylor’s Scientific Management and Weber’s Bureaucratic model.- Scientific Management: Taylor’s approach, although it included humanistic elements like the ‘mental revolution’ and fair treatment of workers, often viewed workers as mere cogs in the machine. This approach was based on the assumption that workers were poorly educated and needed to follow management’s directives without question. The mechanistic model of management proved to be highly efficient during this period, but it also faced criticism for being too restrictive of human behaviour.
- Bureaucratic Model: Weber’s model of bureaucracy was criticized for being rigid and not taking into account the human aspects of work. Despite its emphasis on efficiency and control, it failed to consider the social and psychological needs of workers.
- Shift in Perspective: The 1930s and 1940s brought about a shift in thinking due to the Hawthorne studies, which highlighted the impact of peer pressure and informal networks on worker performance. These studies demonstrated that factors beyond monetary benefits, such as group norms and social relationships, played a crucial role in influencing worker behaviour. This led to the development of the socio-technical approach to work design, which aimed to align technical requirements with social needs.
- Socio-Technical Approach: This approach emphasized the importance of designing work systems that consider both technical and social aspects. It recognized that the technical needs of a job should be met in conjunction with the social system in which the work is performed. This marked a significant shift from the earlier mechanistic and bureaucratic models.
- Group Dynamics: There was a growing interest in studying how individuals interact within groups and how these interactions affect organisational performance. This research focused on the role of group norms, peer influence, and social relationships in shaping worker behaviour and productivity.
- Emergence of New Thinkers: In the late 1950s and early 1960s, thinkers like Frederick Herzberg, Douglas McGregor, Chris Argyris, and Rensis Likert introduced new perspectives on management and organisational behaviour. Herzberg’s theories on job enrichment and motivation, McGregor’s theories on managerial assumptions about workers, Argyris’s exploration of traditional management practices’ impact on individuals, and Likert’s emphasis on participative leadership styles contributed to a new understanding of work design and organisational leadership.
- Herzberg’s Job Enrichment: Herzberg’s approach to job enlargement and enrichment aimed to increase workers’ productivity by giving them a greater sense of ownership and responsibility in their work. This aligned with the findings of the Hawthorne studies, which highlighted the importance of social and psychological factors in influencing performance.
- Participative Leadership: Rensis Likert’s perspective on participative leadership challenged traditional hierarchical practices that expected workers to be submissive and dependent. His approach emphasized the importance of involving employees in decision-making processes and recognizing their contributions to the organisation.
- Paradigm Shift: The combination of socio-technical thinking and the new perspectives introduced by these thinkers led to a paradigm shift in managerial thinking. It demanded a new way of looking at work design and organisational leadership, focusing on the interplay between technical requirements, social needs, and human behaviour.
- Experiments and Innovations: Industries and business groups began experimenting with new initiatives and practices based on the insights from academia. The focus shifted to how to effectively utilize employees and groups to shape individual and organisational performance. This period marked the beginning of a more humanistic and participative approach to management, laying the foundation for modern organisational behaviour and leadership theories.
The Interaction-Influence System
- To enhance the skills, resources, and motivation of individuals at various levels within an organization, Likert introduced the concept of the "interaction-influence" system. This concept underscores the modern management perspective that values the dynamic interaction between employees, their environment, and fellow members within the organization.
- In this context, the "environment" refers to the operational setting of the organization, which directly impacts its day-to-day functioning. Influential thinkers like Chester Barnard, Abraham Maslow, Douglas McGregor, and Fredrick Herzberg have emphasized the significance of individual roles, organizational leadership, group dynamics, motivation, and job satisfaction. Likert, echoing the Human Relations Movement, highlighted how the environment shapes organizational design.
According to Likert, the effectiveness of the "interaction-influence" system determines an organization's ability to optimize the skills and resources of individuals and work groups. The following are the characteristics of an ideal "interaction-influence" system.
- High Employee Commitment: The goals and values of every member are reflected in the work groups and the organization as a whole. This means that employee commitment is high, leading to greater productivity compared to mere compliance with rules.
- Self-Driven Performance: The drive for high performance and skill development comes from the members themselves. They are capable of identifying the need to critically reflect on their own behavior, going beyond problem-solving.
- Experience-Driven Decision Making: Every member brings their experience to the work, influencing the organization’s decisions and policies.
- Alignment of Goals and Methods: An effective "interaction-influence" system aligns goals, values, methods, communication, decision-making, and control in a cohesive manner.
However, in practice, this system may face conflicts, such as:
- Seniority vs. Merit: Disagreements may arise regarding whether to prioritize seniority or merit in decision-making.
- Commitment vs. Compliance: Conflicts may occur between fostering commitment and ensuring compliance with rules.
In a working team with members of varying experience, age, or knowledge, potential conflicts include:
- Decision-Making Authority: Disputes over who has the authority to make decisions.
- Employee Identification: Emphasis on employees’ identification with their work and in building teams.
As task complexity increases, the demand for group interaction also rises, leading employees to exercise personal judgment and intuition in situations that do not fit established rules. This can conflict with traditional hierarchical settings that prioritize rule compliance.
Critics of the Bureaucratic Theory and Scientific Management Approach have pointed out their over-reliance on rule compliance. Human Relations thinkers argue that organizations overly dependent on rule compliance may eventually face rule defiance. While the "interaction-influence" system appears contrary to rule compliance, achieving this balance requires effective management of internal conflicts.
