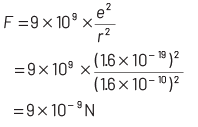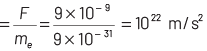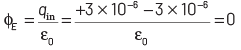NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Electric Charges & Fields | Physics Class 12 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Two identical charged conducting spheres A and B have their centres separated by a certain distance. Charge on each sphere is q and the force of repulsion between them is F. A third identical uncharged conducting sphere is brought in contact with sphere A first and then with B and finally removed from both. New force of repulsion between spheres A and B (Radii of A and B are negligible compared to the distance of separation so that for calculating force between them they can be considered as point charges) is best given as: [NEET 2025]
(a) F/2
(b) 3F/8
(c) 3F/5
(d) 2F/3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Let the charge on each sphere A and B be q and the separation be d.
Therefore, the force between spheres A and B is:
F = (1 / (4πɛ₀)) × (q² / d²) ... (1)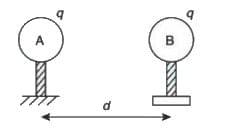
When spheres A and C are touched and then separated, charge on each will be:
(q + 0) / 2 = q / 2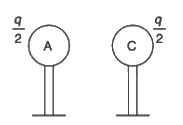
Now sphere B is touched with sphere C. Charge on each will be:
(q + q/2) / 2 = (3q) / 4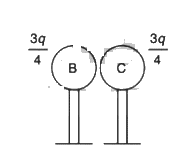 Now the force between sphere A and sphere B will be:
Now the force between sphere A and sphere B will be: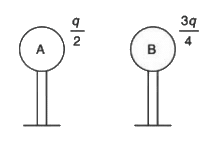 F' = (1 / (4πɛ₀)) × (q/2 × 3q/4) / d²
F' = (1 / (4πɛ₀)) × (q/2 × 3q/4) / d²
= (3/8) × (1 / (4πɛ₀)) × (q² / d²)
⇒ F' = (3/8) × F
2024
Q1: A thin spherical shell is charged by some source. The potential difference between the two points C and P (in V) shown in the figure is: [NEET 2024]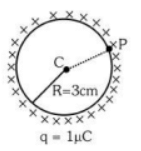 (Take
(Take 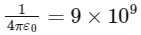 SI Units)
SI Units)(a) 3 x 105
(b) 1 x 105
(c) 0.5 x 105
(d) Zero
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
For uniformly charged spherical shell,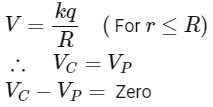
Q2: Two identical rectangular plane sheet A and B each of surface charge density ε0Cm−2 are placed parallel to each other as shown in figure. The electric field at the mid point P will be: [NEET 2024]
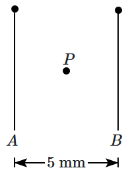 (a) 2 NC-1
(a) 2 NC-1
(b) 1 NC-1
(c) 0.5 NC-1
(d) zero
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The electric field produced by a uniformly charged infinite sheet with surface charge density σ is given by the formula:
E = σ / (2ε₀)
Where:
- E is the electric field.
- σ is the surface charge density.
- ε₀ is the permittivity of free space (8.85 × 10⁻¹² C²/N·m²).
Step-by-Step Analysis:
- Electric Field due to One Sheet: Each sheet A and B generates an electric field E = σ / (2ε₀) at points on both sides of the sheet. The direction of the electric field is perpendicular to the surface of the sheet and points away from the sheet if the charge is positive.
- Electric Fields at Point P (Midpoint):
- Let’s assume the charge densities of the sheets are σ.
- For sheet A, the electric field at point P (midpoint) will point towards sheet A if the charge is positive.
- For sheet B, the electric field at point P (midpoint) will point away from sheet B if the charge is positive.
- Net Electric Field at Point P:
- Since the electric fields produced by sheet A and sheet B at the midpoint are opposite in direction, they cancel each other out.
- The magnitude of the electric field produced by each sheet is the same and they act in opposite directions at point P.
Hence, the net electric field at point P is zero.
Conclusion:
The electric field at the midpoint between the two sheets will be zero due to the cancellation of the fields produced by the two identical sheets. Therefore, the correct answer is (d) zero.
