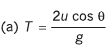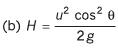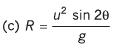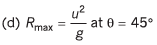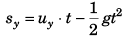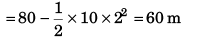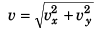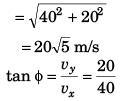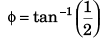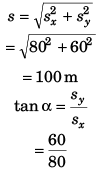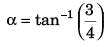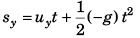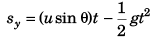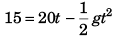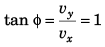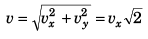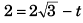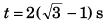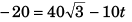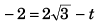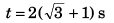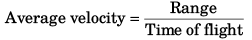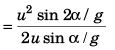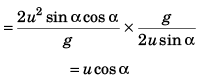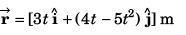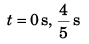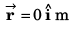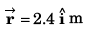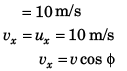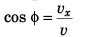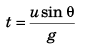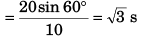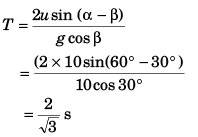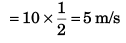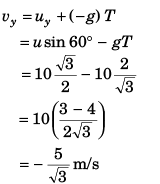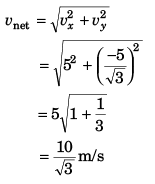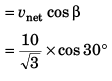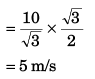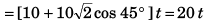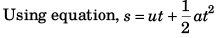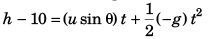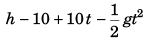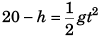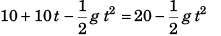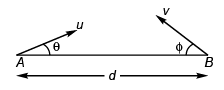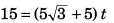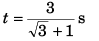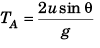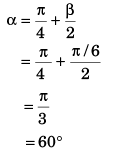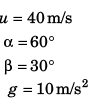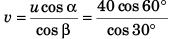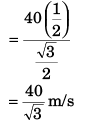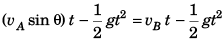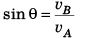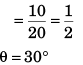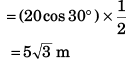DC Pandey Solutions: Projectile Motion | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Introductory Exercise 4.1
Q.1. Projectile motion is a 3-dimensional motion. Is this statement true or false.
Ans. False
A particle projected at any angle with horizontal will always move in a plane and thus projectile motion is a 2-dimensional motion. The statement is thus false.
Q.2. Projectile motion (at low speeds) is uniformly accelerated motion. Is this statement true or false.
Ans. True
At high speed the projectile may go to a place where acceleration due to gravity has some different value and as such the motion may not be uniform accelerated.
The statement is thus true.
Q.3. A particle is projected with speed u at angle θ with vertical.
Find:
(a) time of flight
(b) maximum height
(c) range
(d) maximum range and corresponding value of 0.
Ans.
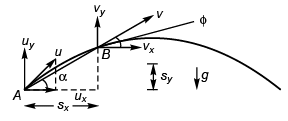
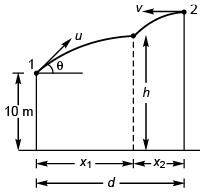
Q.4. A particle is projected from ground with velocity 40√2 m/s at 45º
Find:
(a) velocity and
(b) displacement of the particle after 2 s. (g = 10 m/s2)
Ans. (a) 20√5 m/s at angle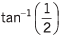 with horizontal, (b) 100 m
with horizontal, (b) 100 m
u = 40√2 m/s, θ = 45°
As horizontal acceleration would be zero.
vx = ux = u cos θ = 40 m/s
sx = uxt = (u cos θ) t = 80 m
A : position of particle at time = 0.
B : position of particle at time = t.
As vertical acceleration would be - g
vy = uy - gt
= u sin θ = gt
= 40 - 20
= 20 m/s
∴
i.e.,
i.e.,
Q.5. A particle is projected from ground with velocity 20√2 m/s at 45°. At what time particle is at height 15 m from ground? (g = 10 m/s2)
Ans. 1 s and 3 s
or
or
or t2 = 4t + 3 = 0
i.e., t = 1 s and 3 s
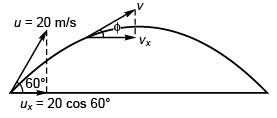
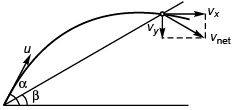
Q.6. A particle is projected from ground with velocity 40 m/s at 60° with horizontal. Find speed of particle when its velocity is making 45° with horizontal. Also find the times (s) when it happens, (g = 10 m/s2)
Ans.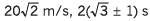
See figure to the answer to question no. 4.
u = 40 m/s, θ = 60°
∴ ux = 40 cos 60° = 20 m/s
Thus, vx = ux = 20 m/s
As φ = 45°
∴ yy = vx = 20 m/s
Thus,
= 20√2 m/s
Before reaching highest point
vy = uy + (- g) t∴ 20 = 40 sin 60° - 10 t
or
⇒
After attaining highest point
i.e.,
or
Q.7. What is the average velocity of a particle projected from the ground with speed u at an angle a with the horizontal over a time interval from beginning till it strikes the ground again?
Ans. u cos α
Q.8. What is the change in velocity in the above question?
