Class 10 Social Science Previous Year Questions - Resources and Development
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: Explain any two problems of the 'global ecology' arising due to indiscriminate use of resources. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Two problems of global ecology arising due to indiscriminate use of resources are:
- Global warming – Excessive exploitation of resources has increased greenhouse gases, leading to rise in global temperatures.
- Ozone layer depletion – Indiscriminate use of resources has resulted in emissions that damage the ozone layer, affecting ecological balance.
Q2: "The development goals of different categories of people may differ." Evaluate the statement. (5 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The development goals of different categories of people may differ because:
- Different needs: A rich farmer may want better irrigation, electricity and fair prices for crops, while a landless labourer may need more days of work and higher wages.
- Different occupations: An industrialist may aim for more profits and cheap raw materials, but factory workers may want better working conditions and higher income.
- Economic status: Rich people may focus on expanding their wealth, while poor people may aim to fulfil basic needs like food, clothing, shelter and education.
- Living conditions: Urban people may demand better transport, education and health facilities, while rural people may focus on land, water and agricultural development.
- Social position: Different social groups also set different goals depending on their culture, traditions and opportunities available to them.
Thus, development has different meanings for different people according to their situation.
Q3: Why is planning necessary for judicious use of resources? Explain. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Planning is necessary for judicious use of resources because resources are unevenly distributed in our country, some regions have plenty while others face shortages. Proper planning helps in balanced development, avoids over-exploitation, and ensures resources are used carefully to meet present as well as future needs.
Or
“Planning is the widely accepted strategy for judicious use of resources.” Explain the statement. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Planning is the widely accepted strategy for judicious use of resources because it helps in proper utilisation of resources according to the needs of different regions. Some areas are rich in certain resources while others face shortages, so planning ensures balanced development, prevents wastage and over-exploitation, and supports sustainable growth.
Q4. Describe any two measures to solve the problem of land degradation. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Two measures to solve the problem of land degradation are:
- Afforestation and proper management of grazing can help to restore the land and check further damage.
- Control of mining activities and proper disposal of industrial effluents after treatment can reduce land and water pollution.
Q5: Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (a) and Reason (R). Read both the statements and choose the correct option:
Assertion (a): India has enormous possibilities of production of solar energy.
Reason (R): Most of the land area of India falls under the cold zone. (1 Mark)
(a) Both (a) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (a).
(b) Both (a) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (a).
(c) (a) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (a) is false, but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) (a) is true, but (R) is false.
- India has great potential for solar energy because it receives abundant sunlight, but most of its land area does not fall under the cold zone.
Q6: Describe any two features of 'arid soils'. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Two features of arid soilsare:
- They are sandy in texture, red to brown in colour, and generally saline in nature.
- They lack humus and moisture due to dry climate and high temperature, but with proper irrigation they can be made cultivable.
Q7: Describe any two features of 'forest soils'. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Two features of forest soils are:
- They are found in hilly and mountainous areas and their texture varies – loamy and silty in valleys, coarse grained on upper slopes.
- In snow-covered areas of Himalayas, these soils are acidic with low humus, but in river terraces and alluvial fans they are fertile.
Q8: A researcher is examining a soil type which is formed by the weathering of volcanic rock and is rich in minerals. Which one of the following soils is it? (1 Mark)
(a) Laterite soil
(b) Alluvial soil
(c) Black soil
(d) Desert soil
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Black soil
Black soil (also called regur soil) is formed from volcanic rock (basalt), is rich in minerals, and is ideal for cotton cultivation.
Q9: “An equitable distribution of resources has become essential for a sustained quality of human life.” Explain the statement. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: An equitable distribution of resources is essential because if resources are used only by a few individuals or countries, it leads to division of society into rich and poor and causes over-exploitation. Fair sharing of resources ensures a sustained quality of life for all and maintains global peace and environmental balance.
Q10: Describe two main characteristics of 'Alluvial Soil'. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Two main characteristics of alluvial soil are:
- It is very fertile, containing adequate amounts of potash, phosphoric acid and lime, suitable for crops like sugarcane, paddy and wheat.
- It consists of sand, silt and clay in different proportions, and is found mainly in the northern plains and river deltas.
