Past Year Questions: Plastic Analysis | Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: The steel angle section shown in the figure has elastic section modulus of 150.92 cm3 about the horizontal X-X axis, which passes through the centroid of the section.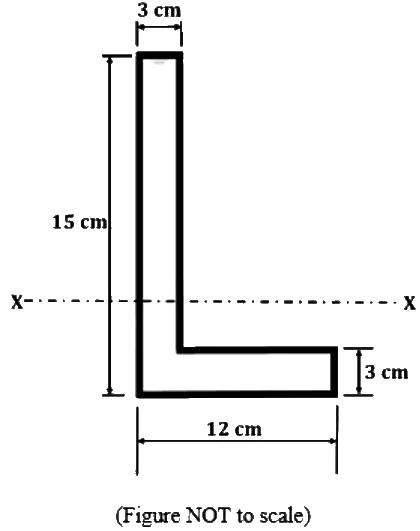 The shape factor of the section is_______ (rounded off to 2 decimal places) [GATE CE 2024 SET-2]
The shape factor of the section is_______ (rounded off to 2 decimal places) [GATE CE 2024 SET-2]
Ans: 1.75 to 1.85
Shape factor = Zp/Ze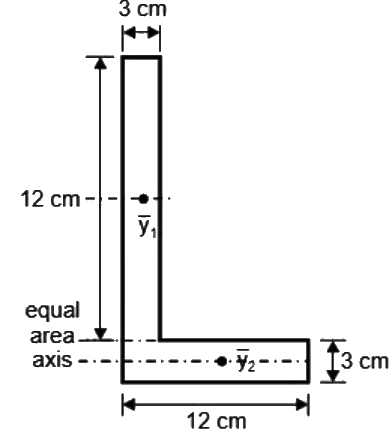
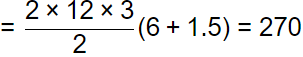
SF = 270/150.92 = 1.79
Q1: For the square steel beam cross-section shown in the figure, the shape factor about z − z axis is SS and the plastic moment capacity is MP. Consider yield stress fy = 250 MPa and a = 100mm. 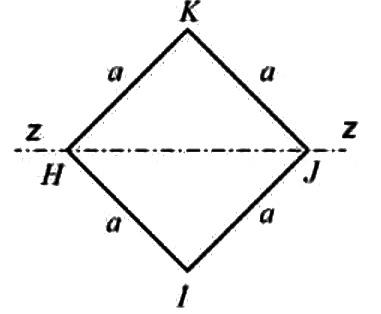 The values of S and MP (rounded-off to one decimal place) are [GATE CE 2022 SET-2]
The values of S and MP (rounded-off to one decimal place) are [GATE CE 2022 SET-2]
(a) S = 2.0, MP = 58.9 kN−m
(b) S = 2.0, MP = 100.2 kN−m
(c) S = 1.5, MP = 58.9 kN−m
(d) S = 1.5, MP = 100.2 kN−m
Ans: (a)
Shape factor for diamond shaped section = 2
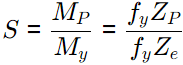
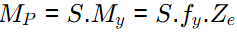
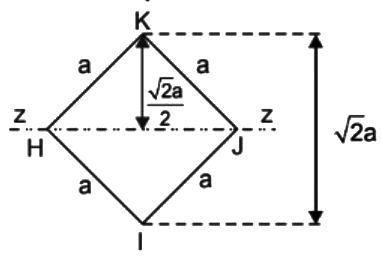 IZZ = a4/12
IZZ = a4/12
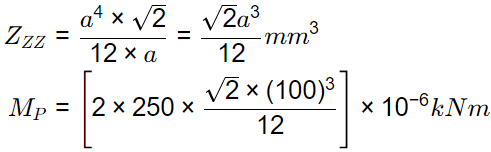
= 58.93 kNm
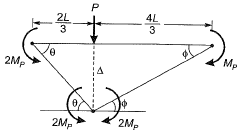
Q1: A prismatic steel beam is shown in the figure.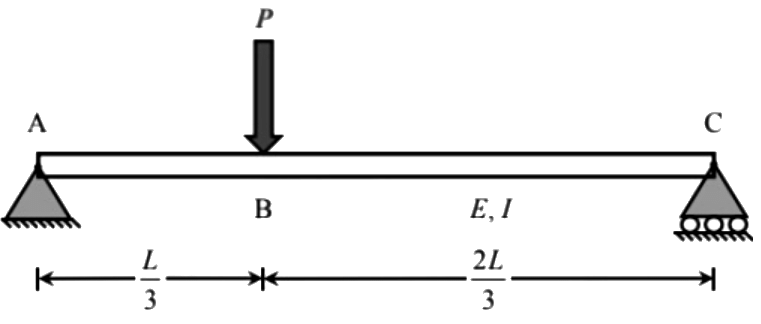 The plastic moment, Mp calculated for the collapse mechanism using static method and kinematic method is [GATE CE 2021 SET-2]
