Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Pathogens & Barriers
Pathogens & Barriers | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Pathogens
- A pathogen is a microorganism that causes diseases. These harmful organisms are responsible for various illnesses in living beings.
- Pathogens are transmitted from one host to another, leading to what are known as communicable diseases.
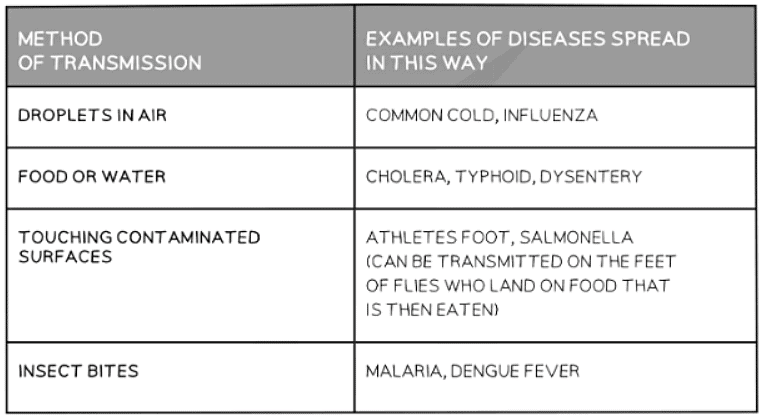
- Different modes of pathogen transmission exist, such as:
- Direct contact: Where pathogens are transferred directly from one individual to another through body fluids like blood or semen. For instance, diseases like HIV, gonorrhea, and hepatitis B & C are transmitted this way.
- Indirect contact: Where the pathogen leaves one host and is transported to another uninfected individual through various means.
Methods of Transmission Table
The Body Defenses
Our body has three primary defense mechanisms against diseases:
- Mechanical barriers: These are protective structures that hinder pathogens from entering the body.
- Skin: Acting as a physical barrier, the skin covers most of the body, preventing pathogen entry. When damaged, it heals itself, often by forming a scab.
- Hairs in the nose: These tiny hairs obstruct pathogens from entering deeper into the nose to avoid inhalation into the lungs.
- Chemical barriers: These are substances produced by body cells that trap or kill pathogens before they can cause diseases.
- Mucus: Generated in various body parts, mucus traps pathogens, facilitating their removal from the body through actions like coughing, blowing the nose, or swallowing.
- Stomach acid: With hydrochloric acid, the stomach acid is potent enough to eliminate pathogens trapped in mucus in the airways, whether swallowed or ingested through food or water.
- Cells: Different types of white blood cells work to prevent pathogens from reaching areas of the body where they can replicate.
- Phagocytosis: This process involves white blood cells engulfing and digesting pathogenic cells.
- Antibody Production: White blood cells produce antibodies that clump pathogenic cells together (agglutination), making it harder for them to move. They also release chemicals that signal other cells to destroy the pathogens.
Question for Pathogens & BarriersTry yourself: Which defense mechanism acts as a physical barrier to prevent pathogen entry into the body?View Solution
The document Pathogens & Barriers | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
101 videos|193 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Pathogens & Barriers - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How do pathogens enter the body? |  |
Ans. Pathogens can enter the body through various ways such as inhalation, ingestion, direct contact with infected individuals, or through breaks in the skin.
| 2. What are some of the body's natural defenses against pathogens? |  |
Ans. The body's natural defenses against pathogens include the skin as a physical barrier, the immune system that produces antibodies, white blood cells that attack and destroy pathogens, and mucous membranes that trap and expel pathogens.
| 3. How does the immune system recognize and respond to pathogens? |  |
Ans. The immune system recognizes pathogens by their unique antigens and produces specific antibodies to neutralize and destroy them. White blood cells are then activated to attack and remove the pathogens from the body.
| 4. Can pathogens develop resistance to the body's defenses? |  |
Ans. Yes, pathogens can develop resistance to the body's defenses through mechanisms like genetic mutations or acquiring resistance genes from other pathogens, making them harder to eliminate and causing infections that are more difficult to treat.
| 5. How can individuals strengthen their immune system to better defend against pathogens? |  |
Ans. Individuals can strengthen their immune system by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and practicing good hygiene habits like washing hands frequently.
Related Searches