Management Styles
The evolution of thought regarding the best way to manage people encompasses a range of interconnected topics and ideas, including organizational structure, organizational functioning, management practices, decision-making, organizational culture, change and learning, and the role of organizations in society. At its core, it involves fundamental questions about power and authority, motivation and responsibility, and the establishment of trust and confidence. However, it is fundamentally rooted in basic assumptions about human nature and behavior.
- Unlike classical thinkers who viewed human beings as essential resources for achieving goals, the pioneers of the Human Relations School believed that organizations are systems of interdependent human beings. Thinkers such as Elton Mayo, Maslow, Herzberg, McGregor, and Likert have studied various aspects of human behavior, including attitudes, expectations, value systems, tensions and conflicts, group dynamics, and their impact on productivity, culture, cohesion, and motivation. Pugh and Hickson (2007), while acknowledging these writers, argued that people not only work for the organization but are the organization. They viewed organizations as "natural systems" whose processes need to be studied on their own rather than as "formal systems" designed to achieve specific ends.
- Based on extensive research involving thousands of managers in different organizational settings, Rensis Likert proposed new methods of management, which he described in terms of six organizational dimensions, including leadership, motivation, communication, decisions, goals, and control. Likert emphasized that managing the human component is the central and most important task of management, as everything else depends on how well it is done. He identified four styles of management on a continuum, ranging from autocratic job-centered management (System 1) to democratic employee-centered management (System 4).
System 1: Exploitative-Authoritative Management
- In the Exploitative-Authoritative Management style, managers have low confidence in their subordinates and rely on fear and threats to ensure compliance.
- This style is characterized by top-down communication and a psychological divide between superiors and subordinates.
- Managers impose decisions with little room for discussion, focusing solely on task completion without considering the aspirations of employees.
System 2: Benevolent-Authoritative Management
- The Benevolent-Authoritative Management Style involves managers who listen to their subordinates' concerns and trust them to some extent.
- While still exercising control, managers delegate routine decisions to subordinates and use rewards rather than threats to ensure compliance.
- This style restricts upward communication, allowing subordinates to share only what managers want to hear.
System 3: Consultative Management
- Consultative Management involves managers who have partial trust in their subordinates.
- While top management makes all policy decisions, they seek input from subordinates on lower-level decisions.
- This style features two-way communication and uses economic rewards to ensure compliance.
- Subordinates have a moderate influence on departmental activities.
System 4: Participative Management
- Participative Management is characterized by trust and confidence in employees, with a focus on group participation and collaborative decision-making.
- Managers involve employees in setting performance goals, rewards, and work methods.
- This style promotes open communication and teamwork, with a close psychological relationship between superiors and subordinates.
- Employees feel a sense of ownership and responsibility for achieving organizational goals.
Likert believed that to be effective, modern organizations must view themselves as interacting groups of people with supportive relationships. He emphasized the importance of creating a work environment where employees feel a personal connection to the organization's objectives and find their jobs meaningful. Likert's later work identified the "System 4 Total Model of Organization", where leaders possess characteristics such as being supportive, approachable, and focused on building cohesive problem-solving teams.
- Leaders in this model foster cooperative relationships among subordinates, provide necessary resources, keep subordinates informed of overall plans, and expect high-quality performance from themselves and others.
- Likert cautioned organizations against making a sudden leap from System 1 to System 4, recommending a gradual transition through the continuum.
- He emphasized the need for involving concerned individuals in the organization, using objective evidence in a supportive manner, and engaging influential people in the organization to facilitate change.
Implications for Managers
Human Asset Accounting:
- Likert criticized the prevailing methods of assessing organizational performance in terms of productivity, costs, and dividends, believing they might not accurately reflect the true value of human resources. He emphasized the importance of understanding both the investment in human resources and their current productive capability.
- To illustrate this, he posed a hypothetical scenario where a firm loses all its personnel except for the President and questioned how much it would cost to rebuild the organization to its current effective state. This led to the development of procedures for estimating the costs associated with recruiting, selecting, and training employees, as well as establishing effective working relationships within the organization.
- Likert stressed the need to differentiate between causal and intervening variables when assessing the state of human organizations. Causal variables, such as organizational structure and management policies, directly influence organizational development, while intervening variables reflect the internal health and performance capabilities of the organization, including employee loyalties, attitudes, and motivations.
- He also noted that the complexity of technology within an industry could impact estimates of organizational performance, predicting that more complex technologies would lead to larger estimates. This perspective aligns with the contemporary approach to human asset accounting, where the integration of workplace automation and human intelligence is expected to create new job roles, such as 'Human-Machine Interaction Analyst.'
Managing Conflicts:
- Likert acknowledged that conflict is a natural part of organizational life and can have both positive and negative consequences depending on how it is managed. He proposed that the 'System 4' management style, characterized by group problem-solving and participatory decision-making, is an effective approach for resolving conflicts in various organizational settings, including industries, schools, and universities.
- To manage tensions within organizations, Likert emphasized the importance of supportive leadership and interaction-influence networks, which foster employee consensus at all management levels. He advocated for the use of integrative goals, de-emphasizing status, and depersonalizing problem-solving to achieve win-win outcomes in conflict situations.