Q3: Match List-I with List-II: [NEET 2024]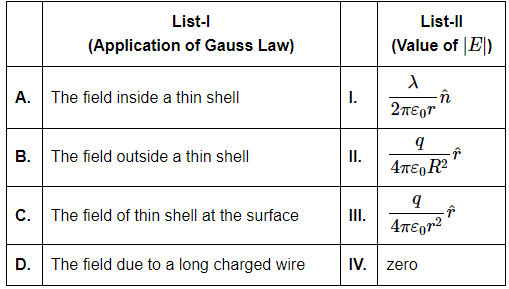 (Here symbols have their usual meaning and R is the radius of the thin shell)
(Here symbols have their usual meaning and R is the radius of the thin shell)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(b) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(c) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(d) A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
A. The field inside a thin shell
According to Gauss' Law, the electric field inside a thin spherical shell of charge is zero. This is because the net flux through a Gaussian surface inside the shell is zero due to symmetry (all contributions from different parts of the shell cancel out).
Matching with: IV. zero
B. The field outside a thin shell
For a spherical shell with charge q on its surface, the field outside the shell behaves as though all the charge is concentrated at the center of the shell. The electric field at a distance r from the center is given by:
Matching with: III. q / (4πε₀ r²) r̂ (r is the distance from the center of the shell)
C. The field of a thin shell at the surface
At the surface of the shell, the electric field behaves as though the entire charge is concentrated at the center, with the field magnitude being:
Matching with: II. q / (4πε₀ R²) r̂
D. The field due to a long charged wire
The electric field produced by an infinitely long straight charged wire with linear charge density λ at a distance r from the wire is given by:
Matching with: I. λ / (2πε₀ r) r̂
Correct answer: (c) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
Q4: A particle of mass m and charge q is placed in a uniform electric field E at t = 0 s. The kinetic energy of the particle after time t is:
(a) Eqm / t
(b) E²q²t² / 2m
(c) 2E²t² / qm
(d) Eq²m / 2t² [NEET 2024]
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- When a charged particle is placed in a uniform electric field E, the force acting on it is F = qE.
- The acceleration of the particle is a = F / m = qE / m.
- Since the particle starts from rest at t = 0, its velocity at time t is v = at = (qE / m)t.
- The kinetic energy (KE) at time t is given by KE = (1/2)mv². Substituting v = (qE / m)t, we get:
KE = (1/2)m[(qE / m)t]² = (q²E²t²) / (2m).
Thus, the correct expression for the kinetic energy of the particle is E²q²t² / 2m, which corresponds to option (b).
Q5: A metal cube of a side 5 cm is charged with 6 μC. The surface charge density on the cube is: [NEET 2024]
(a) 0.125 × 10⁻³ C m⁻²
(b) 0.25 × 10⁻³ C m⁻²
(c) 4 × 10⁻³ C m⁻²
(d) 0.4 × 10⁻³ C m⁻²
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
To calculate the surface charge density, we use the formula:
Surface charge density (σ) = Charge / Area
First, we need to find the area of one face of the cube.
- The side of the cube is given as 5 cm.
- The area of one face of the cube is:
Area = side² = (5 cm)² = (0.05 m)² = 0.0025 m²
Now, the total charge on the cube is 6 μC = 6 × 10⁻⁶ C.
The cube has 6 faces, so the total surface area of the cube is:Total surface area = 6 × 0.0025 m² = 0.015 m²
Now, calculating the surface charge density:σ = (6 × 10⁻⁶ C) / 0.015 m² = 0.4 × 10⁻³ C/m²
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) 0.4 × 10⁻³ C/m².
2023
Q1: If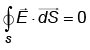 over a surface, then [NEET 2023]
over a surface, then [NEET 2023] (a) The number of flux lines entering the surface must be equal to the number of flux lines leaving it
(b) The magnitude of the electric field on the surface is constant
(c) All the charges must necessarily be inside the surface
(d) The electric field inside the surface is necessarily uniform
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)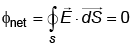
⇒ Net flux through the surface is zero.
⇒ Therefore, the number of flux lines entering the surface must be equal to the number of flux lines leaving it.
The electric potential at point P due to the dipole is (ε0 = permittivity of free space and 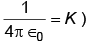
Q2: An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° with an electric field of intensity 2 × 10⁵ NC-1. It experiences a torque equal to 4 N-m. If the dipole length is 2 cm, calculate the magnitude of the charge on the dipole: [NEET 2023]
(a) 2 mC
(b) 8 mC
(c) 6 mC
(d) 4 mC
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
To calculate the charge on the dipole, we can use the formula for the torque experienced by an electric dipole in an external electric field:
Torque (τ) = pE sinθ
Where:
- τ is the torque experienced by the dipole (4 N-m),
- p is the dipole moment,
- E is the electric field intensity (2 × 10⁵ N/C),
- θ is the angle between the dipole moment and the electric field (30°).