Q11: Explain the main features of alluvial soil. (5 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The main features of alluvial soilare:
- Widespread distribution: Alluvial soil is the most important and widely spread soil in India. It is mainly found in the northern plains, Rajasthan and Gujarat, and in the deltas of rivers like the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri.
- Composition: It is made up of sand, silt and clay in varying proportions. Coarse particles are found near river valleys, while fine particles are found in the plains.
- Classification by age: It is divided into Bangar (old alluvial) and Khadar (new alluvial). Bangar has more kankar nodules and is less fertile, while Khadar is finer and more fertile.
- Fertility: It is very fertile and rich in potash, phosphoric acid and lime, which makes it suitable for crops like sugarcane, paddy, wheat and pulses.
- Cultivation and population: Due to its high fertility, areas with alluvial soils are densely populated and intensively cultivated.
Thus, alluvial soil is the backbone of Indian agriculture.
Q12: Describe any two characteristics of laterite soil. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Two characteristics of laterite soilare:
- It develops in areas of tropical and subtropical climate with heavy rainfall and alternate wet and dry seasons, leading to intense leaching.
- It is generally acidic, nutrient-poor and prone to erosion, but with proper conservation it is suitable for crops like tea, coffee and cashew nut.
Q13: Explain the various stages of resource planning and its need in India. (5 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Need of Resource Planning in India:
Resources in India are not evenly distributed. Some states like Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh are rich in minerals, while Rajasthan has solar and wind energy but lacks water. Arunachal Pradesh has water resources but poor infrastructure. Hence, resource planning is needed to ensure balanced development and sustainable use of resources.
Stages of Resource Planning:
- Identification and inventory of resources – This includes surveying, mapping, and qualitative and quantitative estimation of resources in different regions.
- Evolving a planning structure – Developing a framework with appropriate technology, skill and institutions to implement resource development plans.
- Matching with national plans – The resource development plans must be linked with the overall national development goals for effective use.
Thus, resource planning in India is essential to avoid resource misuse, achieve balanced growth, and secure resources for future generations.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: Choose the correctly matched pair. (CBSE 2024)
(a) Ferrous - Natural Gas
(b) Non-Ferrous - Nickel
(c) Non-Metallic Minerals - Limestone
(d) Energy Minerals – Cobalt
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Non-Ferrous - Nickel
(a) Ferrous - Natural Gas: This is incorrect. Ferrous refers to metals that contain iron, such as iron and steel. Natural gas is a fossil fuel, not a metal, so this pair is not correctly matched.
(b) Non-Ferrous - Nickel: This is correct. Non-ferrous metals are those that do not contain iron. Nickel is a non-ferrous metal, often used in making alloys like stainless steel, so this is the correctly matched pair.
(c) Non-Metallic Minerals - Limestone: This is incorrect. Non-metallic minerals are minerals that do not have metallic properties. Limestone is indeed a non-metallic mineral, but it's typically classified under building materials rather than a generic category like non-metallic minerals. However, it's not the best answer in this list.
(d) Energy Minerals – Cobalt: This is incorrect. Energy minerals are minerals used for energy production, like coal, oil, and natural gas. Cobalt is a metal used in alloys and electronics, not primarily as an energy mineral.
So, the correct pair is (b) Non-Ferrous - Nickel.
Q2: Suggest any two ways to solve the problem of land degradation. (CBSE 2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: There are two ways to address the issue of land degradation:
(1) Planting more trees and managing grazing activity can both help to some extent.
(2) In arid regions, planting plant shelter belts and stabilising sand dunes with thorny bushes are two of the most effective techniques.
(3) In industrial and suburban areas, wasteland management, control of mining activity, and control of industrial effluent disposal and discharge will all help to lessen land degradation.
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q3: Match the column - 1 with column - 2 and choose the correct option: (2023)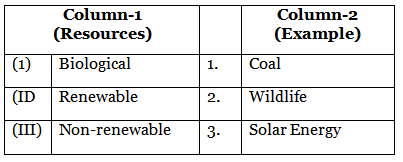 (a) I,1 - II,3 - III,2
(a) I,1 - II,3 - III,2(b) I,3 - II,2 - III,1
(c) I,2 - II,3 - III,1
(d) I,1 - II,2 - III,3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
(I) Biological matches with 2. Wildlife because wildlife includes living organisms, which are biological resources.