- Likert's concept of supportive behavior, which builds trust and openness, is central to his management style and conflict resolution approach. He believed that leaders should meet or exceed the support and involvement expectations of their team members, without overwhelming them.
Linking Pin Model:
Likert's Linking Pin Model suggests that members of an organization have dual roles in overlapping groups, with a focus on group functions and processes rather than individual roles. The central principles of this model include:
- Supportive relationships among organizational members
- Multiple overlapping structures with groups consisting of superiors and their subordinates
- Group problem-solving by consensus within groups
- Overlapping memberships between groups, with members serving as "linking pins"
Members in linking-pin positions are expected to facilitate seamless resource flow and communication between groups. This model is endorsed by Graen et al. (1977), who highlight the benefits of open and honest information transmission, increased influence, greater job satisfaction and commitment, and enhanced cooperation. Likert believed that the quality of work life and organizational effectiveness would be significantly influenced by the individuals occupying linking-pin roles. The interpersonal and intergroup competence of these individuals would contribute to effective working relationships, regardless of status, power, and experience.
System 4: An Effective Strategy for Public Administration
- The success of any organisation, regardless of its setting, is largely determined by its people and their participation in decision-making. Adams (1992) emphasises the need for participative approaches to ensure a decent and dignified existence for individuals within organisations. Rensis Likert, building on this idea, believed that a more democratic and less hierarchical administration would allow subordinates to work responsibly, aligning with Maslow's concept of self-actualisation needs.
- Likert's "System 4" is a people-centric approach that focuses on the human effort and direction within an organisation. He argued that all activities are initiated and determined by the people within the institution, and managing the human component is the most crucial task for effective management. Likert's research found that participative leadership could significantly improve productivity, satisfaction, and overall organisational performance.
- For instance, in the 1970s, Joshua Agsalud, the Director of the Department of Labour and Industrial Relations in Hawaii, implemented System 4 principles to enhance performance and job satisfaction. This involved using organisational development tools to measure employee attitudes and stimulate cooperative planning, leading to substantial improvements in individual performance and job satisfaction. Likert also developed the Likert Scale, a psychometric tool that helps identify areas needing attention by collecting data on respondents' opinions.
- To successfully implement System 4, aspiring managers need a clear understanding of leadership and interactional processes, which can be gained through reading and experiential training. Likert believes that System 4 offers a vibrant opportunity for governmental agencies to improve human resources, productivity, and service excellence, especially in the face of challenges like constrained resources and increased citizen demands.
An Evaluation of Likert's Approach
- Likert's ambition to develop an ideal organisation introduced valuable concepts in organisational behaviour, such as the interaction-influence system, participatory decision making, the linking-pin model, and human asset accounting.
- Methodologically, he created the widely used Likert scale, which continues to impact various fields, including research.
- However, Likert's views faced criticism.
- Critics argue that his Linking Pin Model merely redraws triangles around traditional hierarchical structures and that it slows down decision-making processes.
- Some, like Zaleznik, see System 4 as an oversimplified package, while others, like Klein, view it as a relative process constrained by existing structures.
- A notable weakness of System 4 is the difficulty in proving its empirical validity and reliability across different organisational settings.
- Despite these criticisms, Likert's contributions to organisational behaviour, especially in survey techniques, are acknowledged.
- His pragmatic approach to problems and the use of the Likert Scale to understand people's attitudes towards various issues are recognised as significant contributions.
- Likert's emphasis on participatory leadership and decision-making, although idealistic, is relevant in contemporary organisations that prioritise democracy and trust.
- The idea of structuring organisations around innovation and openness, as suggested in System 4, is not new but has evolved from management practices aimed at fostering a participatory and democratic environment.
Conclusion
Likert's focus on the applicability of his concepts in the public sector and his later work as a consultant and mentor for building teams and organisations highlight his commitment to improving organisational practices. His efforts to support emerging scholars and contribute to the field of management science through empirical research and the development of survey techniques solidify his position among eminent management thinkers. By emphasising the importance of interaction and influence within organisations, participatory decision-making, and the need for democratic and trust-based structures, Likert's work provides a foundation for understanding and improving organisational behaviour and management practices.Chris Argyris: Introduction
Chris Argyris was a prominent social scientist known for his significant contributions to the Socio-psychological School of Thought. He challenged the traditional mechanistic and technocratic principles of organisations, arguing that they failed to align with adult personality and psychological needs.
Argyris believed that formal organisational structures were not sufficiently mature to support individuals in achieving psychological success, which could lead to both human and organisational decline. He advocated for change in individuals, organisations, and their interpersonal relationships to reduce conflicts of interest and enhance productivity. His work has been instrumental in understanding organisational learning, action research, and the dynamics between people and organisations.
Chris Argyris: A Profile
- Early Life and Education. Chris Argyris was born in Newark, New Jersey, and pursued his education in psychology and economics, earning his degrees from various institutions, including Kansas University and Cornell University, where he obtained his Ph.D. in Organisational Behaviour.
- Academic Career. Argyris began his academic career at Yale University, focusing on the impact of formal organisational structures on individuals. He later moved to Harvard University, where he continued his research and teaching until retirement.
- Research Focus. His early research explored how individuals adapt to formal organisational structures and control systems, leading to several publications. He later shifted his focus to organisational change, the behaviour of senior executives, and the role of social scientists in research and action.
