Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Photosynthesis
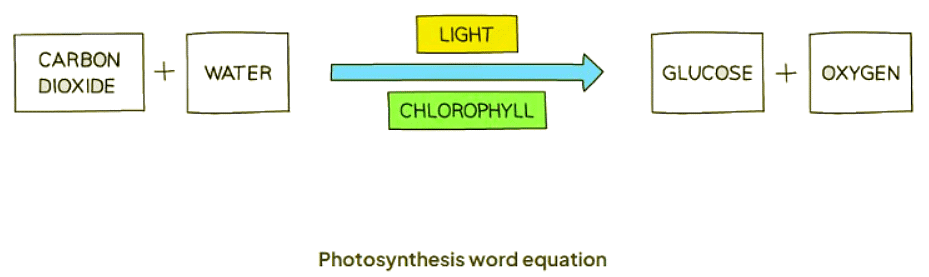
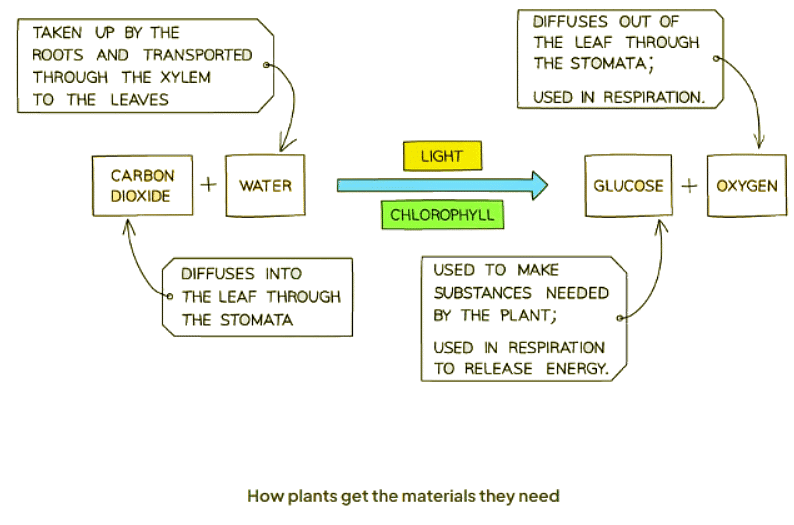
- Through photosynthesis, green plants convert the raw materials carbon dioxide and water into the carbohydrate glucose.
- As a byproduct, oxygen is generated and released.
- Chlorophyll, a pigment in plants, captures sunlight to provide the energy necessary for this reaction.
- Essentially, photosynthesis is the process wherein plants produce carbohydrates using light energy.
- This process is represented by the following equation:
Photosynthesis Word Equation
Question for PhotosynthesisTry yourself: What is the purpose of photosynthesis in plants?View Solution
The document Photosynthesis | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
101 videos|194 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Photosynthesis - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is photosynthesis? |  |
Ans. Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This process involves the absorption of sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce oxygen and glucose.
| 2. What are the main stages of photosynthesis? |  |
Ans. The main stages of photosynthesis are light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions. During the light-dependent reactions, light energy is used to split water molecules and produce ATP and NADPH. In the light-independent reactions, ATP and NADPH are used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
| 3. Why is photosynthesis important for plants and other organisms? |  |
Ans. Photosynthesis is essential for plants and other organisms because it is the primary source of energy for all living things. Plants use the glucose produced during photosynthesis as a source of food, and the oxygen released is crucial for the respiration of both plants and animals.
| 4. How does the structure of a plant leaf support photosynthesis? |  |
Ans. The structure of a plant leaf is specifically adapted to support photosynthesis. The flat shape of the leaf maximizes the surface area exposed to sunlight, while the presence of chloroplasts containing chlorophyll allows for the absorption of light energy needed for photosynthesis.
| 5. What factors can affect the rate of photosynthesis in plants? |  |
Ans. Factors such as light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, temperature, and water availability can all impact the rate of photosynthesis in plants. For instance, low light levels or inadequate carbon dioxide can limit the rate of photosynthesis, while optimal conditions can enhance the process.
Related Searches





