(II) Renewable matches with 3. Solar Energy since solar energy can be replenished naturally and is sustainable.
(III) Non-renewable matches with 1. Coal because coal is a fossil fuel that cannot be replaced once used.
Q4: Which of the following is correctly matched? (2023)
(a) Alluvial Soil - Gangetic plain
(b) Black Soil - Himalayan Region
(c) Arid Soil - Western Ghats
(d) Laterite Soil - Desert Area
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Alluvial soil is formed by the deposition of fine particles such as silt, clay, and sand carried by rivers and streams. The Gangetic plain, which includes regions around the Ganges and its tributaries, is known for having extensive deposits of alluvial soil. This type of soil is fertile and supports agriculture, making it suitable for the cultivation of various crops.
On the other hand, the other options do not represent accurate soil-geography matches:
(b) Black Soil is commonly found in the Deccan Plateau, not the Himalayan Region.
(c) Arid Soil is typically found in arid and semi-arid regions, not in the Western Ghats.
(d) Laterite Soil is often found in tropical regions with high rainfall and temperature, such as parts of the Western Ghats, but it is not associated with desert areas.
Therefore, the correct answer is (a) Alluvial Soil - Gangetic plain.
Q5: Which of the following is correctly matched? (CBSE 2023)
(a) Alluvial Soil - Consists of sand and silt
(b) Black Soil - Salt content is high
(c) Arid Soil - Diffusion of iron in crystalline
(d) Laterite Soil - Made up of Lava flows
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
(a) Alluvial Soil consists of sand, silt, and clay, as it is formed by the deposition of sediments carried by rivers and streams. This type of soil is typically fertile and well-drained, making it suitable for agriculture.
(b) Black Soil is characterised by its high clay content, not high salt content. It is known for its moisture retention and nutrient richness, including calcium carbonate and potash.
(c) Arid Soil is associated with arid and semi-arid regions and is characterized by low organic content and high salinity, but the diffusion of iron in crystalline is not a defining characteristic of arid soil.
(d) Laterite Soil is formed through the weathering of rocks and typically contains high amounts of iron and aluminum oxides. It is not directly made up of lava flows.
Therefore, the correct answer is (a) Alluvial Soil - Consist of sand and silt.
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q6: Which among the following is NOT a problem of resource development? (2022) [Old NCERT](a) Depletion of resources to satisfy the greed of a few individuals
(b) Accumulation of resources in a few hands
(c) Indiscriminate exploitation of resources
(d) An equitable distribution of resources
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Equitable distribution of resources is essential for effective resource development.
- It ensures that all communities benefit from available resources.
- Without equity, some regions may remain underdeveloped despite having resources.
- Fair distribution helps in reducing economic disparities.
Q7: In which one of the following states overgrazing is the main reason for land degradation? (2022)
(a) Maharashtra
(b) Punjab
(c) Haryana
(d) Uttar Pradesh
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Overgrazing is the main cause of land degradation in states like, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Gujarat
Q8: Deforestation due to mining has caused severe land degradation in which one of the following states? (2022)
(a) Odisha
(b) Tamil Nadu
(c) Kerala
(d) Gujarat
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete leaving deep scars and traces of overburdening. This is a major cause of land degradation in Odisha.
Q9: Which one of the following human activities has contributed most in land degradation? (2022)
(a) Deforestation
(b) Overgrazing
(c) Mining
(d) Over-irrigation
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Deforestation has contributed most in land degradation. It makes the soil infertile for any use therefore it causes droughts and land pollutions.
Q10: Two statements are given below as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the most appropriate option. (2022)
Assertion (A): Indian farmers should diversify their cropping pattern from cereals to high-value crops.
Reason (R): This will increase income and reduce environmental degradation simultaneously.
(a) Both A and R are correct, and R is the correct explanation of the A.
(b) Both A and R are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of the A.
(c) A is correct, but R is incorrect.
(d) A is incorrect, but R is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Indian farmers should diversify their cropping pattern from cereals to high-value crops. This will increase income and reduce environmental degradation simultaneously. Because fruits, medicinal herbs, flowers, vegetables, bio-diesel crops like jatropha and jojoba need much less irrigation than rice or sugarcane. India’s diverse climate can be harnessed to grow ranges of high-value crops.
