NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Haloalkanes & Haloarenes | Chemistry Class 12 PDF Download
From 2014 to 2025, a total of 26 questions on organic chemistry, specifically focusing on haloalkanes and haloarenes, appeared in the NEET/AIPMT exams. Typically, one or two questions were included each year (2014–2018, 2020, 2021, and 2025), with no questions in 2019. Notable peaks occurred in 2022 with six questions, 2023 with five questions, and 2024 with five questions. These questions covered key topics such as reaction mechanisms (SN1, SN2, elimination, Wurtz, Swarts, etc.), halide classification (benzylic, allylic, vinylic, aryl), stereochemistry (chirality, racemization, inversion), and synthesis methods, with no specific difficulty distribution provided in the data.
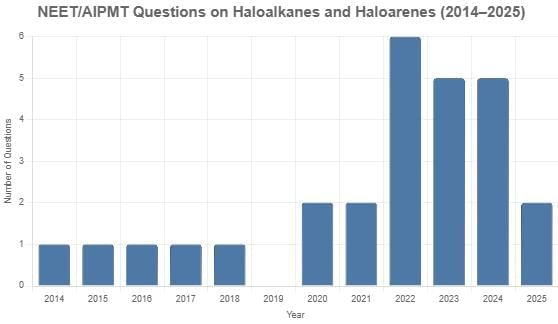
2025
Q1: Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R). (2025)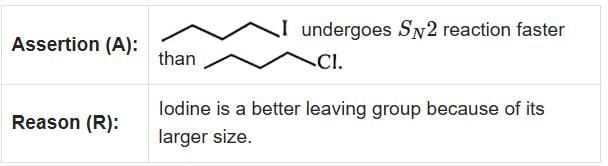 In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) is True but (R) is False
(b) (A) is False but (R) is True
(c) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(d) Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Ans: (c)
- Assertion (A): "undergoes SN2 reaction faster than ." This statement is true because iodine is a better leaving group compared to bromine due to its larger size and ability to stabilize the negative charge more effectively.
- Reason (R): "Iodine is a better leaving group because of its large size." This statement is true and correctly explains the assertion.
In SN2 reactions, the leaving group plays a crucial role in determining the reaction rate. Since iodine is a better leaving group than bromine, the substrate with iodine will undergo the SN2 reaction faster.
Therefore, the correct answer is Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Q2: How many products (including stereoisomers) are expected from monochlorination of the following compound? (2025)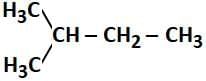 (a) 5
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 2
(d) 3
Ans: (b)
- In the given compound:
CH₃-CH₂-CH₂-CH₃ (butane)
The monochlorination can occur at different positions along the carbon chain, specifically at the 2nd and 3rd carbon atoms, where the chlorine atom can replace a hydrogen atom. When chlorine atoms are substituted at the 2nd and 3rd carbons, they create chiral centers at those positions, leading to the formation of two stereoisomers (R and S forms) for each of these sites.

- The possible products include:
- Chlorination at the 2nd carbon creates a chiral center, leading to 2 stereoisomers (R and S forms).
- Chlorination at the 3rd carbon also creates a chiral center, leading to 2 stereoisomers (R and S forms).
- Chlorination at the 1st and 4th carbons does not create chiral centers and leads to only one product each.
Thus, the total number of products formed from monochlorination, including stereoisomers, is 6: 2 from the 2nd carbon, 2 from the 3rd carbon, and 1 each from the 1st and 4th positions.
2024
Q1: The compound that will undergo SN1 reaction with the fastest rate is
(a) 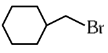
(b) 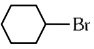
(c) 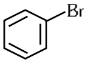
(d) 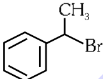 (2024)
(2024)
Ans: (d)
Reactivity towards ,SN1 depends upon stability of carbocation.
Order of stability is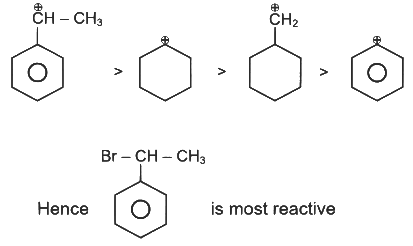
Q2: CCl₂F₂ is one of the most common haloalkanes used in industries. The reaction through which it is manufactured from tetrachloromethane is called: (NEET 2024)
(a) Finkelstein reaction
(b) Sandmeyer's reaction
(c) Swarts reaction
(d) Wurtz-Fittig reaction
Ans: (c)
The Swarts reaction is a reaction used to prepare haloalkanes by halogen exchange, often involving the use of fluorine. In the case of CCl₂F₂ (dichlorodifluoromethane), it is typically manufactured from tetrachloromethane (CCl₄) by replacing chlorine atoms with fluorine atoms using a fluorine source in the presence of a catalyst.