- Contributions to Organisational Learning. Argyris, along with Donald Schon, developed theories on individual and organisational learning, emphasising the role of human reasoning in diagnosis and action. Their works, including "Organisational Learning" and "Theory in Practice," have significantly influenced the field.
- Later Works. Argyris continued to develop his ideas on organisational defences and knowledge for action in his later works, contributing to the understanding of organisational behaviour and management.
Theoretical Underpinnings of Chris Argyris’ Theories
Chris Argyris and Donald Schön (1978) believed in the strong connection between organisational structure and individual personalities. They argued that both are mutually responsible for their development. Organisations and individuals should learn from each other and from their environment. Changes in the environment impact the workplace, and individuals act as learning agents for the organisation. During the mid-20th century, when industrial growth was evident, urban living standards improved in various aspects like food, shelter, housing, healthcare, and education. This period also marked a shift in people’s mindsets from materialistic to less materialistic values, aligning with Maslow's Middle-level and Higher-level Needs. However, Argyris noted that traditional organisational structures failed to adapt to this changing mindset and continued to use the outdated ‘carrot and stick’ or ‘mechanistic approach’ towards employees. This approach, along with rigid organisational structures and leadership styles, hindered personal growth and development, leading to a decline for both individuals and organisations.
Argyris’ Intervention Strategies for Organisational Change include:
- Immaturity-Maturity Theory
- Improving Interpersonal Competence
- Innovative Organisational Structures (Non-Pyramidal and Matrix)
- Group Sensitivity Training (T-Group)
Immaturity-Maturity Theory
The Immaturity-Maturity Theory was proposed by Chris Argyris in his book “Personality and Organisation.” The theory aims to explain the relationship between human behaviour and organisational structure. Argyris compared the bureaucratic/pyramidal values (similar to Theory ‘X’ assumptions about people) with a more humanistic/democratic value system (akin to Theory ‘Y’ assumptions).
Key Points of the Theory:
- Immaturity to Maturity Continuum: Individuals develop from immaturity, characterized by laziness, lack of interest, and apathy, to maturity, where they become active, independent, and self-controlled.
- Bureaucratic Values: Traditional organisations treat employees as immature, using principles like task specialization, unity of direction, chain of command, and span of control, which make employees feel dependent and fearful.
- Humanistic Values: Organisations that treat employees as mature individuals, respecting their interpersonal competence and allowing them to share ideas and participate in decision-making, foster better relationships and trust.
- Impact of Leadership: Argyris found that authoritarian leadership styles reinforce the damage caused by bureaucratic structures, making employees passive and competitive for the leader’s favour.
- Positive Leadership: Managers who treat employees as responsible adults and involve them in decision-making achieve higher productivity and better outcomes.
Seven Changes for Personality Growth:
- From Passive to Active: Individuals move from being passive like infants to active like adults.
- From Dependent to Independent: Individuals become more independent and self-reliant.
- From Few to Many Behaviours: Individuals learn to behave in various ways instead of a few.
- From Shallow to Deep Interests: Individuals develop deeper and stronger interests over time.
- Long-term Perspective: Individuals gain a better understanding of the long-term past and future.
- From Subordinate to Equal or Superior: Individuals move from subordinate roles to equal or superior positions.
- Higher Awareness and Self-control: Adults develop higher awareness and strong self-control.
Argyris believed that these changes occur on a continuum, and a healthy personality develops from immaturity to maturity.
Improving Interpersonal Competence
Interpersonal competence refers to an individual's ability to interact effectively with others and navigate social situations within a community or organisation. Argyris argued that organisations following a mechanistic approach exhibited low levels of interpersonal competence. Employees in such organisations tended to be distrustful, fearful, and engaged in unhealthy competition, leading to a lack of cooperation and poor performance.
He advocated for organisations to prioritise the improvement of intellectual, mechanical, and interpersonal skills. Interpersonal skills, in particular, were often neglected but are crucial for organisational success. Argyris identified three essential conditions for developing interpersonal competence:
- Self-acceptance: This involves valuing oneself positively and recognising one's worth.
- Confirmation: Confirmation refers to reality-testing one's self-image and ensuring it aligns with how others perceive you.
- Essentiality: Essentiality is about having the opportunity to utilise one's core abilities and express central needs within the organisation.
Argyris outlined four types of behaviour that indicate interpersonal competence, arranged in order of frequency and potency:
- Owning up to ideas and feelings: Taking responsibility for one's thoughts and emotions.
- Being open to others' ideas and feelings: Welcoming and considering the perspectives of others.
- Experimenting with new ideas and feelings: Trying out new concepts and emotions to expand understanding.
- Helping others to own up, be open, and experiment: Assisting colleagues in recognising and exploring their own ideas and feelings.
By fostering interpersonal competence, organisations can create a positive and collaborative environment that enhances overall performance and productivity.
Alternative Organisational Structures
- According to Argyris, different types of jobs and activities require different organisational structures. He believed that the future organisations would need a mix of both old and new organisational forms.
- He proposed several new organisational structures:
1. Pyramidal Structure:
- This is a traditional and rigid structure best suited for routine tasks and non-innovative activities.
- It is designed for individuals who are comfortable with repetitive tasks and do not prioritise psychological needs.
2. Modified Formal Organisational Structure:
- This structure is hierarchical but operates democratically in terms of processes and operations.
- It is similar to Likert’s System 4, allowing subordinates to be part of their superior’s decision-making unit.