Q11: Identify the soil which ranges from red to brown in colour and saline in nature. (2022)
(a) Red soil
(b) Laterite soil
(c) Arid soil
(d) Alluvial soil
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Arid soil is red to brown in colour and saline in nature. It is sandy in texture and lacks humus and moisture.
Q12: Which one of the following forces leads to maximum soil erosion in plains? (2022)
(a) Wind
(b) Glacier
(c) Running water
(d) Earthquake
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Running water leads to the maximum soil erosion in plains. It is of different types like gully erosion and sheet erosion.
Previous Year Questions 2021
Q13: Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow: (2021 C)Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete leaving deep scars and traces of overburdening. In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha, deforestation due to mining have caused severe land degradation. In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra, overgrazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation. In the states of Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh, over-irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to water logging leading to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil. The mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generates huge quantity of dust in the atmosphere. It retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil after it settles down on the land. In recent years, industrial effluents as waste have become a major source of land and water pollution in many parts of the country.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(i) In which one of the following states is over grazing the main reason for 'land degradation'?
(a) Gujarat
(b) Himachal Pradesh
(c) Punjab
(d) Madhya Pradesh
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Both (a) & (d)
Overgrazing is a significant cause of land degradation in several states. The states primarily affected include:
- Maharashtra
- Madhya Pradesh
- Rajasthan
- Gujarat
These areas experience severe land degradation due to excessive grazing by livestock.
(ii) Which one of the following is a major source of water pollution?
(a) Rainfall
(b) Landslide
(c) Over-irrigation
(d) Industrial waste
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Industrial waste
Industrial waste is a significant contributor to water pollution. It introduces harmful substances into water bodies through improper disposal.
(iii) Why is 'over-irrigation' responsible for land degradation?
(a) Increases the salinity of soil
(b) Decreases the water absorption capacity of soil
(c) Increases landslides
(d) Decreases the fertility of soil
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Decreases the fertility of soil
Over-irrigation leads to land degradation by (d) decreasing the fertility of soil through leaching away essential nutrients.
(iv) Which one of the following is the main reason of 'land degradation' in Jharkhand?
(a) Overgrazing
(b) Over-irrigation
(c) Industrial waste
(d) Mining
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Mining
The main reason for 'land degradation' in Jharkhand is (d) Mining.
Q14: Which among the following is not a problem of resource development ?
(a) Depletion of resources for satisfying the greed of few individuals
(b) Accumulation of resources in few hands
(c) Indiscriminate exploitation of resources
(d) An equitable distribution of resources (CBSE Term-1 2021) [Old NCERT]
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The problems of resource development include:
(a) Depletion of resources for satisfying the greed of a few individuals: This leads to unsustainable resource use.
(b) Accumulation of resources in a few hands: This creates inequality and limits access for the broader population.
(c) Indiscriminate exploitation of resources: This results in environmental degradation and resource depletion.
However, (d) An equitable distribution of resources is not a problem; rather, it is a solution or goal for fair and sustainable resource development. Equitable distribution ensures that resources are accessible to all and are used responsibly.
Thus, the correct answer is (d) An equitable distribution of resources.
Previous Year Questions 2020
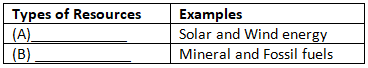
Q15: Fill in the blanks of the following table with suitable information: (2020)Resource on the basis of exhaustibility
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) - Renewable (B) - Non-renewable
Q16: Fill in the blanks. (Delhi 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) - Fishery, Water (B) - Water, Fossil fuels
Q17: Fill in the blanks of the following table with suitable information. (2020)
Type of resources: On the basis of ownership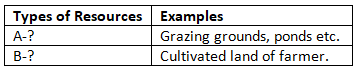
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) - Community owned resources (B) - Individual resource
Q18: Describe the importance of judicious use of resources. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The importance of judicious use of resources includes:
- Sustainability: It helps maintain the availability of resources for future generations.
- Limited Availability: Resources are finite and must be used wisely.
- Development: Resources are essential for any developmental activities.
Q19: Describe the different steps of 'resource planning". (2020,2017,2014)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The different steps of resource planning are:
(i) Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country.
(ii) Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set-up.
(iii) Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans.