- Finkelstein reaction involves halide exchange with NaI in acetone.
- Sandmeyer's reaction is used to synthesize aryl halides from arylamines.
- Wurtz-Fittig reaction involves the formation of biaryl compounds using alkyl or aryl halides.
Thus, the correct reaction is Swarts reaction, where halogen exchange occurs, especially for the conversion of CCl₄ to CCl₂F₂.
Q3: Which of the following is the most preferred method for preparing pure alkyl chlorides from alcohols? (NEET 2024)
(a) R–OH + HCl 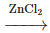 R–Cl + H₂O
R–Cl + H₂O
(b) R–OH + PCl₅ → R–Cl + POCl₃ + HCl
(c) R–OH + SOCl₂ → R–Cl + SO₂ + HCl
(d) R–OH + PCl₃ → R–Cl + H₃PO₃
Ans: (c)
The reaction between alcohols and thionyl chloride (SOCl₂) is the most preferred method for preparing pure alkyl chlorides. This method is preferred because it produces a high yield of the desired alkyl chloride and the by-products, SO₂ and HCl, are gases that can be easily removed.
- Option (a) involves direct reaction with HCl, which is less efficient and produces water as a by-product, making it less desirable.
- Option (b) with PCl₅ is also effective but can be more aggressive and may result in side reactions.
- Option (d) with PCl₃ produces phosphoric acid (H₃PO₃), which is less efficient compared to SOCl₂.
Thus, (c) is the correct and most efficient method.
Q4: The major product C in the below-mentioned reaction is: (NEET 2024)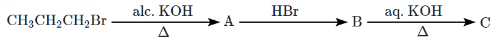 (a) Propan-1-ol
(a) Propan-1-ol
(b) Propan-2-ol
(c) Propane
(d) Propyne
Ans: (b)
- Alcoholic KOH: This is used for elimination reactions, specifically for the dehydrohalogenation of CH₃CH₂CH₂Br (1-bromopropane), resulting in the formation of propene (C₃H₆).
- HBr: The next step adds HBr to propene, which undergoes an electrophilic addition to form 2-bromopropane (B).
- Aqueous KOH: Finally, aqueous KOH promotes substitution, replacing the Br in 2-bromopropane with OH, leading to the formation of propan-2-ol (2-propanol).
Thus, the final product C is Propan-2-ol.
Q5: The following reaction method 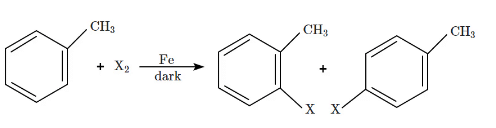 is not suitable for the preparation of the corresponding haloarene products, due to the high reactivity of halogen, when X is:
is not suitable for the preparation of the corresponding haloarene products, due to the high reactivity of halogen, when X is:
(a) F
(b) I
(c) Cl
(d) Br (NEET 2024)
Ans: (a)
The reaction shown is a halogenation of a methylbenzene (toluene), where X₂ (a halogen) reacts in the presence of Fe (iron) to form a haloarene.
- When X = F (fluorine), it is too reactive for this type of reaction. Fluorine is highly reactive, and it can cause unwanted side reactions, making it unsuitable for this halogenation method.
- For I (Iodine), Cl (Chlorine), and Br (Bromine), the halogenation proceeds more smoothly due to the relatively lower reactivity of these halogens in comparison to fluorine.
Therefore, fluorine (F) is the halogen that makes this reaction unsuitable due to its high reactivity.
Thus, the correct answer is (a) F.
2023
Q1: The given compound is an example of ______. (NEET 2023)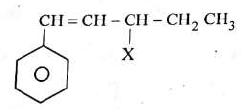
(a) Benzylic halide
(b) Aryl halide
(c) Allylic halide
(d) Vinylic halide
Ans: (a)
The compound features a halogen (X) attached to a carbon atom that is directly adjacent to a benzene ring (C₆H₅), specifically on the CH₂ group of the side chain (CH=CH-CH₂-X). This position is known as the benzylic position.