- This structure is generally more efficient than the pyramidal one.
3. Participative Structure:
- This structure is less hierarchical and more flexible, encouraging organic collaboration.
- It provides equal opportunities for all employees to participate in problem-solving and decision-making based on their potential.
- It is ideal for activities requiring creativity and imagination, such as group and inter-departmental projects.
4. Matrix Organisation:
- This structure combines project organisation with functional organisation, creating a flat structure where all members have equal power and responsibility.
- It promotes teamwork and self-discipline, eliminating traditional superior-subordinate relationships.
- It is suitable for tasks requiring multiple skills or specialisation.
Decision-Making Involvement:
- The key difference between these structures is the level of involvement required in decision-making.
- The pyramidal structure involves fewer people in decision-making, while the matrix structure requires equal participation from all individuals.
Flexibility in Structure Use:
- Argyris emphasised that no single structure should be used all the time.
- Future organisations will vary their structures based on the types of decisions that need to be made.
- He proposed establishing “decision rules” to determine which structure to use under specific conditions.
T-Groups:
- Argyris introduced the T-Group experiment in the 1960s to enhance employees' personal effectiveness. This program emphasizes understanding oneself and others, group dynamics, and organizational structure. Participants receive feedback, experiment with new behaviors, and develop self-awareness and sensitivity to others' personalities.
- In his study, Argyris found that delegating more responsibilities to lower-level employees and improving information flow from the ranks led to better decision-making. Initially, T-group training aimed at personal growth and self-insight, focusing on individual change rather than environmental modification. However, this approach gradually contributed to organizational improvement. Argyris and his colleagues did not advocate for formal T-groups in organizations, but recommended them for specific decisions within formal structures.
Argyris recommended the widespread use of T-Groups in public administration to enhance socio-emotional processes. He argued for long-term change programs in governmental organizations to satisfy higher-order needs of employees, focusing on behavior and leadership style changes of senior participants and fostering innovative attitudes.
Organisational Learning
- Chris Argyris made significant contributions to the field of organisational learning. He, along with Donald Schön, studied and conceptualized how learning occurs within organizations. They argued that organizations are not just collections of individuals, but rather, individuals play a crucial role in the learning process of the organization.
- According to Argyris and Schön, organizational learning involves detecting and correcting errors in the organization’s theory-in-use, which is the underlying understanding of how things work. When members of an organization act as learning agents, they respond to changes in the internal and external environment by identifying and rectifying errors, and then embedding these corrections into the organization’s shared understanding.
Single-Loop Learning:
- Single-Loop Learning occurs when an organization detects and corrects an error without questioning its underlying goals, values, plans, or rules.
- It is like a thermostat that learns to adjust the temperature without questioning the criteria for what constitutes a comfortable temperature.
- In this type of learning, the organization continues to operate within its existing framework and simply adjusts its actions to achieve the same objectives.
Double-Loop Learning:
- Double-Loop Learning involves a deeper level of scrutiny where the governing variables themselves are questioned and subjected to critical examination.
- This type of learning may lead to a change in the organization’s goals, values, or rules, resulting in a shift in how strategies and outcomes are framed.
- Double-Loop Learning allows organizations to not only correct errors but also to re-evaluate and potentially alter the fundamental assumptions that guide their actions.
Conclusion
- Chris Argyris’s theory of organisational learning, while facing criticism, made a significant impact on the understanding of human relations and participative approaches in organisations.
- His focus on cognitive interventions aimed to improve the relationship between individuals and organisations, enhancing adaptability and effectiveness.
- Despite limitations, Argyris’s work remains a historical milestone, emphasising the need for a shift in mindset among employees, leadership styles, and organisational structures for better productivity.
- The unit highlighted the theoretical foundations of organisations, alternative structures, and the concepts of single-loop and double-loop organisational learning.
Douglas McGregor: Introduction
People have different reasons for working. Some seek money, others look for challenges, and some desire power. What each individual in an organisation wants from their work plays a crucial role in determining their motivation. Motivation is essential for all organisations. Often, the difference between highly effective organisations and those that are less effective lies in the motivation of their members. Therefore, managers need to understand the nature of individual motivation, especially in work situations.
Motivation refers to the forces that lead people to behave in certain ways. Managers aim to motivate people within the organisation to perform at high levels. However, managing motivation is one of the most challenging aspects. If motivation is lacking, managers face the complex task of figuring out what will encourage employees to work harder. Given the importance of motivation in managerial processes, we will discuss the motivational models of Douglas McGregor and Victor Vroom in the context of organisations.
Theories of Motivation
Motivation is the driving force behind individuals' actions, and understanding what motivates people in organizational settings is crucial for enhancing productivity and job satisfaction. Over the years, various theories have emerged to explain the different aspects of motivation, ranging from content theories that focus on specific needs to process theories that examine the cognitive factors involved in motivation.
Content Theories of Motivation:
Content theories of motivation aim to identify the specific needs that drive individuals and how these needs can be fulfilled to motivate them effectively.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs suggests that human needs are arranged in a hierarchy, from basic physiological needs to higher-level psychological needs such as esteem and self-actualization. According to Maslow, individuals are motivated to fulfill these needs in a specific order, starting from the most basic.
Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory proposes that there are two sets of factors that influence motivation and job satisfaction: hygiene factors and motivators. Hygiene factors, such as salary and working conditions, can prevent dissatisfaction but do not necessarily lead to motivation. On the other hand, motivators, such as recognition and opportunities for growth, are essential for enhancing motivation and job satisfaction.
McClelland's Theory of Needs emphasizes three primary needs that drive individuals: the need for achievement, the need for affiliation, and the need for power. According to McClelland, individuals are motivated by the desire to excel, the desire to build relationships, and the desire to influence others.
Alderfer's ERG Theory categorizes human needs into three core groups: existence needs, relatedness needs, and growth needs. Existence needs encompass basic material and physiological requirements, relatedness needs involve interpersonal relationships, and growth needs pertain to personal development and self-improvement. Alderfer's theory suggests that these needs can be pursued simultaneously rather than sequentially, as proposed by Maslow.
Process Theories of Motivation
Process theories of motivation focus on the cognitive processes that precede and influence motivation and effort. These theories explore how individuals perceive their ability to satisfy their needs and the equity of their need satisfaction.
Vroom's Expectancy Theory posits that motivation is based on the expectation that effort will lead to performance and that performance will lead to desired outcomes. The theory emphasizes the importance of valence (the value of the outcome) and expectancy (the belief that effort will lead to performance) in determining motivation.
Porter and Lawler's Model builds upon Vroom's theory by incorporating additional factors such as individual abilities and role perception. The model suggests that motivation is influenced by the perceived likelihood of achieving desired outcomes and the perceived value of those outcomes.
Equity Theory introduced by behaviorists, emphasizes the importance of perceived fairness in motivation. According to this theory, individuals are motivated by the desire for equitable treatment in comparison to others. If individuals perceive inequity in their treatment, it can lead to decreased motivation and job satisfaction.
McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y provides insights into human nature and its impact on work motivation. Theory X assumes that individuals are inherently lazy and need to be closely supervised, while Theory Y suggests that individuals are self-motivated and seek responsibility. Understanding these differing views on human nature can help organizations tailor their motivational strategies accordingly.
Views of Douglas McGregor
- Douglas McGregor, born in 1906 in Detroit, USA, was a Professor of Industrial Management at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. In his pursuit of productivity, McGregor developed two managerial approaches known as Theory X and Theory Y, which he presented in his book "The Human Side of Enterprise" in 1960. Influenced by Abraham Maslow, McGregor made Maslow's ideas the starting point for his work.
- McGregor's central argument is that the theoretical assumptions management holds about controlling its human resources shape the entire character of an enterprise. He examines these assumptions, which underpin managerial actions, to understand human behavior in the workplace. Theory X and Theory Y represent different perspectives on human behavior and motivation, with McGregor advocating for a view that recognizes the potential for high performance in organizations.
Major Works of Douglas McGregor:
- The Human Side of Enterprise (1960): This is McGregor's most famous work, where he introduced Theory X and Theory Y.
- Leadership and Motivation (1966): In this book, McGregor delves deeper into the concepts of leadership and motivation within organizations.
- The Professional Manager (1967): McGregor discusses the role and challenges of professional managers in this work.
Theory X and Theory Y
Theory X and Theory Y are two contrasting views on human behavior and motivation in the workplace that were introduced by Douglas McGregor. These theories reflect different assumptions about how people behave at work and what motivates them.Theory X
Theory X is based on the following assumptions:- Laziness: The average person is lazy and tries to work as little as possible.
- Lack of Ambition: People do not have strong ambitions, dislike taking responsibility, and prefer to be directed by others.
- Self-Centeredness: Individuals are naturally self-centered and indifferent to the needs of the organization.
- Resistance to Change: People are resistant to change and new ideas.
- Limited Intelligence: Most individuals are gullible and lack intelligence.
According to Theory X, people are passive or resistant to organizational needs and require persuasion, rewards, punishments, or control to meet those needs. This theory is based on a traditional view of management that emphasizes control and direction, often referred to as "the carrot and the stick" approach.
Critique of Theory X
- McGregor believed that while the assumptions of Theory X may not have changed significantly, the behavioral patterns of individuals have evolved due to changes in industrial organizations, management philosophy, and practices. He argued that Theory X is not a valid representation of human nature and fails to motivate employees toward organizational goals.
- Research, such as the Hawthorne studies and findings by Likert and other behavioral studies, suggests that the assumptions of Theory X are not accurate. McGregor himself questioned the validity of Theory X, stating that the "carrot and stick" approach works only under specific circumstances and is ineffective when individuals have reached a basic level of subsistence and are motivated by higher needs.
- McGregor's conclusion is that as long as Theory X assumptions continue to influence managerial strategies, organizations will fail to recognize and utilize the potential of the average human being.
Theory Y
Theory Y presents an alternative view that emphasizes integration rather than traditional concepts of direction and control. It assumes that:
- People are not naturally resistant to organizational needs: Theory Y suggests that individuals can be motivated to work towards organizational goals and that their personal goals can align with those of the organization.
- People have the potential to develop and accept responsibility: This theory posits that individuals have the capacity to take on responsibilities and contribute to the organization in meaningful ways.
- People can be motivated towards management goals: Theory Y believes that with the right environment and motivation, individuals can be inspired to work towards the objectives set by management.
- Management should facilitate goal achievement: This theory emphasizes the role of management in creating conditions where individuals can achieve their personal goals while contributing to the organization's objectives.
