Performance Management | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
What is Performance Management?
- It's a key process in managing people at work.
- Happens all year round through communication between a manager and an employee.
- Aims to achieve the organization's goals.
Why is Performance Appraisal Important?
- It's a formal evaluation that reviews how well an employee has been doing over a longer period.
- Originated in the 1950s in the United States as a way to motivate and develop employees.
How is Performance Management Described?
- It's seen as a systematic process.
- The main goal is to improve how people perform within the organization.
Definition by SHRM (Society for Human Resource Management)
Performance management is an organized way of:
- Monitoring results of work activities,
- Collecting and evaluating performance to see if goals are achieved,
- Using performance information to make decisions, allocate resources, and communicate if objectives are met.
Evolution and Objectives of Performance Management in Organizational Context
- Origins and Purpose:
- Initially designed for private businesses.
- Aims to improve employee performance for overall corporate success.
- Evolution of Concept:
- Started with evaluating past performance.
- Evolved to include future performance considerations.
- Explores new management approaches aligned with organizational goals.
- Key Principles from Lunger (2006):
- Stresses starting performance management from organizational development strategies, goals, and values.
- Includes functions like customer satisfaction, group and team performance, cross-sector and cross-function appraisal.
- Highlights the importance of performance monitoring, development, and evolving measurement practices over time.
- Armstrong's Perspective:
- Performance management's goal is to enhance organizational members' performance.
- Achieved through strategically developing team capabilities.
- Emphasizes the need for an integrated system for successful organizational operations.
Performance Management Cycle

- Overview: Performance management is like a continuous improvement cycle for companies.
- Cycle Components:
- Planning Stage:
- Involves strategic planning to set program objectives and envision the organization's future.
- Executing Stage:
- Carries out programs aligned with the strategic plan to achieve organizational objectives and mission.
- Monitoring Stage:
- Measures positive changes in skills, attitudes, or behaviors.
- Analyzing and Sharing Stage:
- Helps organizations make sense of collected data.
- Enables learning about what's going well and how objectives are being achieved.
- Adapting Stage:
- Organizations learn from the data.
- Use insights to create effective programs aligned with the organizational mission.
- Planning Stage:
- Common Belief:
- Performance management is thought to improve organizational outcomes.
- Contrary Viewpoint:
- Some theorists, like Pulakos and O'Leary, argue that current systems focus too much on paperwork, neglecting the crucial aspect of training managers and employees in effective performance behaviors.
- Positive Outlook:
- Mone and London suggest that if performance management systems aim to boost employee engagement, it can lead to higher performance levels.
- Key Insights:
- Gruman and Saks emphasize the importance of promoting employee engagement as a driver for enhanced performance within performance management systems.
- Engagement Management Model:
- Developed by Gruman and Saks.
- Comprises three components: performance agreement, engagement facilitation, and performance and engagement appraisal and feedback.
- Aimed at fostering employee engagement, ultimately contributing to improved performance.
Engagement Management Model Developed by Gruman and Saks (2011)

Navigating the Performance Management Model
- Starting Point - Performance Agreement:
- Begins with setting goals and objectives for employees within the organization.
- Includes reviewing and agreeing upon a psychological contract.
- Aims to establish shared goals for both individuals and the organization.
- Efficient Performance Management Process:
- Assists managers in assessing and measuring individual performance.
- Optimizes productivity by aligning daily actions with strategic business objectives.
- Provides clarity on performance expectations, accountability, and documentation for reimbursement and career planning decisions.
- Key Functions:
- Guides skill development and learning activity choices.
- Establishes certification for legal purposes.
- Supports decisions and reduces disagreements.
- Building a Successful System:
- Requires time, resources, and support from the board, executive director, and senior managers.
- Involves the formation of a committee comprising employees, managers, and board members for increased buy-in, understanding, and support.
- Communication is Key:
- When introducing a new performance management system or modifying an existing one, effective communication is crucial.