Ans. 2u sin α (downwards)
Change in velocity
= (- u sin α) - (+ u sin α)
= - 2u sin α
= 2u sin α (downward)
Q.9. Under what conditions the formulae of range, time of flight, and maximum height can be applied directly in case of a projectile motion?
Ans. Between two points lying on the same horizontal line.
Formulae for R, T and Hmax will be same if the projection point and the point where the particle lands are same and lie on a horizontal line.
Q.10. A body is projected up such that its position vector varies with time as 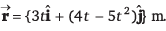 Here, t is in seconds.
Here, t is in seconds.
Find the time and x-coordinate of particle when its y-coordinate is zero.
Ans. time = 0, 0.8 s, x-coordinate = 0, 2.4 m
y-coordinate will be zero when 4t - 5t2 = 0
i.e.,
t = 0 belongs to the initial point of projection of the particle.
∴
i.e., x = 0 m
At t = 0.8 s,
i.e., x = 2.4 m
Q.11. A particle is projected at an angle 60° with horizontal with a speed v = 20 m/s. Taking g = 10 m/s2. Find the time after which the speed of the particle remains half of its initial speed.
Ans.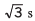
vx = ux = 10 m/s
⇒
= 10/v
= 10/10
[as, v = 20/2(given)]
= 1 i.e., φ = 0°
∴ Speed will be half of its initial value at the highest point where φ = 0°.
Thus,
Introductory Exercise 4.2
Ques 1: A particle is projected along an inclined plane as shown in figure. What is the speed of the particle when it collides at point A? (g = 10 m/s2)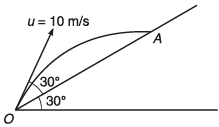
Ans: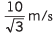
Sol: Time of flight
Using, v = u + at
vx = ux = u cos 60°
Q2: In the above problem what is the component of its velocity perpendicular to the plane when it strikes at A?
Ans: 5 m/s
Sol: Component of velocity perpendicular to plane
Ques 3: Two particles A and B are projected simultaneously from the two towers of height 10 m and 20 m respectively. Particle A is projected with an initial speed of 10√2 m/s at an angle of 45° with horizontal, while particle B is projected horizontally with speed 10 m/s. If they collide in air, what is the distance d between the towers?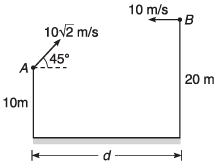
Ans: 20 m
Sol: Let the particle collide at time t.
x1 = (u cos θ) t
and x2 = vt
∴ d = x2 - x1
= (v + u cos θ) t
For vertical motion of particle 1:
i.e.,…(i)
or
For the vertical motion of particle 2:
i.e.,…(ii)
Comparing Eqs. (i) and (ii),
⇒ t = 1 s
∴ d = 20 m
Ques 4: Two particles A and B are projected from ground towards each other with speeds 10 m/s and 5√2 m/s at angles 30° and 45° with horizontal from two points separated by a distance of 15 m. Will they collide or not?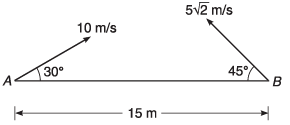
Ans: No
Sol: u = 10 m/s
v = 5√2 m/sθ = 30°
φ = 45°
d = 15 m
Let the particles meet (or are in the same vertical time t).
∴ d = (u cos θ) t + (v cos φ) t
⇒ 15 = (10 cos 30° + 5√2 cos 45°) t
or
or
= 1.009 s
Now, let us find time of flight of A and B
= 1 s
As TA < t, particle A will touch ground before the expected time t of collision.
∴ Ans: NO.
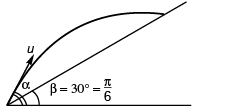
Ques 5: A particle is projected from the bottom of an inclined plane of inclination 30°. At what angle α (from the horizontal) should the particle be projected to get the maximum range on the inclined plane.
Ans: 60°
Sol: For range to be maximum
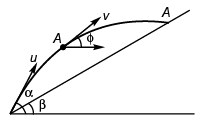
Ques 6: A particle is projected from the bottom of an inclined plane of inclination 30° with velocity of 40 m/s at an angle of 60° with horizontal. Find the speed of the particle when its velocity vector is parallel to the plane. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Ans: 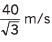
Sol: At point A velocity
of the particle will be parallel to the inclined plane.
∴ φ = β
vx = ux = u cos α
vx = v cos φ = v cos β
or u cos α = v cos β
⇒
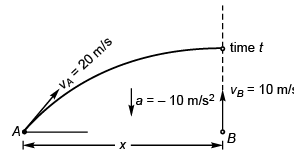
Ques 7: Two particles A and B are projected simultaneously in the directions shown in figure with velocities vA = 20 m/s and vB = 10 m/s respectively. They collide in air after 1/2 s.
Find:
(a) the angle θ
(b) the distance x.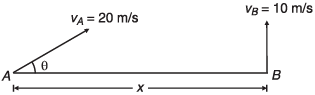
Ans: (a) 30°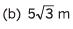
Sol: (a) At time t, vertical displacement of A
= Vertical displacement of B
i.e., vA sin θ = vB
∴ θ = 30°
(b) x = (vA cos θ) t
|
95 videos|367 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions: Projectile Motion - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the definition of projectile motion? |  |
| 2. What are the key factors affecting the range of a projectile? |  |
| 3. How can we calculate the maximum height of a projectile? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the launch angle in projectile motion? |  |
| 5. How does air resistance affect projectile motion? |  |