Pedigree Analysis | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
- Pedigree is a genealogical table, chart or diagram representing the ancestral line of an individual man or animal having a long span of life and low reproductive ability. Pedigree analysis is the process of determination of the exact mode of inheritance of a gene when sufficient family information is available.
- By this, determination of genotypes and phenotypes of past, present as well as future generations; the nature of inheritance, whether sex-linked or autosomal and dominant or recessive; probable ratio of inheritance of a gene and segregation are possible. To express the phenotype of individuals of a family for a few generations following symbols are used in the hypothetical pedigree of five generations (Fig. 55.1).

The symbols used are:
- Circle (O) a female;
- Square (□) a male;
- Diamond (◊) a sib (sibling) of unknown (either) sex;
- Darkened or shed symbols for the rarer genetic phenotype;
- Connection between circle and square (□—O), marriage line;
- Horizontal line (O—□) below the parents connecting off-springs (siblings) is sib-ship line;
- Generations, denoted by roman letter I, II, III, IV etc., on a side;
- Off-springs in each generation are numbered from left side in order of birth;
- Identical (monozygotic) twin (arise from splitting of a common zygote) represented by a common connection with sib-ship line (11-5 & 6);
- Dizygotic twins with separate connection with sib-ship line (IV-6 & 7)’;
- Numbers within the symbols (II-7 to 10) are sibs not individually listed;
- The connection of sib-ship line and marriage line:
- Inbred dominant with no genetic segregation;
- Out cross and no segregation;
- Test cross from which a recessive (male) results;
- Out cross by chance producing a recessive (female);
- Inbred recessives produce only recessive (tt; nontaster);
- Inbred dominants in a cousin marriage, also a back-cross type, producing no phenotypic segregation but only dominant of the Tt, TT varieties (taster).
Problem I: Transmission of Autosomal Recessive Trait
- The figure 55.2 illustrates an hypothetical family pedigree for albinism* in which the albino individuals are designated by shading symbols.

- Determine whether the gene is dominant or recessive and probable genotype of each individual.
- In the given pedigree the albino daughters (II-6 & 7) from normal parents (I-3 & 4) and from albino father (I-1) and normal mother (I-2) normal children are born. Thus the albino character skip over the generation and appears in alternate generation. So the gene is recessive one. In case of a dominant trait, the affected individuals appear in all generations, there would be no generation skipping.
- Here parents I-3 & 4 are the carrier and heterozygous for the recessive gene of albinism. The frequency of children that are affected is about one-fourth (1/4 th) of the total off-springs in lllrd generation born from two normal parents (II-4 & 5). This fact also supports that this gene is recessive.
- A dominant trait is usually transmitted by mating between an affected parent, heterozygous and a homozygous parent to about half of the off-springs. As the gene is recessive (a) to the normal (+) the genotype of 1-1 is a = a, because the recessive trait can express itself only in homozygous condition. Affected daughters (II-6 & 7) appeared from normal parents (l-3 & 4).
- So the genotypes of I-3 & 4 be =. Similar explanation is applicable for II-4 & 5. The probable genotype of all the individuals are as follows.

Problem II: Transmission of Autosomal Dominant Trait
The figure (Fig. 55.4, 55.5) illustrates an hypothetical family pedigree for a rare trait chondrodystrophy*.
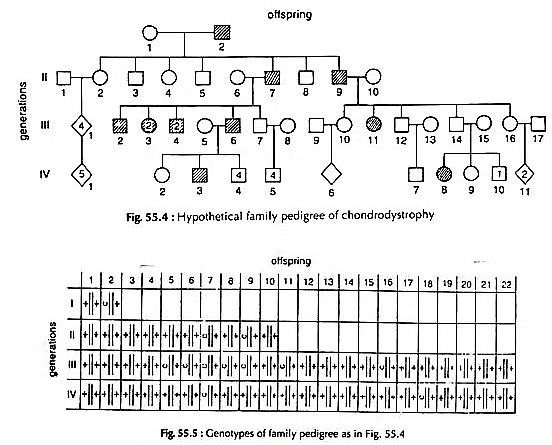
Determine whether this gene is dominant or recessive and show the genotype of each individual.
Explanation:
- In the given pedigree, chondrodystrophy appeared in each and every generation where any one of the parent is affected by this trait. That means, the inherited trait did not skip any generation. Whereas no chondrodystrophy observed by marriage between two normal individuals of which one of them having chondrodistrophic history in their past generation (III-7 & 8, III-9 & 10, III-12 & 13, etc.). So the trait is dominant.
- In this pedigree it is assumed to be caused by a gene present in the lst generation (I-2). If the trait was recessive, then all the normal individuals of llnd generation (II-2,3, 5 & 8) were heterozygous carrier. So there was a chance of appearance of chondrodistrophic off-springs from the marriage of such heterozygous individuals with normal one. But no such information is evident from this pedigree.
- Let the chondrodistrophic gene be ‘c’. As it is a dominant trait over normal ‘†’, so the genotype of I-2 must be C/†, because normal off-springs were born from him. If he was homozygous for this dominant trait then all his children must be chondrodistrophic.
The probable genotype of the individuals are as follows:
Problem III: Transmission of Sex-linked Recessive Trait
The following pedigree (Fig. 55.6, 55.7) represent the phenotype of a family where red- green colour blind individuals are indicated by shade.
Determine the nature of trait and explain.