- Managers should clearly communicate the purpose and steps of the performance management process to employees before implementation.
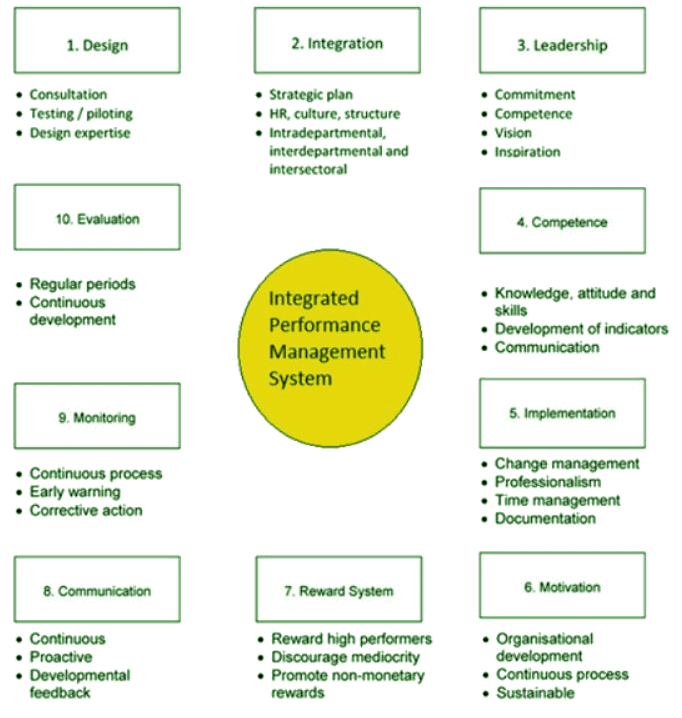
Challenges in Performance Management
- Business Impact:
- Problem: Hampers business results due to managerial burdens.
- Solution: Integration with strategic planning, HR processes, and organizational systems is vital.
- Communication Hurdles:
- Problem: Reluctance in open communication during reviews.
- Solution: Emphasizes the need for timely and constructive feedback for accurate performance assessment.
- Integration Issues:
- Problem: Lack of synergy with strategic planning, HR, and organizational culture.
- Solution: Design the system to meet the specific needs of the organization.
- Leadership Support:
- Problem: Ineffectiveness without strong leadership commitment.
- Solution: Senior management must support and be committed to implementing the system.
- Skill Development:
- Problem: Inadequate skills in using the system.
- Solution: Management teams should acquire the necessary skills, including developing performance indicators and competencies.
- Reward System:
- Problem: Lack of a comprehensive reward system.
- Solution: Develop and communicate a reward system, including financial rewards, public acknowledgments, promotions, and learning opportunities.
- Critical Role of Communication:
- Problem: Communication is a critical factor.
- Solution: Effective communication is essential for the success of the performance management system.
- Inspiration Challenges:
- Problem: Lack of inspiration.
- Solution: A well-designed and communicated reward system can inspire employees.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:
- Problem: Lack of monitoring and evaluation.
- Solution: Regularly monitor and evaluate the performance management process for effectiveness.
An Integrated Performance Management System
Conclusion
In Conclusion, performance management encompasses activities and strategies aimed at helping businesses, government agencies, and non-profit organizations achieve their goals more effectively. It serves as a means to enhance organizational performance, involving a continuous process where managers and employees collaborate to plan, monitor, and evaluate individual work objectives and contributions. This holistic approach integrates an organization's plans, activities, assessments, and analyses with the overarching objective of improving overall organizational effectiveness.
FAQs on Performance Management - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the evolution of performance management in an organizational context? |  |
| 2. What are the objectives of performance management in an organizational context? |  |
| 3. What is the performance management cycle? |  |
| 4. What is the engagement management model developed by Gruman and Saks (2011)? |  |
| 5. How does performance management benefit organizations and employees? |  |


