Benzylic halide: A halide where the halogen is bonded to a carbon next to a benzene ring.
Aryl halide: The halogen would be directly attached to the benzene ring, which is not the case here.
Allylic halide: The halogen would be attached to a carbon adjacent to a carbon-carbon double bond, but here the double bond (CH=CH) is not directly involved in the halogen attachment in the context of allylic classification; the benzylic position takes precedence due to the benzene ring.
Vinylic halide: The halogen would be attached to a carbon of a double bond, which does not apply.
Thus, the correct classification is benzylic halide.
Q2: The following compound would be classified as: (NEET 2023)
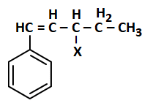
(a) Vinylic halide
(b) Benzylic halide
(c) Aryl halide
(d) Allylic halide
Ans: (a)
The compound has a halogen (X) attached directly to one of the carbons of a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C), specifically on the CH group within the CH=C(CH₃)₂ structure adjacent to the benzene ring.
Vinylic halide: A halide where the halogen is bonded to a carbon atom of a double bond.
Benzylic halide: The halogen would be attached to a carbon adjacent to the benzene ring, which is not the case here as the halogen is on the double-bonded carbon.
Aryl halide: The halogen would be directly attached to the benzene ring, which does not apply.
Allylic halide: The halogen would be attached to a carbon adjacent to a double bond but not on the double bond itself, which is not the configuration here.
Q3: The correct order for the rate of α , β-dehydrohalogenation for the following compounds is: (NEET 2023)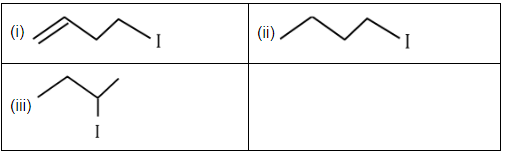 (a) (i) < (ii) < (iii)
(a) (i) < (ii) < (iii)
(b) (ii) < (i) < (iii)
(c) (iii) < (ii) < (i)
(d) (ii) < (iii) < (i)
Ans: (d)
The rate of α, β-dehydrohalogenation generally depends on the stability of the resulting product and the ease of the elimination process. Here's the reasoning based on the given compounds:
- Compound (i): This compound has a double bond that is directly adjacent to the halogen (C-H and C-I). This structure allows for the most stable product and makes the elimination process most favorable. Hence, this will undergo dehydrohalogenation fastest.
- Compound (ii): This compound has a branched structure, which may create more steric hindrance than compound (i), but it still allows for elimination to occur relatively easily. The product formed will be stable, but not as stable as in compound (i).
- Compound (iii): This compound has a more stable and less hindered α, β-positions for elimination. However, it involves a slightly less favorable elimination due to the position of the halogen.
Thus, the order of dehydrohalogenation rates is: (ii) < (iii) < (i).
Hence, the correct option is D. (ii) < (iii) < (i).
Q4: A reaction among the following can generate isonitriles as a major product. (NEET 2023)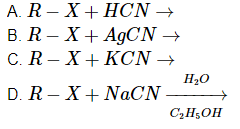
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) (D) only
(b) (C) and (D) only
(c) (B) only
(d) (A) and (B) only
Ans: (c)
- Reaction A: R–X + HCN →
This reaction will produce a nitrile (R–CN), not an isonitrile (R–NC). So, this does not lead to the formation of isonitriles. - Reaction B: R–X + AgCN →
This is the correct reaction. When R–X reacts with AgCN, an isonitrile (R–NC) is formed, as AgCN (silver cyanide) is known to produce isonitriles through this nucleophilic substitution. Thus, Reaction B forms isonitriles. - Reaction C: R–X + KCN →
This reaction produces a nitrile (R–CN), not an isonitrile. So, this does not form isonitriles either. - Reaction D:
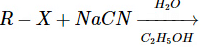
This reaction typically leads to the formation of nitriles, not isonitriles.
Therefore, only Reaction B produces isonitriles as a major product.
Thus, the correct answer is Option c (B) only.