Theory Y promotes a cooperative relationship between management and employees, aiming for maximum output with minimal control and direction. It suggests that there is no inherent conflict between organizational and individual goals, and that employees' best interests align with those of the organization.
Key Features of Theory Y:
- Decentralization of Power: Theory Y advocates for distributing power and decision-making authority within the organization.
- Delegation of Responsibility: Employees are given responsibilities and the authority to make decisions related to their work.
- Job Enlargement: Employees are encouraged to take on a broader range of tasks and responsibilities.
- Employee Participation: Employees are actively involved in decision-making processes and management practices.
- Consultative Management: Managers consult with employees and consider their input in decision-making.
- Participative Performance Appraisal: Employees participate in the evaluation of their performance and contribute to setting performance standards.
Theory Y focuses on building positive relationships within the organization, creating an environment that fosters commitment to organizational objectives, and providing opportunities for individuals to exercise initiative, creativity, and self-direction in achieving these goals. McGregor views Theory Y as an invitation to innovate and emphasizes the importance of integrating individual and organizational needs. Over time, Theory Y has become a widely accepted concept in management, with a shift towards more democratic administration in organizations.
Comparison of Theory X and Theory Y
Theory X and Theory Y present contrasting views on human nature and motivation. Here are the key differences between the two theories:
- Attitude Towards Work: Theory X believes that people are inherently averse to work, while Theory Y views work as a natural activity for individuals, similar to play.
- Ambition and Responsibility: Theory X assumes that people lack ambition and try to avoid responsibilities, whereas Theory Y believes that individuals are eager to take on responsibilities and are motivated to contribute to the organization.
- Creativity: Theory X suggests that most people have limited creative abilities, while Theory Y posits that creativity is widely distributed among individuals in the workforce.
- Motivating Factors: In Theory X, lower-level needs are the primary motivators, whereas Theory Y emphasizes higher-order needs, although unmet lower-level needs are also important.
- Self-Motivation: Theory X claims that people lack self-motivation and require external control and supervision, while Theory Y asserts that individuals are self-directed, creative, and prefer to have control over their work.
- Authority and Decision-Making: Theory X advocates for a scalar chain system and centralization of authority, whereas Theory Y promotes decentralization and greater employee participation in decision-making.
- Leadership Style: Theory X favors autocratic leadership, while Theory Y encourages democratic and supportive leadership styles.
Managerial Implications of Theories X and Y
The managerial implications of Theory X and Theory Y, as described by Harold Koontz and his colleagues, highlight how these theories influence managerial actions and decision-making processes. Here are the key points:
Theory X Implications:
- Setting Objectives and Developing Plans: Managers influenced by Theory X would focus on establishing clear objectives and detailed plans to achieve them, emphasizing control and supervision.
- Implementing Plans through Leadership: Leadership in a Theory X context would involve directing and controlling employees closely to ensure compliance and performance.
- Controlling and Appraising Performance: Performance appraisal and control mechanisms would be strict, with a focus on measuring performance against set standards and taking corrective actions when necessary.
Theory Y Implications:
- Setting Objectives and Developing Plans: Managers adopting Theory Y would involve employees in setting objectives and developing plans, encouraging participation and input from team members.
- Implementing Plans through Leadership: Leadership would focus on empowering employees, providing them with the autonomy to make decisions and take ownership of their work.
- Controlling and Appraising Performance: Performance appraisal would be participative, with employees involved in assessing their performance and contributing to setting performance standards.
A Critical Evaluation
- McGregor's rejection of traditional concepts of administration has been questioned. He dismissed ideas like control and direction, but these concepts still hold value for understanding human motivation.
- Theory X, which McGregor does not favor due to its focus on control tactics, does have some merit. Despite the emergence of various motivation theories, the basic idea of using rewards and punishments (the carrot and stick approach) remains strong and can still motivate people.
- McGregor's theory, while influential, has not been adequately tested despite the research it generated. He made a significant contribution to human motivation theory by challenging the assumptions underlying formal organizations and proposing Theory Y, which is based on a better understanding of human motivation.
- Theory Y challenges the notion of the "economic man" and traditional ideas of direction and control. Although current research in human motivation has advanced beyond Theory Y, it does not render the theory irrelevant.
- McGregor considered Theory Y an invitation for innovation. His ideas on leadership, management development, and professional management are still valuable for current administrative practices.
Vroom's Expectancy Theory of Motivation
Vroom's Expectancy Theory of Motivation offers a process-oriented perspective on how individuals are motivated in the workplace. Unlike content theories that focus on needs and their prioritization, Vroom's theory emphasizes the relationships among various factors that influence motivation dynamically.
Key Concepts of Vroom's Expectancy Theory:
- Value: Value refers to the importance or desirability of a specific outcome to an individual. It represents what the individual hopes to achieve through their actions.
- Expectancy: Expectancy is the belief or perception that a certain level of effort will lead to a specific level of performance. It reflects the individual's confidence in their ability to perform the required tasks.
- Force: Force is synonymous with motivation in this context. It is calculated as the sum of the products of valences (values) and expectations. Essentially, it represents the strength of the motivation to choose a particular course of action.
How the Theory Works:
- According to Vroom, individuals are motivated to take actions to achieve certain goals based on their expectations that these actions will lead to the desired outcomes. The force driving their motivation is determined by the interplay of what they value (valence) and their belief in the likelihood of achieving it (expectancy).