Q20: “Resource Planning is essential for the sustainable existence of all forms of life.” Support the statement with examples. (2020 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Resource planning is crucial for the sustainable existence of all forms of life. It plays a key role in managing resources effectively.
Here are some important points:
- Identification of Resources: Resource planning helps to identify various resources available in different regions.
- Reducing Waste: It aids in minimising the wastage of resources, ensuring they are used efficiently.
- Equal Distribution: It promotes fair distribution of resources, especially in areas facing shortages.
Q21: How much percentage of forest area is desired in a geographical area to maintain ecological balance as outlined in the National Forest Policy? (2020 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 33%
According to India's National Forest Policy, it is desirable to have 33% of the geographical area under forest cover to maintain ecological balance. This target aims to ensure environmental stability, preserve biodiversity, and support sustainable development.
Q22: Explain with examples, the ways to solve the problem of land degradation in the Himalayan region. (2020 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Ways to solve the problem of land degradation in Himalayan region.
(i) Afforestation is the solution for any kind of land degradation.
(ii) Proper management of grazing. It is the one of the main reasons of land degradation in hilly areas.
(iii) Adopting terrace farming in hilly areas, as it increase water retention capacity of soil.
Q23: Read the following features of a soil and name the related soil: (2020)
(a) Develops in high rainfall area
(b) Intense leaching process takes place.
(c) Humus content is low.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Laterite soil
Develops in high rainfall areas: Laterite soil forms in regions with heavy rainfall and high temperatures, which accelerate the process of leaching.
Intense leaching process takes place: Due to heavy rainfall, soluble minerals are washed away, leaving the soil poor in essential nutrients.
Humus content is low: The leaching process also reduces the organic content in the soil, resulting in low humus.
These characteristics are typical of Laterite soil, which is commonly found in parts of India with tropical monsoon climates, such as Kerala, Karnataka, and parts of Maharashtra.
Q24: Give one example of the main commercial crop cultivable in laterite soil. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Tea, coffee, and cashew nut are the main commercial crops that thrive in laterite soil.
- Tea is widely cultivated in regions with suitable rainfall.
- Coffee grows well in the hilly areas of Karnataka and Kerala.
- Cashew nut is primarily found in Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh.
Q25: Why is the issue of sustainability important for development? Explain. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Sustainable economic development means development that is viable keeping the requirements of both the present and future generations in mind.
(1) It is a development that doesn’t compromise with the environment, provides equal opportunities to grow, utilise resources for both the present and upcoming generations.
(2) The issue of sustainability is important for development because without the same, man will use resources without care, destroying the environment, preventing all chances of survival and development in future.
(3) If not for sustainability, people would start exploiting finitely available resources and end up finishing them soon, thus destroying Earth’s balance
Q26: Describe the importance of judicious use of resources. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The importance of judicious use of resources are :
(1) Multiple environmental and socioeconomic problems may arise if resources are used in an indiscriminate manner.
(2) Most of the resources are non-renewable. The continuous usage of these resources may result in exhaustion of the resources. This may stunt development and growth of the people.
(3) It will enhance the status of a person and would not impede development in general for future generations. They have to be used with caution.
Q27: Read the features of a soil and name the related soil:
(1) This soil ranges from red to brown in colour.
(2) It is generally sandy in texture and is saline.
(3) It lacks humus and moisture. (CBSE 2020, 14)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Arid soil is characterised by the following features:
- Ranges in colour from red to brown.
- Generally has a sandy texture and is saline.
- Lacks humus and moisture.
This type of soil is typically found in dry regions and can be made cultivable with proper irrigation.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q28: How is over irrigation responsible for land degradation in Punjab? (Delhi 2019) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Over irrigation in Punjab leads to significant land degradation through the following processes:
- Water logging: Excessive irrigation saturates the soil, preventing proper drainage.
- Increased salinity: Water logging raises the salt concentration in the soil, harming plant growth.
- Alkalinity issues: The accumulation of alkaline substances further reduces soil fertility.
These factors collectively lower the soil's fertility, making it less suitable for agriculture.
Q29: How is cement industry responsible for land, degradation? (Delhi 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Grinding and crushing of limestone for the cement industry generate a large amount of dust. As the dust settles down on the soil it reduces the process of infiltration of water into the soil.
