Process of Strategic Planning and Implementation | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| The particular steps for Strategic Planning |

|
| Importance of Strategic Planning |

|
| The advantages of Strategic planning |

|
| Implementation |

|
Introduction
Strategic Planning is a methodical approach aimed at defining the long-term goals of an organization and formulating policies and strategies to guide the allocation, utilization, and disposal of resources in order to fulfill the vision and mission of the firm. Senior management is primarily responsible for this process. Strategic planning entails a problem-solving procedure wherein strategic objectives are defined, and plans are devised to achieve them. The objectives of strategic planning encompass grasping the advantages of strategic planning, comprehending the outcomes of strategic planning, and acquiring knowledge about the essential factors for successful planning and execution.
Purpose of Strategic Planning:
- Making important decisions and agreeing on actions that define an organization.
- Guides what the organization is, what it does, and why it does it.
How Strategic Planning Helps an Organization:
Setting Goals: Helps in establishing clear goals or objectives for the organization.
Analyzing Environment and Resources: Involves studying the organization's surroundings and its available resources.
Generating and Evaluating Options: Comes up with different strategic options and assesses their effectiveness.
Planning Implementation: Plans how to put the chosen strategies into action.
Designing Control Systems: Creates systems to monitor and control the progress of the plans.
Different components relate to each other with the strategic plan.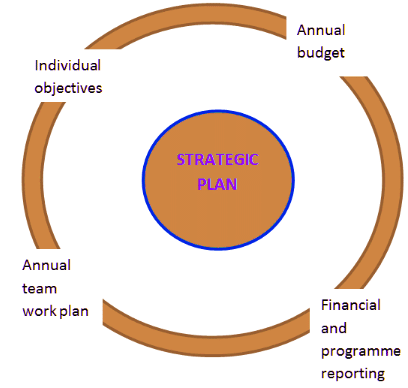
The particular steps for Strategic Planning
Stages of Strategic Planning
Environmental Scanning: Looking at the surroundings to understand what's happening.
Evaluation of Issues: Examining and understanding the important problems.
Forecasting: Predicting or estimating what might happen in the future.
Goal Setting: Deciding on the main objectives or goals.
Implementation: Putting the plan into action.
Monitoring: Keeping an eye on things to make sure they are going as planned.
Components of a Written Strategic Plan
Executive Summary: A brief overview of the plan.
Vision Statement: A statement describing what the organization aims to achieve.
Mandate and Scope of Work: Defining the organization's purpose and the extent of its activities.
Summary Analysis of External and Internal Environment: Looking at what's happening outside and inside the organization.
Main Strategic Issues: Identifying the key problems that need to be addressed.
Aims Accompanying Strategies: Deciding on the goals that go along with the plans.
Assessment of Human Resource Needs: Figuring out what kind of people and skills are required.
Budget Protection: Ensuring there's enough money to carry out the plan.
Importance of Strategic Planning
Key to Success:
- Vital for long-term growth and survival of businesses, as observed in top-performing companies.
Direction and Focus:
- Helps managers define the mission, providing direction and focus to organizational activities.
Preventing Confusion:
- Essential for success; without proper planning, confusion and unethical practices may arise.
Current Focus on Strategic Management:
- Researchers are increasingly studying strategic management.
Positive Correlation:
- Adeyemi (1992) found a positive link between strategic management and organizational performance in some Nigerian banks.
Components Influencing Success:
- Success or failure of strategic planning depends on factors like the environment, organizational structure, and strategic decision-making.
Optimizing Performance:
- Ansoff (1979) suggests that when these components align well, organizational performance is optimized.
Modernization Support:
- Lorange (1979) proposes that strategic planning is crucial for modernization, supporting and enhancing the planning process.
Rational and Focused:
- Effective strategic planning need not be overly detailed or complicated but should be rational and focused on carrying out strategic decisions.
The advantages of Strategic planning
Methodical Approach:
- Strategic planning is a systematic way of planning, making it easy to understand the methods and procedures for implementing strategies.
Structured Problem Solving:
- Provides a structured approach to analyze and think about complex strategic problems, encouraging management to question and challenge assumptions.
Involvement of People:
- Can involve people in developing strategies, fostering a collaborative approach.
Effective Communication:
- Acts as a tool for management to effectively communicate the organization's goals to its members.
Control Mechanism:
- Helps control and monitor performance regularly against agreed objectives.
Drawbacks of Strategic Planning
Difficulty and Time-Consuming: Strategic planning can be challenging and time-consuming.
Delayed Results: Immediate results are seldom achieved in strategic planning.
Limits to Rational and Risk-Free Options: Often confines organizations and executives to more rational and less risky choices.
Implementation
Implementation is the practical process of translating strategies and plans into actions aimed at achieving the strategic objectives and goals set by an organization.
Importance:
- Implementation is a critical phase in the strategic planning process. Organizations that formulate strategic plans must integrate a well-defined process for applying and executing the plan.
Tailored Process:
- The specific implementation process can vary among organizations based on their unique needs, structure, and objectives.
Detailed Expression:
- While strategies are often formulated at a high level, successful implementation requires expressing them in detailed policies and communications. This ensures that the workforce throughout the organization understands and can act upon the strategy.
Employee Support:
- The success of strategic plans depends on the support of employees who directly engage with customers, suppliers, and organizational resources targeted by the strategy. Employee buy-in is crucial for effective implementation.
Departmental Involvement:
- Implementation spans various departments such as marketing, research and development, procurement, human resources, production, and information technology. Each department plays a role in executing the strategic plan.
Resource Allocation:
- Identifying the resources and capabilities required to support the new strategy is essential. This includes considering any organizational changes needed for successful implementation.
Monitoring and Revision:
- Strategic plans need to be continuously monitored and, if necessary, revised. Control systems and feedback mechanisms are crucial for assessing whether the strategy is being implemented accurately and effectively.
Factors Affecting Implementation
1. Senior Management Commitment:
- Research indicates that the commitment of senior management is a prerequisite for successful strategy implementation. Senior executives must actively support and dedicate themselves to the implementation process.
2. Middle Manager Involvement:
- Middle managers' involvement is critical for the success of implementation. Their knowledge and understanding of the strategy should be considered in the planning phase, and they should be actively engaged throughout the process.
3. Effective Communication:
- Communication is identified as a major success factor in strategy implementation. Establishing two-way communication programs that allow employees to ask questions and receive information about the formulated strategy is crucial for its successful execution.
Steps for Successful Implementation
1. Evaluate the Strategic Plan:
- Managers should thoroughly review the strategic plan, identifying potential challenges and highlighting elements that might be unrealistic or excessively costly in terms of time or money.
2. Create a Vision:
- Develop a clear vision outlining the goals and objectives of the strategic plan. This vision provides a roadmap for the implementation process and emphasizes its importance.
3. Select Team Members:
- Form a competent team to support the management in implementing the strategies. Designate a team leader to motivate the team and address any questions or problems that may arise during the process.
4. Schedule Progress Meetings:
- Regularly schedule meetings to discuss progress, present goals, and objectives. These meetings provide an opportunity to assess whether the implementation is on schedule, ahead, or behind, and to make any necessary adjustments.
5. Involve Upper Management:
- Keep the organization's executives informed about the progress of implementation. Regular progress reports make the management an integral part of the process, allowing them to address concerns or potential changes promptly.
FAQs on Process of Strategic Planning and Implementation - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the steps involved in strategic planning? |  |
| 2. Why is strategic planning important? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of strategic planning? |  |
| 4. What is the implementation process of strategic planning? |  |
| 5. How can strategic planning be implemented effectively? |  |