The plastic moment, Mp calculated for the collapse mechanism using static method and kinematic method is [GATE CE 2021 SET-2]
(a) MP, static > 2PL/9 = MP, kinematic
(b) MP, static = 2PL/9 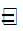 MP, kinematic
MP, kinematic
(c) MP, static = 2PL/9 = MP, kinematic
(d) MP, static < 2PL/9 = MP, kinematic
Ans: (c)
 At collapse, Mpθ + Mpϕ = PΔ
At collapse, Mpθ + Mpϕ = PΔ
⇒ 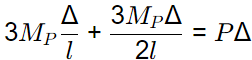
Mp = 2Pl/9
Also, MP, static = MP, kinematic
Q1: The ratio of the plastic moment capacity of a beam section to its yield moment capacity is termed as [GATE CE 2020 SET-2]
(a) aspect ratio
(b) load factor
(c) shape factor
(d) slenderness ratio
Ans: (c)
Ratio of Mp/My = Shape factor
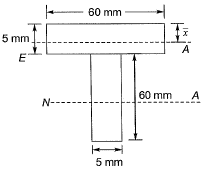
Q1: If the section shown in figure turns from fully elastic to fully plastic, the depth of neutral axis (NA), decreases by [2019 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
decreases by [2019 : 2 Marks, Set-I]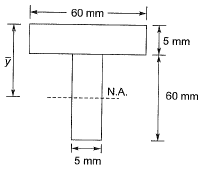
(a) 12.25 mm
(b) 15.25 mm
(c) 10.75 mm
(d) 13.75 mm
Ans: (d)
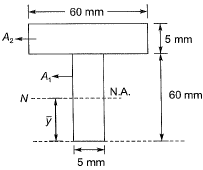
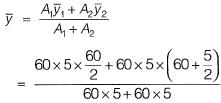
= 46.25 mm
NA - Neutral axis
The section is unsymmetrical about the NA and hence the equal area axis (EA) has to be located
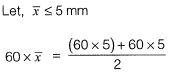
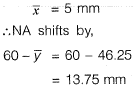
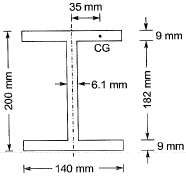
Q1: The dimension of a symmetrical welded l-section are shown in the figure.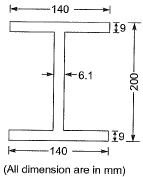
The plastic section modulus about the weaker axis (in cm3, up to one decimal place) is _____. [2018 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
Ans:
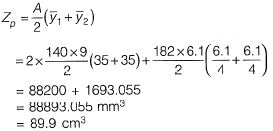
Note: Keep in wind the units and decimal places.
