Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE > Problem Solving with Areas
Problem Solving with Areas | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Adding & Subtracting Areas
What is meant by an awkward shape (a compound shape)?
- Sometimes the shape we need to find the area of isn't a standard shape in Area - Formulas.
- However, we can determine the area by combining standard shapes.
- These are commonly known as Compound Shapes, and you might also encounter the term Compound Area.
Finding the area of an awkward shape (compound area)
- When tasked with determining the area of a complex shape, the key approach is to break down this shape into recognizable standard shapes and then sum their areas.
Solved Example
Example 1: Find the area of the pentagon shown in the diagram below.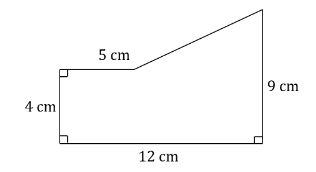 Ans: Separate the diagram into two shapes that you are familiar with and know the formulae for the areas of.
Ans: Separate the diagram into two shapes that you are familiar with and know the formulae for the areas of.
This pentagon can easily be split into a rectangle and a triangle.
Use the values given to find the length of the base and the height of the triangle and add these to the diagram.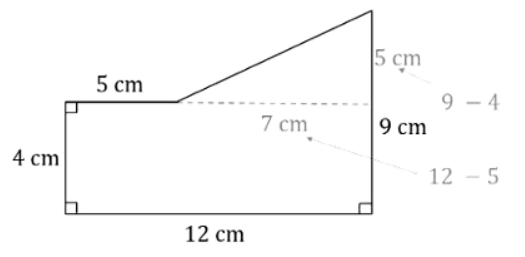 The total area will be the area of the rectangle + the area of the triangle.
The total area will be the area of the rectangle + the area of the triangle.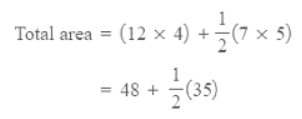
Area = 65.5 cm2
Problem Solving with Areas
What is problem solving?
Problem solving, as far as GCSE Mathematics is concerned, usually has two key features:
- A question is presented within a real-life context, such as Mary painting a bedroom in her house.
- Multiple mathematical topics are typically required to solve the problem, like Area and Percentages.
Problem solving with areas
- Area is a fundamental mathematical concept extensively utilized in real-world applications.
- Tasks like laying a carpet, painting a house, or designing a sports field involve calculations related to Area.
- Many area-related problems also involve monetary calculations due to the costs associated with such tasks.
How to solve problems
When tackling problems that involve areas, consider the following:
- To tackle problem-solving queries effectively, it's crucial not to solely fixate on the specific query but rather explore the possibilities offered by the given information.
- This approach often prompts you to consider alternative avenues, potentially unveiling a path towards addressing the initial question.
- Such queries might feature in exams with or without calculators, depending on the complexity of the numerical values provided.
The document Problem Solving with Areas | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
38 videos|413 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Problem Solving with Areas - Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How do you find the area of a rectangle? |  |
Ans. To find the area of a rectangle, you multiply the length by the width. The formula for the area of a rectangle is A = length x width.
| 2. What is the formula for finding the area of a triangle? |  |
Ans. The formula for finding the area of a triangle is A = 1/2 x base x height, where the base is the length of the triangle's base and the height is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite vertex.
| 3. How can you add the areas of two different shapes together? |  |
Ans. To add the areas of two different shapes together, you first calculate the area of each shape using the appropriate formula. Once you have the individual areas, you simply add them together to get the total combined area.
| 4. Can you subtract the area of one shape from another? |  |
Ans. Yes, you can subtract the area of one shape from another. To do this, calculate the area of both shapes separately. Then, subtract the area of the smaller shape from the area of the larger shape to find the difference in area.
| 5. Is it possible to add the area of a circle to the area of a square? |  |
Ans. Yes, it is possible to add the area of a circle to the area of a square. Simply calculate the area of each shape using their respective formulas, and then add the two areas together to find the total combined area.
Related Searches