Q5: Identify 'X' in the following reaction. (NEET 2023)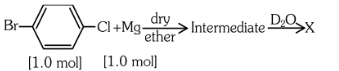 (a)
(a) 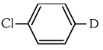
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans: (a)
The reaction shown is a Grignard reaction. In the reaction, Cl–C6H4–Br (a chlorobromobenzene) reacts with Mg in dry ether to form a Grignard reagent, which is an intermediate. The Grignard reagent reacts with D₂O (heavy water), resulting in the substitution of the Br atom by a deuterium (D) atom in the final product. This forms D–C6H4–Cl, where D is the deuterium atom.
Thus, X is D–C6H4–Cl, which corresponds to option (a).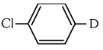
2022
Q1: Which of the following is suitable to synthesize chlorobenzene? (NEET 2022)
(a) 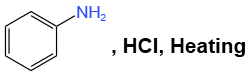
(b) Benzene, Cl2, anhydrous FeCl3
(c) Phenol, NaNO2, HCl, CuCl
(d) 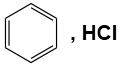
Ans: (b)
To synthesize chlorobenzene (C₆H₅Cl), we typically use a chlorination reaction where benzene reacts with chlorine (Cl₂) in the presence of a catalyst like anhydrous FeCl₃ (ferric chloride).
Here’s how the reaction works:
- Benzene (C₆H₆) reacts with chlorine (Cl₂) in the presence of anhydrous FeCl₃ (a Lewis acid catalyst).
- The catalyst FeCl₃ helps in generating a highly reactive chlorine radical or chlorine cation (Cl⁺).
- This reactive species then reacts with the benzene ring, substituting one of the hydrogen atoms on the ring with a chlorine atom, forming chlorobenzene (C₆H₅Cl).
The reaction is:
C₆H₆ + Cl₂ → C₆H₅Cl + HCl
- Option (a) refers to aniline (C₆H₅NH₂), and although it can undergo chlorination, it’s not the most direct method for synthesizing chlorobenzene.
- Option (c) involves phenol, which undergoes nitration followed by chlorination but is not as direct as option (b).
- Option (d) does not provide a suitable chlorination method for benzene to produce chlorobenzene.
Thus, Option (b) is the correct and most suitable method for synthesizing chlorobenzene.
Q2: Identify the statement that is incorrect regarding chirality: (NEET 2022)
(a) A racemic mixture shows zero optical rotation
(b) SN1 reaction yields a 1:1 mixture of both enantiomers
(c) The product obtained by SN2 reaction of haloalkane having chirality at the reactive site shows the inversion of configuration
(d) Enantiomers are superimposable mirror images on each other
Ans: (d)
(a) A racemic mixture shows zero optical rotation because it contains equal amounts of both enantiomers, which rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions, canceling each other out.
(b) An SN1 reaction typically yields a 1:1 mixture of both enantiomers because the intermediate carbocation can be attacked by the nucleophile from either side, leading to both possible configurations.
(c) In an SN2 reaction, the nucleophile attacks the carbon opposite to the leaving group, causing inversion of configuration at the reactive site.
(d) This is incorrect. Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other, meaning they cannot be placed on top of one another and align perfectly.
Q3: The correct reaction among the following is: (NEET 2022)
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 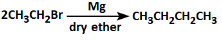
(d) 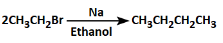
Ans: (b)
Option Brepresents the Wurtz Fitting Reaction, a well-known organic reaction. This reaction involves the coupling of two molecules of alkyl halide in the presence of sodium metal (Na) and dry ether.
Here’s the process:
C6H5-CH2Br (Benzyl bromide) is treated with sodium metal (Na) in dry ether.
This reaction leads to the formation of stilbene (C6H5-CH=CH-C6H5), which is a disubstituted alkene formed by the coupling of two benzyl radicals (C6H5-CH2) via the metal-mediated mechanism.
The metal (Na) helps in creating the free radicals of the alkyl group, leading to the formation of the C-C bond between two benzyl groups, thus forming stilbene (trans- or cis-).
This reaction is an example of the Wurtz Coupling reaction where two alkyl halides (like benzyl bromide) are coupled to form a more complex product, in this case, stilbene.
Thus, Option B correctly represents the reaction mechanism and product formation.
Why the other options are incorrect:
- Option A: This reaction appears to show a halogen exchange (i.e., no net new bonds are formed), which is incorrect for this context.
- Option C: This reaction suggests the formation of an alkyl magnesium halide (Grignard reagent), but it is not part of the Wurtz reaction and doesn't produce the correct product.