The dipole moment p is related to the charge q and the length of the dipole l by the formula:p = q × l
Given:
- τ = 4 N-m
- E = 2 × 10⁵ N/C
- θ = 30°
- l = 2 cm = 0.02 m
Now, substitute the values into the torque formula:
4 = (q × 0.02) × (2 × 10⁵) × sin(30°)
Since sin(30°) = 1/2, the equation becomes:
4 = (q × 0.02) × (2 × 10⁵) × 1/2
Simplifying:
4 = (q × 0.02) × 10⁵
Now solve for q:
q = 4 / (0.02 × 10⁵) = 4 / 2000 = 2 × 10⁻³ C = 2 mC
Therefore, the magnitude of the charge on the dipole is 2 mC, so the correct answer is (a) 2 mC.
Q3: According to Gauss's law in electrostatics, the electric flux through a closed surface depends on: [NEET 2023]
(a) the area of the surface
(b) the quantity of charges enclosed by the surface
(c) the shape of the surface
(d) the volume enclosed by the surface
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Gauss's law states that the electric flux (Φ) through a closed surface is directly proportional to the net charge (Q) enclosed by that surface, and it is independent of the shape, size, or area of the surface. Mathematically, Gauss’s law is expressed as:
Φ = (Q_enc) / ε₀
Where:
- Φ is the electric flux through the surface,
- Q_enc is the net charge enclosed by the surface,
- ε₀ is the permittivity of free space.
Thus, the flux only depends on the enclosed charge, not on the surface's area, shape, or the volume it encloses. Therefore, the correct answer is (b).
Q4: A charge Q μC is placed at the centre of a cube. The flux coming out from any one of its faces will be (in SI units): [NEET 2023]
(a) Q / ε₀ × 10⁻⁶
(b) 2Q / 3ε₀ × 10⁻³
(c) Q / 6ε₀ × 10⁻³
(d) Q / 6ε₀ × 10⁻⁶
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
According to Gauss's Law, the total electric flux (Φ) through a closed surface is given by:
Φ = Q_enc / ε₀
Where:
- Φ is the total flux through the surface,
- Q_enc is the charge enclosed within the surface,
- ε₀ is the permittivity of free space.
For a cube, the total flux is distributed equally through all six faces, since the charge is at the centre. Therefore, the flux through one face of the cube is:
Φ_face = (Q / ε₀) / 6 = Q / 6ε₀
Since the charge is in microcoulombs (μC), we multiply by 10⁻⁶ to convert it to coulombs (C).
Thus, the flux coming out from any one of the faces is: Q / 6ε₀ × 10⁻⁶
2022
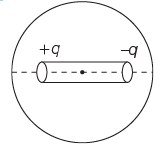
Q1: Two point charges –q and +q are placed at a distance of L, as shown in the figure 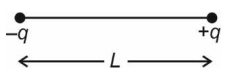
The magnitude of electric field intensity at a distance R(R >>L) varies as:
(a) 1/R3
(b) 1/R4
(c) 1/R6
(d) 1/R2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
For R >>L, arrangement is an electric dipole 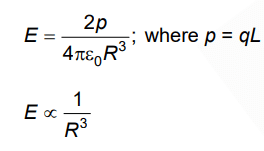
2021
Q1: Polar molecules are the molecules:
(a) acquire a dipole moment only when the magnetic field is absent.
(b) having a permanent electric dipole moment.
(c) having zero dipole moment.
(d) acquire a dipole moment only in the presence of an electric field due to displacement of charges.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Polar molecules have centers of positive and negative charges separated by some distance, so they have permanent dipole moments.
Q2: A dipole is placed in an electric field as shown. In which direction will it move? 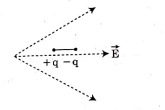
(a) towards the left as its potential energy will decrease.
(b) towards the right as its potential energy will increase.
(c) towards the left as its potential energy will increase.
(d) towards the right as its potential energy will decrease.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
E1| > |E2| as field lines are closer at charge +q, so the net force on the dipole acts towards the right side.