Q30: Highlight the importance of contour ploughing. (AI 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Contour ploughing is a vital agricultural practice that involves tilling sloped land along lines of consistent elevation.
Its importance includes:
- Water conservation: Helps to retain rainwater, reducing runoff.
- Soil erosion reduction: Minimises soil loss from surface erosion.
- Improved crop yield: Enhances soil moisture retention, benefiting crops.
By following the natural contours of the land, contour ploughing effectively slows down water flow, preventing erosion and promoting sustainable farming.
Q31: Which type of soil is most suitable for growing the crop of cashew nut? (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Laterite soil is the most suitable type for growing cashew nuts.
Key characteristics include:
- Develops in tropical and subtropical climates.
- Forms due to intense leaching from heavy rainfall.
- Typically deep and acidic (pH < 6.0).
- Commonly found in southern states, especially in the Western Ghats.
- Rich in humus where vegetation is dense; otherwise, it can be nutrient-poor.
In regions like Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Kerala, red laterite soils are particularly favourable for cashew cultivation.
Q32: Which soil type is the most widely spread and important soil in India? (2019,2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Alluvial soil is the most widely spread and significant type of soil in India.
- It covers the entire northern plains, formed by deposits from three major Himalayan river systems: the Indus, the Ganga, and the Brahmaputra.
- Alluvial soil also extends into Rajasthan and Gujarat through a narrow corridor.
- In the eastern coastal plains, it is found particularly in the deltas of the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri rivers.
This soil is known for its high fertility, making it ideal for growing crops like:
- Sugarcane
- Paddy
- Wheat
- Other cereals and pulses
Regions with alluvial soil are often intensively cultivated and densely populated due to their agricultural productivity.
Q33: Describe any three main features of 'Alluvial soil’ found in India. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Alluvial soil is a significant type of soil found in India, characterised by the following features:
- Widespread Presence: Alluvial soil is the most important and widely distributed soil type across India.
- Fertility: It contains essential nutrients like potash, phosphoric acid, and lime, making it ideal for crops such as sugarcane, paddy, and wheat.
- High Productivity: Regions with alluvial soil are highly fertile, leading to intensive cultivation and dense populations. In drier areas, the soil can be treated and irrigated to enhance productivity.
Q34: Describe any three main features of the black soil. (CBSE 2019, 32/2/3)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Black soil has several important features:
- Composition: It consists of very fine, clayey material.
- Moisture retention: This soil is known for its ability to hold moisture effectively.
- Nutrient-rich: It contains essential nutrients like calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash, and lime.
- Aeration: During hot weather, it develops deep cracks, which aids in soil aeration.
Q35: Which one of the following is an example of Cultivable Wasteland?
(a) Gross cropped Area
(b) Uncultivable Land
(c) Barren Wasteland
(d) Current fallow Land (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Cultivable wasteland refers to land that has the potential for cultivation but has not been farmed for at least five years.
Key points include:
- This land may be fallow or overgrown with shrubs, making it currently unused for agriculture.
- With appropriate efforts, it can be converted into productive agricultural land.
- Therefore, uncultivated land can be considered an example of cultivable wasteland if it has the potential for farming.
Q36: Highlight the importance of Contour ploughing. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Contour ploughing is essential for maintaining soil health and preventing erosion.
Here are its key benefits:
- Reduces soil erosion caused by wind and water.
- Helps retain moisture in the soil, promoting better crop growth.
- Improves soil structure, making it more fertile.
- Minimises runoff, allowing water to soak into the ground.
By following the natural contours of the land, contour ploughing effectively slows down water flow and protects the soil.
Q37: How are mining activities responsible for land degradation in Jharkhand? (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Mining activities are responsible for land degradation in Jharkhand due to several factors:
- Mining sites are often abandoned after excavation, leaving behind deep scars on the landscape.
- This abandonment leads to significant land disruption and loss of vegetation.
- Deforestation caused by mining further exacerbates the problem, contributing to severe land degradation.
Q38: Why should we use natural resources properly and judiciously? Explain your views. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The importance of judicious use of resources are:
(1) Multiple environmental and socioeconomic problems may arise if resources are used in an indiscriminate manner.
(2) Most of the resources are non-renewable. The continuous usage of these resources may result in exhaustion of the resources. This may stunt development and growth of the people.