- Option D: This is an elimination reaction where the halide reacts with sodium in ethanol, leading to an alkene, but it is not the Wurtz coupling reaction.
Thus, Option B is the correct reaction for the given conditions.
Q4: The product formed in the following reaction sequence is: (NEET 2022)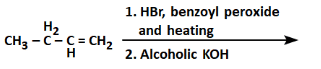 (a)
(a) 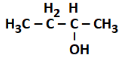
(b) CH3−CH=CH−CH3
(c) CH3−CH2−CH=CH2
(d) CH3−CH2−CH2−CH2−OH
Ans: (c)
The given reaction sequence involves two steps:
First step:
- The reaction involves the use of HBr (Hydrobromic acid) with benzoyl peroxide (a radical initiator). This is an example of free radical addition to an alkene.
- In the presence of benzoyl peroxide, the HBr adds to the alkeneCH₃-CH₂-CH=CH₂ in a free radical mechanism, leading to the formation of bromoalkane as a product.
In this case, the reaction would add the H from HBr to the carbon with fewer hydrogens (the secondary carbon in the alkene), and the Br will add to the other carbon, resulting in CH₃-CH₂-CH(Br)-CH₃ (4-bromobutene).
Second step:
- The next reaction is carried out with alcoholic KOH, which induces an elimination reaction (E2 mechanism) on the bromoalkane formed in the first step.
- Alcoholic KOH induces a dehydrohalogenation, removing HBr from the molecule. The bromine is eliminated along with a hydrogen atom from the adjacent carbon, leading to the formation of an alkene.
The elimination will result in the formation of CH₃-CH₂-CH=CH₂, which is but-2-ene, a symmetrical alkene.
Q5: Predict the order of reactivity of the following four isomers towards an SN2 reaction: (NEET 2022)
(I) CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂Cl
(II) CH₃CH₂CH(Cl)CH₃
(III) (CH₃)₂CHCH₂Cl
(IV) (CH₃)₃CCl
(a) (IV) > (III) > (II) > (I)
(b) (I) > (II) > (III) > (IV)
(c) (I) > (III) > (II) > (IV)
(d) (IV) > (II) > (III) > (I)
Ans: (c)
In an SN2 reaction, the reactivity depends on the steric hindrance at the carbon attached to the leaving group. The more hindered the carbon, the slower the reaction.
- (I) CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂Cl: The carbon attached to the chlorine is a primary carbon, with minimal steric hindrance, making it the most reactive.
- (III) (CH₃)₂CHCH₂Cl: This is a secondary carbon, with more steric hindrance than the primary carbon, but still less than a tertiary carbon.
- (II) CH₃CH₂CH(Cl)CH₃: This is a secondary carbon with slightly more steric hindrance compared to (III), so it reacts slower.
- (IV) (CH₃)₃CCl: This is a tertiary carbon, which is highly hindered, so it is the least reactive in an SN2 reaction.
Thus, the correct order is (I) > (III) > (II) > (IV).
Q6: Which of the following methods is incorrect for the synthesis of alkenes? (NEET 2022)
(a) Treatment of alkynes with Na in liquid NH₃
(b) Heating alkyl halides with alcoholic KOH
(c) Treating alkyl halides in aqueous KOH solution
(d) Treating vicinal dihalides with Zn metal
Ans: (c)
- (a) Treatment of alkynes with Na in liquid NH₃: This is a correct method to synthesize alkenes. It is known as the reduction of alkynes to alkenes using sodium (Na) in liquid ammonia (NH₃). This reaction is a Birch reduction, which converts alkynes to trans-alkenes (anti-addition).
- (b) Heating alkyl halides with alcoholic KOH: This is a correct method to synthesize alkenes. When alkyl halides react with alcoholic KOH, they undergo elimination (E2 mechanism), resulting in the formation of alkenes. This is a typical reaction used for dehydrohalogenation.
- (c) Treating alkyl halides in aqueous KOH solution: This is an incorrect method for synthesizing alkenes. In aqueous KOH, alkyl halides typically undergo substitution reactions rather than elimination, resulting in the formation of alcohols instead of alkenes.
- (d) Treating vicinal dihalides with Zn metal: This is a correct method to synthesize alkenes. When vicinal dihalides (compounds with two halogens on adjacent carbon atoms) are treated with zinc (Zn) metal, they undergo reduction, leading to the formation of alkenes via elimination (Wurtz-type reaction).