A system always moves to decrease its potential energy.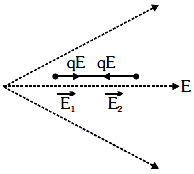
2020
Q1: A short electric dipole has a dipole moment of 16×10-9 C m. The electric potential due to the dipole at a point at a distance of 0.6 m from the center of the dipole, situated on a line making an angle of 60° with the dipole axis is: 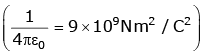
(a) 400 V
(b) Zero
(c) 50 V
(d) 200 V
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: D
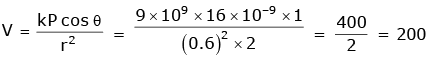
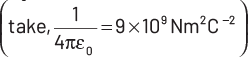
Q2: A spherical conductor of radius 10 cm has a charge of 3.2 × 10−7 C distributed uniformly. What is the magnitude of electric field at a point 15 cm from the centre of the sphere? 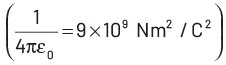
(a) 1.28 × 105 N/C
(b) 1.28 × 106 N/C
(c) 1.28 × 107 N/C
(d) 1.28 × 104 N/C
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Given, radius, r = 10 cm = 10 × 10 −2 m Charge, q = 3.2 × 10 −7 C Electric field, E = ?
Electric field at a point (x = 15 cm) from the centre of the sphere is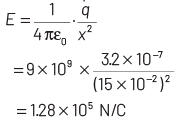
Hence, correct option is (a).
Q3: The electric field at a point on the equatorial plane at a distance r from the centre of a dipole having dipole moment r P is given by (r >> separation of two charges forming the dipole, ε 0 = permittivity of free space)
(a) 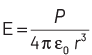
(b) 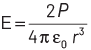
(c) 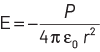
(d) 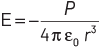
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Electric field due to electric dipole on equatorial plane at a distance r from the centre of dipole is given as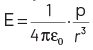
2019
Q1: A hollow metal sphere of radius R is uniformly charged. The electric field is due to the sphere at a distance r from the
center.
(a) Increases as r increases for both r < R and r > R
(b) Zero as r increases for r < R, decreases as r increases for r > R
(c) Zero as r increases for r < R, increases as r increases for r > R
(d) Decreases as r increases for both r < R and r > R
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Charge Q will be distributed over the surface of a hollow metal sphere.
(i) For r < R (inside)
By Gauss law,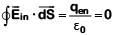
⇒ Ein = 0 (∵ qen = 0)
(ii) For r > R (outside)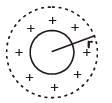
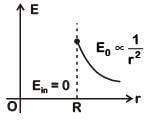

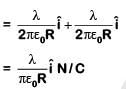
Q2: Two parallel infinite line charges with linear charge densities +λ C/m and λl C/m are placed at a distance of 2R in free space. What is the electric field mid-way between the two line charges?
(a) Zero
(b)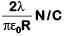
(c)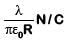
(d)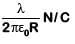
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)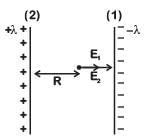

Electric field due to line charge (1)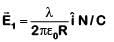
Electric field due to line charge (2)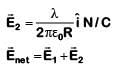
Q3: Two point charges A and B, having charges +Q and –Q respectively, are placed at a certain distance apart, and the force acting between them is F. If 25% charge of A is transferred to B, then the force between the charges becomes :
(a) F
(b) 9F/16
(c) 16F/9
(d) 4F/3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)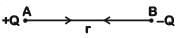
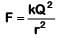
If 25% of the charge of A transferred to B then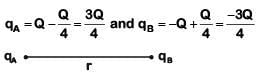
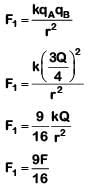
2018
Q1: An electron falls from rest through a vertical distance h in a uniform and vertically upward-directed electric field E. The direction of the electrical field is now reversed, keeping its magnitude the same. A proton is allowed to fall from rest through the same vertical distance h. The time fall of the electron, in comparison to the time fall of the proton is:
(a) Smaller
(b) 5 times greater
(c) 10 times greater
(d) equal