(3) It will enhance the status of a person and would not impede development in general for future generations. They have to be used with caution.
Previous Year Questions 2018
Q39: Classify resources based on origin. [2018,2015,2014] View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Resources can be categorised on the basis of origin:
- Abiotic resources: These are non-living elements, including land, water, air, and minerals.
- Biotic resources: These come from the biosphere and include living things such as humans, plants, and animals.
Q40: ‘Sustainable Development is a crucial step for the development of a country’. Explain with suitable examples. (CBSE 2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Sustainable development is crucial for development of a country as it:
(1) Promotes use of renewable resources like solar energy, tidal energy, etc.
(2) Puts a check on over usage of resources.
(3) Promotes protection and conservation of resources for future generation
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q41: Explain the three stages of Resource Planning in India. (CBSE 2017-16)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Three stages of Resource Planning in India are as given below:
(a) Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of resources.
(b) Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans.
(c) Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans.
Q42: What are the three stages of resource planning in India? Why is it essential to have resource planning? (2017,2014)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
The three stages of resource planning in India are:
- Identification and inventory of resources: This includes surveying, mapping, and estimating the resources available across the country.
- Planning structure: Developing a framework that incorporates appropriate technology, skills, and institutions to implement resource development plans.
- Matching plans: Aligning resource development strategies with national development goals.
Resource planning is essential because:
- Resources are limited, so planning ensures their proper use and conservation for future generations.
- Resources are unevenly distributed across the country, necessitating careful planning.
- It helps in the production of resources and protects them from over-exploitation.
Q43: Name the soil type which is widely found in western Rajasthan. Explain two important characteristics of the soil type which makes it unsuitable for cultivation. (CBSE 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Arid Soil is commonly found in Western Rajasthan.
Its two main characteristics that make it unsuitable for cultivation are:
- Sandy texture: The soil is primarily sandy, which leads to poor water retention.
- High salt content: It has a high level of salinity, making it difficult for most plants to grow.
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q44: Give one difference between renewable and nonrenewable resources. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Renewable: Replenished by nature e.g., crops and plants.
Non-renewable: Resources which get exhausted after years of use, e.g., crude oil.
Q45: What is Agenda 21? List its two principles. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Agenda 21 was adopted at first International Earth Summit held in 1992 at Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
The two principles are as follows:
(i) Combat environmental damage, poverty, and disease through global cooperation, focusing on common interests and shared responsibilities.
(ii) Each local government should create its own local Agenda 21.
Q46: Classify the resources on the basis of exhaustibility. State two characteristics of each. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Renewable Resources: Resources that can be replenished after a short period of time are called renewable resources.
For example: agricultural crops, wind energy, water, forest, wildlife, etc.
(ii) Non-renewable Resources: Resources which take million years of time to replenish are called non-renewable resources.
For example: fossil fuels. We must remember that some resources like metals are recyclable.
Q47: "In India, some regions are rich in certain types of resources but deficient in some other resources". Do you agree with the statement? Support your answer with any three examples. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Yes, there are regions which are rich in certain types of resources but are deficient in some other resources.
(i) Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh are rich in minerals and coal deposits.
(ii) Arunachal Pradesh has abundance of water resources but lacks in infrastructural development.
(iii) Rajasthan is endowed with solar and wind energy but lacks in water resources.
(iv) Ladakh has rich cultural heritage but lacks in water resources and infrastructure.
Q48: Explain the two types of soil erosion mostly observed in India. Explain three human activities responsible for soil erosion. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Types of soil erosion:
- Gully erosion: This occurs when running water cuts through clayey soil, forming deep channels known as gullies. The affected land becomes unfit for cultivation and is referred to as badland or ravines.
- Sheet erosion: In this type, water flows as a sheet over large areas, washing away the topsoil.
Human activities causing soil erosion:
- Deforestation: The removal of trees leads to a loss of soil stability.
- Over-grazing: Excessive grazing by livestock can strip the land of vegetation.
- Mining: Excavation activities disturb the soil and leave it vulnerable to erosion.
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q49: Which is the most widespread relief feature of India? (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Plains are the most widespread relief feature of India.
Q50: Suggest any six measures to solve the problem of land degradation. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The problem of land degradation can be addressed through several effective measures:
- Afforestation: Planting trees to restore forest cover.