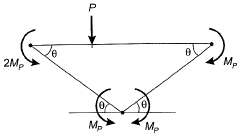
Q1: A fixed-end beam is subjected to a concentrated load (P) as shown in the figure. The beam has two different segments having different plastic moment capacities (MP, 2Mp) as shown.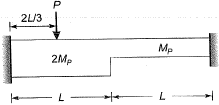
The minimum value of load (P) at which the beam would collapse (ultimate load is) [2016 : 2 Marks, Set-II]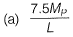
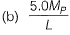
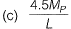
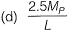
Ans: (a)
Ds = 2
∴ Number of plastic hinge required for complete collapse = Ds + 1
= 2 + 1 = 3
Mechanism 1:
⇒ 
For principal of virtual work done,
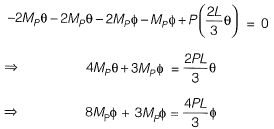
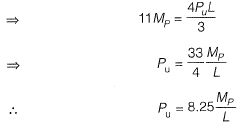
Mechanism 2:
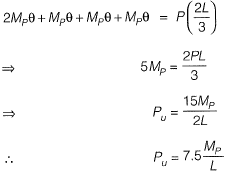
Q1: A fixed end beam is subjected to a load, W at 1 /3rd span from the left support as shown in the figure. The collapse load of the beam is [2015 : 2 Marks, Set-II]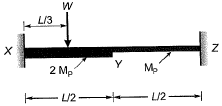
(a) 16.5 Mp/L
(b) 15.5 Mp/L
(c) 15.0 Mp/L
(d) 16.0 Mp/L
Ans: (c)
No. of plastic hinges formed at collapse
= r + 1 = 3
There can be two collapse mechanisms
Case (I)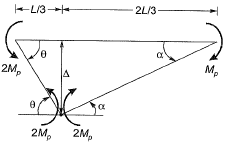
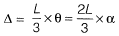
⇒ θ = 2α
Internal work done = External work done
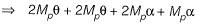
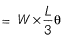
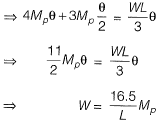
Case (II)
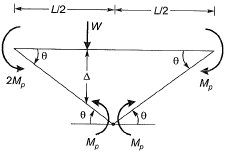
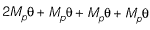
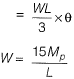
Hence, minimum collapse load is 15Mp/L.
Q2: For formation of collapse mechanism in the following figure, the minimum value of Pu is 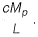 Mp and 3Mp denote the plastic moment capacities of beam sections as shown in this figure. The value of c is ____. [2015 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
Mp and 3Mp denote the plastic moment capacities of beam sections as shown in this figure. The value of c is ____. [2015 : 2 Marks, Set-I]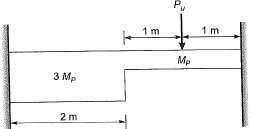
Ans: As L is not defined in question. So, by assuming L = 1 m
Mechanism 1: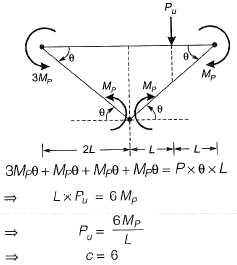
Mechanism 2: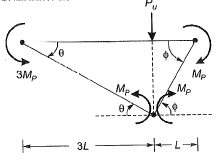
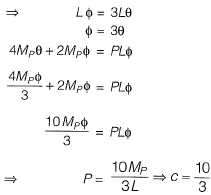
Failure load obtained out of two mechanisms
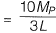
∴ 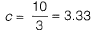
Q1: A prismatic beam (as shown below) has plastic moment capacity of M , then the collapse load MP of the beam is [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-II]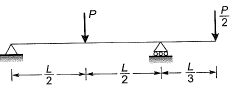
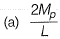
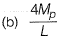
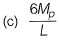
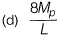
Ans: (c)
Here degree of static indeterminacy = 0
∴ Number of plastic hinges required for mechanical equlibrium
= Ds + 1 = 0 + 1 = 1
Mechanism 1:
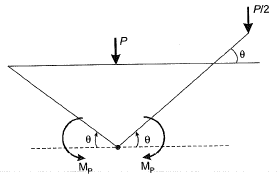
From principal of virtual work
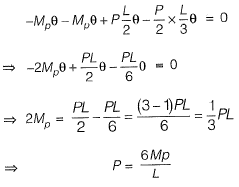