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)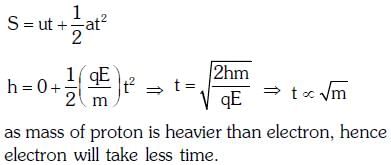
Q2: A toy car with charge q moves on a frictionless horizontal plane surface under the influence of a uniform electric field Due to the force
Due to the force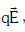 its velocity increases from 0 to 6 m/s in one-second duration. At that instant, the direction of the field is reversed. The car continues to move for two more seconds under the influence of this field. The average velocity and the average speed of the toy car between 0 to 3 seconds are respectively:
its velocity increases from 0 to 6 m/s in one-second duration. At that instant, the direction of the field is reversed. The car continues to move for two more seconds under the influence of this field. The average velocity and the average speed of the toy car between 0 to 3 seconds are respectively:
(a) 2 m/s, 4 m/s
(b) 1 m/s, 3 m/s
(c) 1 m/s, 3.5 m/s
(d) 1.5 m/s, 3 m/s
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
0 < t < 1s : velocity increases from 0 to 6 m/s
1 < t < 2s : velocity decreases from 6 to 0 m/s
but the car continues to move forward
2 < t < 3s : since field strength is same ⇒ same acceleration
∴ car's velocity increases
from 0 to –6 m/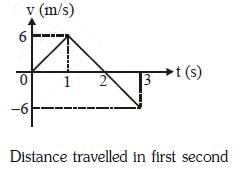
2017
Q1: Suppose the charge of a proton and an electron differ slightly. One of them is − e and the other is (e + ∆e). If the net of electrostatic force and gravitational force between two hydrogen atoms placed at a distance d (much greater than atomic size) apart is zero, then ∆e is of the order [Given mass of hydrogen, mh = 1.67 × 10−27 kg]
(a) 10−20 C
(b) 10−23 C
(c) 10 −37C
(d) 10 -47C
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Net charge on one H-atom q = − e + e + ∆e = ∆e Net electrostatic repulsive force between two H-atoms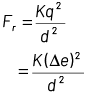 Similarly, net gravitational attractive force between two H-atoms
Similarly, net gravitational attractive force between two H-atoms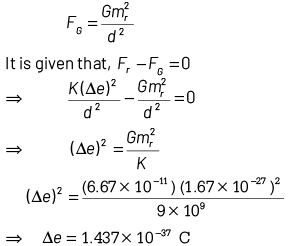
2016
Q1: Two identical charged spheres suspended from a common point by two mass-less strings of lengths ℓ are initially at a distance d (d << ℓ) apart because of their mutual repulsion. The charges begin to leak from both spheres at a constant rate. As a result, the spheres approach each other with a velocity v. Then v varies as a function of the distance x between the spheres, as:
(a) v ∝ x-1
(b) v ∝ x1/2
(c) v ∝ x
(d) v ∝ x-1/2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
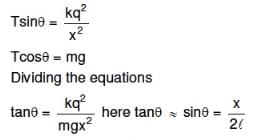
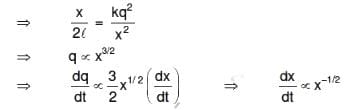
Q2: An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° with an electric field of intensity 2 × 105 N C-1. It experiences a torque equal to 4 N m. Calculate the magnitude of charge on the dipole, if the dipole length is 2 cm.
(a) 8 mC
(b) 6 mC
(c) 4 mC
(d) 2 mC
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
E = 2 × 105 N/C
l = 2 cm
τ = 4 Nm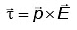 4 = pEsinθ
4 = pEsinθ
4 = p × 2 × 105 × sin30°
p = 4 × 10–5 cm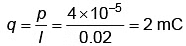
2015
Q1: The electric field in a certain region is acting radially outward and is given by E = Ar. A charge contained in a sphere of radius = a centered at the origin of the field will be given by:
(a)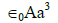
(b)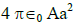
(c)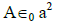
(d)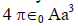
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)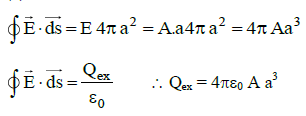
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Electric Charges & Fields - Physics Class 12
| 1. What are the basic properties of electric charges? |  |
| 2. How does Coulomb's law describe the force between two charges? |  |
| 3. What is the concept of electric field and how is it calculated? |  |
| 4. How do conductors and insulators differ in terms of electric charges? |  |
| 5. What role do electric field lines play in understanding electric fields? |  |


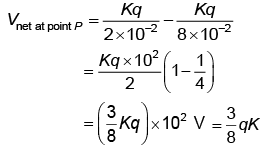 × 102 V
× 102 V