- Thorny bushes: Growing these in arid areas to combat desertification.
- Grazing management: Implementing proper practices on permanent pastures.
- Industrial waste disposal: Ensuring safe disposal of industrial waste.
- Shelter belts: Planting rows of trees to protect against wind erosion.
- Mining control: Regulating mining activities to prevent land damage.
 Land Degradation
Land Degradation
Q51: Discuss the factors responsible for land degradation in India. (2015,2014)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The important factors responsible for land degradation in India are as follows:
(i) Deforestation: By an estimate over one million hectares of forest is lost every year in India.
(ii) Erosion: Loss of vegetation cover makes land more susceptible to erosion. Wind and water have left vast tracts of land barren. Water erodes top soil to an extent of around 12,000 million tons per annum
(iii) Over-irrigation : Successive cropping and overirrigation, leads to water-logging and consequent salinisation and alkalisation. This situation mainly arises due to poor drainage.
(iv) Floods and Droughts : Drought is both man-made and environment-induced. Man has played a key role in the creation of drought-prone areas by over-exploitation of natural resources like forests, degradation by grazing, excessive withdrawal of ground water, silting of tanks, rivers, etc. Floods, on the other hand, are caused by heavy rains in a very short period. Each situation could have been altered had there been good vegetation cover. Vegetation helps in reducing run-off, increasing infiltration and reducing soil erosion.
(v) Over-grazing : India has the worlds largest cattle population, but not enough pasture land. This has led to serious problems as animals have encroached into forest lands and even agricultural lands. Land degradation due to over-grazing leads to desert like conditions.
(vi) Pollution : Pollution of land is caused by disposal of solid waste, leftover from domestic, industrial and agricultural sectors. Another major source of land pollution is the creation of derelict land due to mining particularly due to surface and underground mining activities.
Q52: Consequences of environmental degradation do not respect national or state boundaries. Support the statements with examples. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Environmental degradation has far-reaching consequences that cross national and state boundaries.
Here are some examples:
- Air Pollution: Emissions from factories in one country can affect air quality in neighbouring countries, leading to health issues.
- Water Contamination: Rivers that flow across borders can carry pollutants from one nation to another, impacting the health of communities downstream.
- Climate Change: Greenhouse gas emissions from one country contribute to global warming, affecting weather patterns and ecosystems worldwide.
- Deforestation: Logging activities in one region can lead to loss of biodiversity and disrupt ecosystems in adjacent areas, impacting wildlife and local communities.
These examples illustrate how environmental issues are interconnected and require cooperative international efforts for effective management.
Q53: Describe any five distinct characteristics of 'Arid soils. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Colour: Arid soils vary from red to brown.
- Texture: They are typically sandy and saline.
- Evaporation: High temperatures lead to faster evaporation, resulting in low humus and moisture.
- Kankar: The soil often contains Kankar, a layer that forms due to calcium accumulation.
- Water Infiltration: The Kankar layer restricts the infiltration of water.
Q54: Why is soil considered as a resource? Explain with five arguments. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Soil is considered a resource for several reasons:
- Essential for survival: Soil is vital for fulfilling our basic needs.
- Renewable resource: It is the most important renewable natural resource.
- Supports plant growth: Soil serves as the medium for plants, containing both organic (humus) and inorganic materials.
- Habitat for organisms: It supports various living organisms on Earth.
- Foundation of life: Soil is fundamental to our existence.
Previous Year Questions 2013
Q55: How is the cement industry responsible for land degradation? (CBSE 2013)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The cement industry is responsible for land degradation in various ways:
- It generates a significant amount of dirt and dust that accumulates on the ground.
- This dust obstructs the infiltration of water into the soil.
- Consequently, it hampers proper percolation of water, which negatively impacts soil health.
|
66 videos|630 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Social Science Previous Year Questions - Resources and Development
| 1. What are the key topics covered in the Class 10 Resources & Development syllabus? |  |
| 2. How can students effectively prepare for the Resources & Development exam? |  |
| 3. What types of questions are commonly asked in the Resources & Development exam? |  |
| 4. Why is sustainable development emphasized in the Resources & Development curriculum? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of previous year questions in exam preparation for Resources & Development? |  |






