Explanation:
- From the given pedigree it is observed that the colour blind children in llnd generation (II-1, 6 & 8) are born from normal parents (I-1, 2 & 3). So the gene responsible for colour blindness is a recessive one. As only 50% of male children are affected by this trait, the trait is carried by the sex chromosome (sex-linked).
- If it be autosomal then there is a probability to get affected daughters. If it be ‘Y’- linked then there is probability of appearance of the colour blindness to all the sons in llnd generation. But these are not evident from the pedigree and the crisscross type inheritance in the pedigree clearly indicate that the trait is a sex-linked recessive.
- Here mother (I-2) is the carrier for the gene and is heterozygous c/†. So all her sons received their X-chromosome from her and Y-chromo some from father (I-1 & 3). For this reason 50% of her sons received the affected gene and rest 50% received normal gene resulting into 1: 1 ratio of colour blind and normal sons.
- At the same time, as fathers are normal, they have one normal X-chromosome and all their daughters received one X-chromosome, result normal eye.
- The probable genotype of the family pedigree displayed is as follows, taking colour blind trait as ‘c’.
Problem IV: Transmission of Y-linked Dominant Trait
In the pedigree (Figs. 55.8, 55.9) the shaded symbols are represent as a rare trait.


State whether you believe it as caused by sex-linked or autosomal and dominant and recessive gene.
Explanation:
- From the given pedigree it is observed that the gene responsible for the affected trait appeared in each generation. At the same time no affected children were born from marriage of normal male and female (I-3 & 4). So the gene is dominant one.
- Another important event is that the trait is always associated with male but never with, females in all the three generations. This finding indicates that the gene is Y-linked, since sons receive their Y-chromosome from father and X-chromosome from mother.
- Here II-2 & 5 children receive their Y-chromosome from parent I-2, who is affected. Similarly, the affected gene is inherited from II-2 to III-3 and II-5 to III-4 & 6 respectively. If the gene be X-linked dominant then all the daughters (II-3 & 4) would be affected, as they would receive one X-chromosome from their father. But in the given pedigree it is not evident. So the gene is Y-linked dominant.
Problem V. Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular dis-trophy is a rare human disease. The given pedigree (Figs. 55.10, 55.11) represent the phenotypes of a certain family with shaded symbols as affected individuals.

Determine the mode of inheritance of the gene.
Explanation:
- In the given pedigree, the affected trait appeared in all generations in which one of the parents (I-2) was affected. At the same time, no affected child was born from marriage of normal individuals (I-3 & 4). So the gene is dominant.
- It is found that the trait has expressed with sex during transmission from generation to generation. In generation III all the daughters (III-1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 9 & 10) are muscular distrophied as their father is affected. But no male children are affected.
- So it is probable that the gene is X-linked, for which all female children of generation III received the affected X- chromosome from their father (II-2 & 6), who received that gene from their affected mother (I-2). The gene is transmitted from mother to son and son to daughter in a crisscross way. So the gene is X-linked dominant.
Exercise:
1. In the pedigree (Figs. 55.12 and 55.13) affected individuals are shaded.
- Indicate the trait is dominant or recessive.
- Mention the trait is either autosomal or sex-linked.
- Determine the genotype of each individual in the pedigree and indicate the choice of genotypes; if you think more than one genotype is possible, for an individual.


2. Describe the following pedigree (Figs. 55.14 & 15). Analyse the mode of inheritance and nature of trait. The shaded individuals are affected. Find out the genotype of the shaded individual.


3. The figure (Fig. 55.16) represents four family pedigrees for a trait in humans. Shaded symbols bear trait. For each pedigree (A, B, C, D), state by answering ‘yes’ or ‘no’ in the appropriate blank space whether transmission of the trait can be accounted for on the basis of each of the listed simple modes of inheritance.
- Pedigree A B C D.
- Autosomal — recessive
- Autosomal — dominant
- X-linked — recessive
- X-linked — dominant

|
181 videos|346 docs
|
FAQs on Pedigree Analysis - Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is an autosomal recessive trait? |  |
| 2. How are autosomal recessive traits transmitted? |  |
| 3. What is an autosomal dominant trait? |  |
| 4. How are autosomal dominant traits transmitted? |  |
| 5. What is a sex-linked recessive trait? |  |




