Mechanism 2: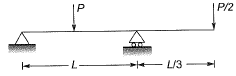
From principal of virtual work, equating external work donw to internal work done
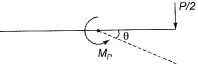
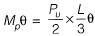
∴ 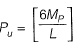
Q2: The ultimate collapse load (P) in terms of plastic moment Mp by kinematic approach for a propped cantilever of length L with Pacting at its mid-span as shown in the figure, would be [2014 : 1 Mark, Set-I]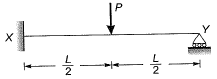
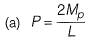
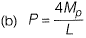
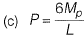
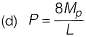
Ans: (c)
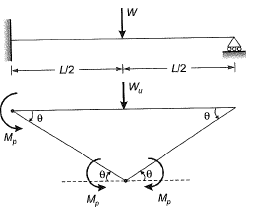
From principal of virtual work
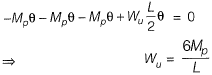
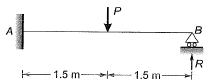
Q1: A propped cantilever made of a prismatic steel beam is subjected to a concentrated load P at mid span as shown.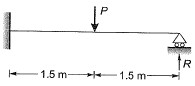
If the magnitude of load Pis increased till collapse and the plastic moment carrying capacity of steel beam section is 90 kNm, determine reaction R (in kN) (correct to 1-decimal place) using plastic analysis ________. [2013 : 2 Marks]
Ans:
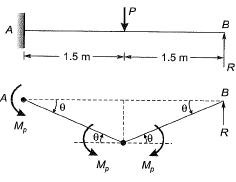
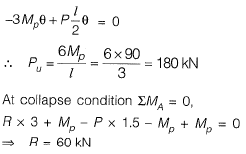
Q2: A propped cantilever made of a prismatic steel beam is subjected to a concentrated load P at mid span as shown.
If load P = 80 kN, find the reaction R (in kN) (correct to 1 decimal place) using elastic analysis______. [2013 : 2 Marks]
Ans: Equating deflection at end B,
Let, l = 3 m
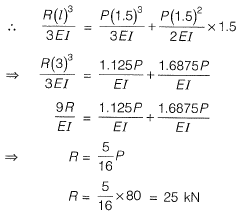
Q3: As per IS 800 : 2007 the cross-section in which extreme fibre can reach the yield stress but can not develop the plastic moment of resistance due to local buckling is classified as [2013 : 1 Mark]
(a) plastic section
(b) compact section
(c) semi compact section
(d) shear section
Ans: (c)
Plastic section: Cross-section which can develop plastic hinges and have the rotation capacity required for the failure of the structure by formation of plastic mechanism.
Compact section: Cross-section which can develop plastic moment of resistance but have inadequate plastic hinge rotation capacity for formation of plastic mechanism before buckling.
Semi compact: Cross-sections, in which the expense fibre in compression can reach yield stress, but cannot develop plastic moment of resistance due to location buckling.
Slender: Cross-sections in which the elements buckle locally even before attainment of yield stress are closed as sledner sections.
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Plastic Analysis - Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is plastic analysis in structural engineering? |  |
| 2. What are the key assumptions made in plastic analysis? |  |
| 3. How does the concept of a plastic hinge work in plastic analysis? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of using plastic analysis over elastic analysis? |  |
| 5. In what scenarios is plastic analysis particularly useful? |  |
















