Plasmid | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Plasmids? |

|
| Properties of Plasmids |

|
| Structure of Plasmids |

|
| Transfer of Plasmid |

|
| Types of Plasmids |

|
What are Plasmids?
- Plasmids are small circular DNA fragments, double-stranded, self-replicating extra chromosomal structures found in many microorganisms.
- The term Plasmid was coined by Joshua Lederberg in 1952.
- Plasmids are important as genetic tools, which are used to introduce, manipulate or delete certain genes from the host cell.
Properties of Plasmids
- They are extra chromosomal DNA fragments present in the cell.
- They are double stranded structures. Exceptions are the linear plasmids in bacteria Streptomyces spp and Borrelia spp.
- They can replicate independently.
- The absence of a plasmid in the cell does not affect cell functioning, but the presence of a plasmid in the cell is usually beneficial.
- Plasmids are also known as sex factors, conjugants, extra chromosomal replicons, or transfer factors.
- Copy number – the copy number refers to the number of copies of plasmid present in the bacterial cell. Usually, small plasmids are present in high numbers and large plasmids are present in few numbers.
- Compatibility of plasmids – this refers to the ability of two different plasmids to coexist in the same bacterial cell.
Structure of Plasmids
1. Every plasmid has certain essential elements. These are as follows –
- Origin of replication (OR) – This refers to a specific location in the strand where the replication process begins. In plasmids, this region is A=T rich region as it is easier to separate the strands during replication.
- Selectable marker site – This region consists of Antibiotic resistance genes which are useful in the identification and selection of bacteria that contain plasmids.
- Promoter region – this is the region where the transcriptional machinery is loaded.
- Primer binding site – this is the short sequence of single-strand DNA which is useful in DNA amplification and DNA sequencing.
- Multiple cloning sites – This site contains various sequences where the restriction enzymes can bind and cleave the double stranded structure.
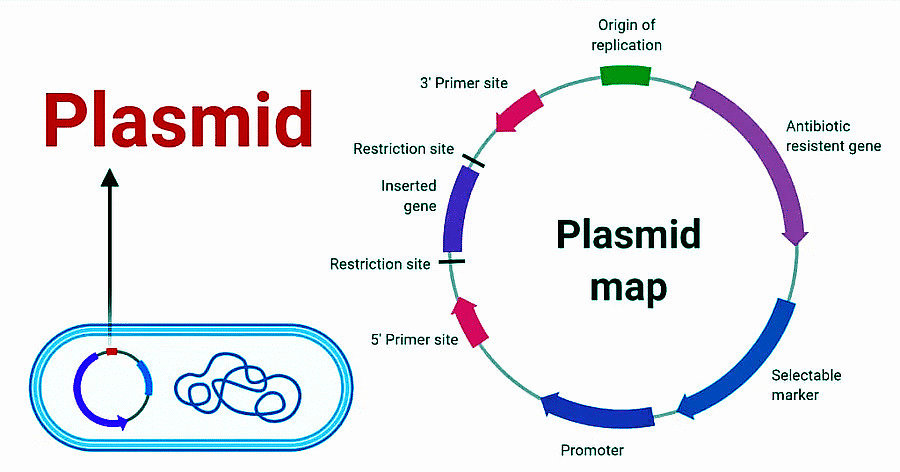
2. The size of the plasmid varies from 2 kb to 200 kb.
3. It is the extrachromosomal element of the cell which is not required for the growth and development of the cell.
4. Most of the plasmids contain the TRA gene, which is the transferred gene and is essential in transferring the plasmid from one cell to another.
Transfer of Plasmid
Plasmids are transferred by the process of Conjugation:
- The process of conjugation involves two cells: a donor cell and a recipient cell.
- The donor cells form a conjugation bridge now as pilus and attaches to the recipient cell.
- One copy of the plasmid is transferred from donor to recipient cell.
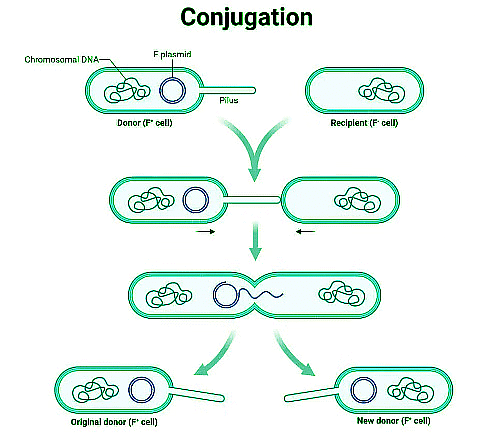
The other methods by which the plasmids can be transferred are transduction and bacterial transformation.
Types of Plasmids
Based on the presence of the TRA gene plasmids can be classified into two types:
- Conjugative plasmids – these plasmids contain TRA (transfer) gene and are commonly seen in bacteria.
- Non-conjugative plasmids – these types of plasmids lack the TRA genes.
Based on functions the plasmids can be classified into the following types:
1. F Plasmids (Fertility plasmids)
They contain the TRA genes and hence can be transferred from one cell to another.
They can replicate inside the bacterial cell.
They cause the synthesis of a pilus, which is a long protein-rich structure that helps in cell-cell interaction.
It also contains a sequence responsible for incompatibility.
2. R plasmid (Resistance plasmids)
These plasmids contain and transmit genes for Antibiotic resistance from one cell to another.
The antibiotic resistance gene protects the bacteria from antibiotics in human medicines and antibiotics naturally present in the soil.
These types of plasmids are usually large in size and present in low copy numbers in the cell.
3. Col Plasmids (Colicin plasmids)
These are known as bacteriocinogenic plasmids because they produce bacteriocins.
These proteins have the ability to kill the closely related bacterial cells which lack Col plasmids.
These plasmids are observed in E. coli.
4. Degradative Plasmids
These types of plasmids have the ability to digest unusual substances such as toluene, camphor, salicylic acid, etc.
The presence of these plasmids in the organism enables the breakdown of various chemicals and substances.
5. Virulence Plasmids
These plasmids produce virulence factors that enable the bacteria to infect other cells. Bactria containing virulence plasmids are able to infect the plant, animal, and human cells.
Example – Ti plasmid is the virulence plasmid present in Agrobacterium tumefaciens which causes crown gall disease in plants.
Functions and Applications of Plasmids
- The important use of plasmids is that they can be used as vectors to insert a specific gene into other organisms due to their capacity to incorporate a gene and replicate inside the cell.
- They are an important factor in bacteria as they carry antibiotic resistance genes.
- Degradative plasmids can be used to degrade industrial chemicals which are a threat to the environment.
- As plasmids are easy to manipulate, they are being used in gene therapy as well.
- Because plasmids are good vectors (a vehicle/factor which is used to transfer a gene from one organism to another) they are used in drug delivery and for hormone production in other cells.
- Plasmids are an important source of horizontal gene transfer.
|
181 videos|351 docs
|
FAQs on Plasmid - Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are plasmids? |  |
| 2. What are the properties of plasmids? |  |
| 3. What is the structure of plasmids? |  |
| 4. How are plasmids transferred between cells? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of plasmids? |  |



