Process Orientation:
- Vroom's theory is considered process-oriented because it focuses on the relationships among variables and how they affect individual behavior over time. This is in contrast to content theories that aim to identify correlates of motivated behavior without considering the dynamic interactions among factors.
Cognitive and Economic Roots:
- The theory draws on cognitive concepts related to choice behavior and the utility concepts from classical economic theory. It suggests that individuals make choices based on the expected utility of different options, weighing the potential outcomes against the effort required to achieve them.
Vroom's Expectancy Theory of Motivation provides a nuanced understanding of how motivation operates in the workplace. By emphasizing the importance of value, expectancy, and the dynamic relationships among these factors, the theory offers valuable insights into the motivational processes that drive individual behavior.
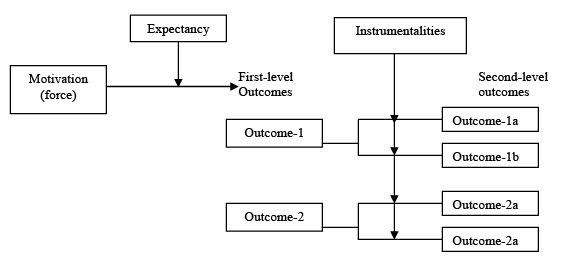
Key Elements of Vroom’s Expectancy Theory:
Vroom’s Expectancy Theory is based on three key elements: expectancy, instrumentality, and valence. Let's explore each element in detail:
- Expectancy: This refers to the belief that increased effort will lead to improved performance. In other words, individuals need to believe that their hard work will result in better outcomes. For example, if a salesperson believes that putting in extra hours will lead to more sales, their motivation to work harder increases.
- Instrumentality: Instrumentality relates to the perception that better performance will result in specific rewards or outcomes. It reflects the belief that achieving a certain level of performance will lead to desired rewards. For instance, if an employee believes that exceeding sales targets will result in a bonus, their motivation to perform well increases.
- Valence: Valence refers to the value or attractiveness of the expected outcomes to the individual. It reflects how much an individual values the rewards or outcomes associated with their performance. For example, if an employee highly values recognition and promotion, they will be more motivated to perform well if they believe their efforts will lead to these outcomes.
Process of Vroom’s Expectancy Theory:
Vroom’s Expectancy Theory involves a rational decision-making process where individuals assess the potential rewards and make choices about their level of effort based on expected results. Here’s how the process works:
- Assessment of Effort-Performance Link: Individuals evaluate the relationship between their effort and expected performance. They consider factors such as their skills, resources, and the difficulty of the task.
- Evaluation of Performance-Outcome Link: Individuals assess the likelihood that their performance will lead to specific outcomes. They consider past experiences, feedback, and the perceived fairness of the reward system.
- Valuation of Outcomes: Individuals determine the value they place on the expected outcomes. They consider their personal goals, aspirations, and the importance of the rewards.
- Decision Making: Based on the assessments and evaluations, individuals make decisions about the level of effort they will put into the task. If they believe that their efforts will lead to desirable outcomes, they are more likely to be motivated to work hard.
Implications of Vroom’s Expectancy Theory:
The theory recognizes that different individuals have varying levels of motivation and that these differences should be considered when designing motivation strategies.
By understanding the specific second-level outcomes that employees value, managers can align organizational goals with employee motivations. This alignment fosters a sense of shared purpose and enhances motivation.
The theory emphasizes the need to establish clear expectancies regarding the relationship between first-level outcomes and organizational objectives. When employees believe that their efforts will directly contribute to organizational goals, their motivation increases.
Vroom’s Expectancy Theory supports the idea that managers should create an environment that facilitates high performance and achievement of first-level outcomes. This involves providing necessary resources, support, and feedback to employees.
The theory aligns with the concept of management by objectives, where clear goals and performance expectations are set to guide employee efforts and enhance motivation.
Limitations of Vroom’s Expectancy Theory:
Vroom’s Expectancy Theory, despite its theoretical strengths, faces challenges in research and practical application. It recognizes the complexities of work motivation but can be difficult to understand and implement in real-world scenarios.
Research studies specifically testing Vroom’s theory are limited, and Vroom himself relied on prior research for support. This indicates the need for further exploration and validation of the theory.
While the theory offers a step forward in understanding motivation, it may not provide managers with practical solutions to motivational problems. Its abstract nature makes it harder to translate into actionable strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Vroom’s Expectancy Theory of Motivation provides a comprehensive framework for understanding how individuals make decisions about their level of effort based on expected outcomes. By focusing on the key components of expectancy, instrumentality, and valence, organizations can design effective motivation strategies that align individual beliefs and values with organizational goals. Despite its limitations in research and practical application, the theory remains valuable in academic discussions and offers insights into the complexities of work motivation.
|
58 videos|242 docs
|
FAQs on Participative Management (R. Likert, C.Argyris, D.McGregor) - Public Administration Optional for UPSC (Notes)
| 1. What is participative management and how is it related to Rensis Likert's theories? |  |
| 2. How did Chris Argyris contribute to the concept of participative management? |  |
| 3. What are Douglas McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y, and how do they relate to participative management? |  |
| 4. What are the key benefits of implementing participative management in organizations? |  |
| 5. How can organizations effectively implement participative management practices? |  |
