Thus, (c) is incorrect because aqueous KOH leads to substitution reactions, not elimination.
2021
Q1: The major product of the following chemical reaction is : (NEET 2021)
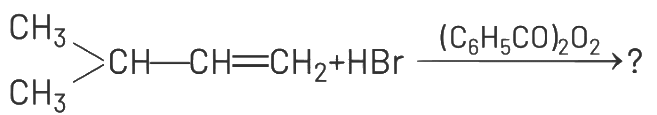 (a)
(a) 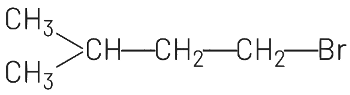
(b) 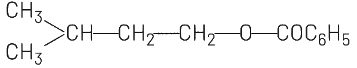
(c) 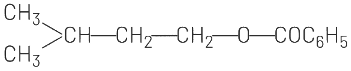
(d) 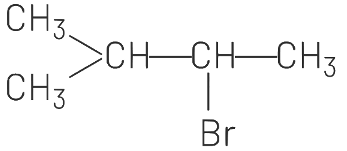
Ans: (d)
The reaction involves the addition of HBr to 2-methyl-2-butene (CH₃-CH=C(CH₃)-CH₃) in the presence of (C₆H₅CO₂)₂, which suggests a radical mechanism due to the peroxide effect. In the presence of peroxides, the addition of HBr follows the anti-Markovnikov rule, where the hydrogen atom adds to the carbon with fewer hydrogen atoms, and the bromine atom adds to the carbon with more hydrogen atoms.
The double bond in 2-methyl-2-butene is between the second and third carbon atoms.
According to the anti-Markovnikov addition, H adds to the third carbon (CH₂), and Br adds to the second carbon (CH). This results in the formation of 2-bromo-3-methylbutane, which is represented as CH₃-CH(CH₃)-CH₂Br. The other options do not align with the expected product of this reaction:
(a) CH₃-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂Br is 1-bromobutane, which is incorrect for this substrate.
(b) and (c) involve ester formation (C₆H₅COO-), which is not consistent with the HBr addition reaction.
(d) correctly represents the anti-Markovnikov product.
Q2: The major product formed in dehydrohalogenation reaction of 2-Bromo pentane is Pent-2-ene.This product formation is based on- (NEET 2021)
(a) Hofmann Rule
(b) Huckel's Rule
(c) Saytzeff's Rule
(d) Hund's Rule
Ans: (c)
Major product formed in dehydrohalogenation reaction of 2-bromopentane is pent-2-ene because according to Saytzeff's Rule, in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the preferred product is that alkene which has greater number of alkyl group(s) attached to the doubly bonded carbon atoms.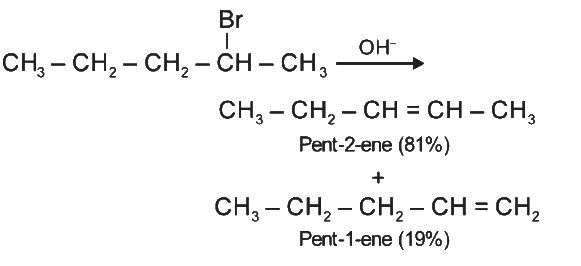
2020
Q1: Which of the following alkane cannot be made in good yield by Wurtz reaction? (NEET 2020)
(a) n-Heptane
(b) n-Butane
(c) n-Hexane
(d) 2,3-Dimethylbutane
Ans: A
Wurtz reaction is used to prepare symmetrical alkanes like
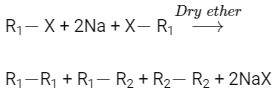
Using Wurtz reaction, n-Heptane can not be produced in good production because it is unsymmetrical alkane.
Q2: Elimination reaction of 2-Bromo-pentane to form pent-2-ene is: (NEET 2020)
(a) β-Elimination reaction
(b) Follows Zaitsev rule
(c) Dehydrohalogenation reaction
(d) Dehydration reaction
(a) (b), (c), (d)
(b) (a), (b), (d)
(c) (a), (b), (c)
(d) (a), (c), (d)
Ans: (c)
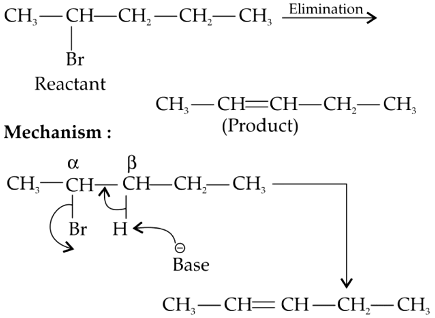
Since β-hydrogen is abstracted it is β-elimination.
