Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Properties of Acids and Bases
Properties of Acids and Bases | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Properties of Acids |

|
| Typical reactions of acids |

|
| Properties of Bases & Alkalis |

|
| Typical Reactions of Bases |

|
Properties of Acids
- Acids have pH values of below 7, taste sour (when edible), and are corrosive.
- Acids can neutralize bases, creating salts and water.
- When acids are mixed with water, they generate positively charged hydrogen ions (H⁺).
- The presence of hydrogen ions is what gives a solution its acidic properties.
Example: Hydrochloric Acid
HCl (aq) → H⁺ (aq) + Cl⁻ (aq)
Typical reactions of acids
Acids and metals
- Metals above hydrogen in the reactivity series react with dilute acids, forming a salt and hydrogen gas.
- Metal-Acid Reaction: Acid + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen
- The name of the salt is determined by the anion within the acid used.
Acid-Base
- Metal oxides and metal hydroxides, also known as alkalis, exhibit basic properties.
- When they interact with acids, a neutralization reaction takes place.
- In such reactions, salts and water are invariably formed.
- The general equation for acid-base neutralization is: Acid + Base → Salt + Water.
Acids with metal carbonates
When acids come into contact with metal carbonates, they undergo a reaction to produce the respective metal salt, carbon dioxide, and water.
Acid + Metal Carbonate → Salt + Carbon Dioxide + Water
Indicators
- Two color indicators are utilized to discern between acids and alkalis.
- Litmus, typically derived from lichens and found in various plants, is a widely employed substance for this purpose.
- Synthetic indicators, organic compounds sensitive to acidity shifts, exhibit varied colors in the presence of acids and alkalis.
- Thymolphthalein and methyl orange represent examples of synthetic indicators commonly used in acid-alkali titrations.
- Two Colour Indicators Table:
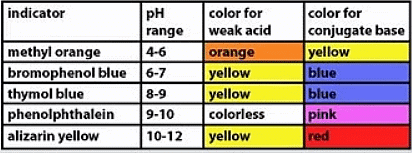
- Synthetic indicators serve the purpose of indicating the endpoint in titrations due to their ability to exhibit a distinct color change when an acid is neutralized by an alkali, and vice versa.
- Litmus, on the other hand, is not ideal for titrations because its color change is not as precise, often transitioning to a purple hue in neutral solutions, making it challenging to determine the endpoint accurately.
- Despite its limitations in titrations, litmus remains valuable as indicator paper, available in red and blue forms, suitable for dipping into solutions or testing gases.
Question for Properties of Acids and BasesTry yourself:What happens when acids react with metals?
View Solution
Properties of Bases & Alkalis
- Bases have pH values above 7.
- A base that is water-soluble is known as an alkali.
- In alkaline conditions, red litmus paper turns blue, methyl orange indicator turns yellow, and thymolphthalein indicator turns blue.
- Bases are substances that can neutralize an acid, producing a salt and water.
- Bases are typically oxides or hydroxides of metals.
- When alkalis are mixed with water, they generate negative hydroxide ions (OH-).
- The presence of OH- ions is what defines an aqueous solution as an alkali.
Example: Sodium Hydroxide
NaOH (s) → Na (aq) + OH- (aq)
Typical Reactions of Bases
Bases and acids
- When a base reacts with an acid, a neutralization reaction takes place.
- Neutralization reactions between acids and bases result in the formation of a salt and water.
- Equation: Acid + Base → Salt + Water
Alkalis and Ammonium Salts
- Ammonium salts undergo decomposition when heated with an alkali.
- Ammonia, despite being a weak base, is volatile and can be displaced by another alkali, resulting in the production of a salt, water, and ammonia.
- Example: NH4Cl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O + NH3
- This reaction serves as a chemical test to confirm the presence of the ammonium ion (NH4).
- Steps:
- Add alkali to the substance with gentle warming.
- Conduct the ammonia gas test using damp red litmus paper.
- If ammonia is present, the damp litmus paper will turn from red to blue.
Question for Properties of Acids and BasesTry yourself:What happens when a base reacts with an acid?
View Solution
The document Properties of Acids and Bases | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
71 videos|147 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Properties of Acids and Bases - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are some common properties of acids? |  |
Ans. Some common properties of acids include their ability to donate hydrogen ions, their sour taste, their ability to turn blue litmus paper red, and their corrosive nature.
| 2. What are some typical reactions of acids? |  |
Ans. Typical reactions of acids include reacting with metals to produce hydrogen gas, reacting with bases to form water and a salt, and reacting with carbonates to produce carbon dioxide gas.
| 3. What are some properties of bases and alkalis? |  |
Ans. Some properties of bases and alkalis include their ability to accept hydrogen ions, their bitter taste, their ability to turn red litmus paper blue, and their slippery or soapy feel.
| 4. What are some typical reactions of bases? |  |
Ans. Typical reactions of bases include neutralizing acids to form water and a salt, reacting with fats and oils to form soap, and reacting with acids to form water and a salt.
| 5. How do acids and bases differ in terms of their chemical properties? |  |
Ans. Acids tend to donate hydrogen ions, have a pH less than 7, and react with metals to produce hydrogen gas. Bases, on the other hand, tend to accept hydrogen ions, have a pH greater than 7, and react with acids to form water and a salt.
Related Searches




