Since more substituted alkene is formed (stable and major product), it follows Zaitsev's rule or Saytzev's rule.
Since H and Br are removed, it is dehydrohalogenation.
2018
Q1. The compound C7H8 undergoes the following reactions : (NEET 2018)
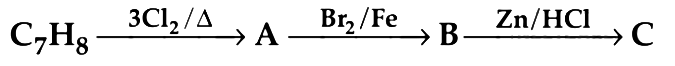
The product ‘C’ is
(a) m–bromotoluene
(b) o–bromotoluene
(c) 3–bromo–2,4,6–trichlorotoluene
(d) p–bromotoluene
Ans: (d)
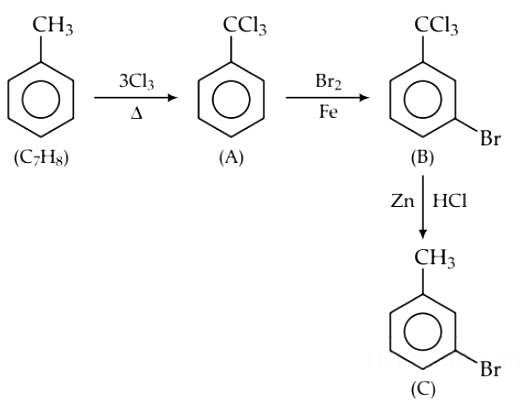
2017
Q1. Identify A and predict the type of reaction (NEET 2017)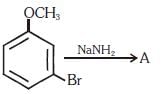
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Ans: (d)
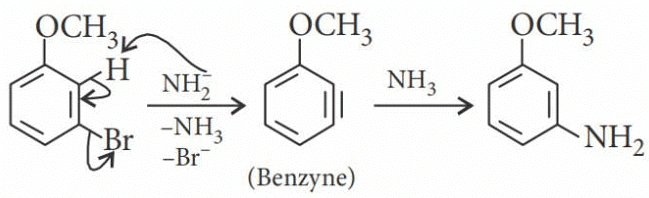
m-Bromoanisole gives only the respective meta substituted aniline. This is a substitution reaction which goes by an elimination-addition pathway.
2016
Q1: Consider the reaction, (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
CH3CH2CH2Br + NaCN
This reaction will be the fastest in
(a) ethanol
(b) methanol
(c) N, N' -dimethylformamide (DMF)
(d) Water
Ans: (c)
The reaction,
CH3CH2CH2Br + NaCN
follows SN2 mechanism which is favoured by polar aprotic solvent i.e., N, N'–dimethylformamide (DMF).
2015
Q1: In an SN1 reaction on chiral centers, there is (NEET / AIPMT 2015
(a) inversion more than retention leading to partial racemisation
(b) 100% retention
(c) 100% inversion
(d) 100% racemisation
Ans: (a)
- In case of optically active alkyl halides, SN1 reaction is accompanied by racemisation. The carbocation formed in the slow step being sp2 hybridised is planar and attack of nucleophile may take place from either side resulting in a mixture of products, one having the same configuration and other having inverted configuration.
- The isomer corresponding to inversion is present in slight excess because SN1 also depends upon the degree of shielding of the front side of the reacting carbon.
2014
Q1: Which of the following compounds will undergo racemisation when solution of KOH hydrolyses? (AIPMT 2014)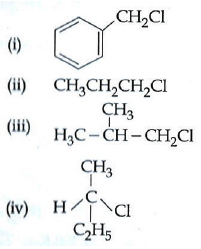
(a) (iii) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: (c)
Out of the given four compounds only (iv) compound is chiral and hence only this compound will undergo racemisation.
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Haloalkanes & Haloarenes - Chemistry Class 12
| 1. What are haloalkanes and haloarenes? |  |
| 2. What are some common uses of haloalkanes and haloarenes? |  |
| 3. How do haloalkanes and haloarenes differ in terms of reactivity? |  |
| 4. What are some environmental concerns associated with haloalkanes and haloarenes? |  |
| 5. How are haloalkanes and haloarenes named according to IUPAC nomenclature? |  |

















