Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Proteins & Active Transport
Proteins & Active Transport | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Importance of Active Transport
- Energy is crucial in active transport since it facilitates the movement of particles against their natural concentration gradient, opposing the direction of diffusion.
- Active transport plays a pivotal role in transporting molecules or ions across membranes, enabling essential biological processes.
- Examples of active transport include the absorption of glucose by epithelial cells in the villi of the small intestine and kidney tubules in the nephron, as well as the uptake of ions from soil water by root hair cells in plants.
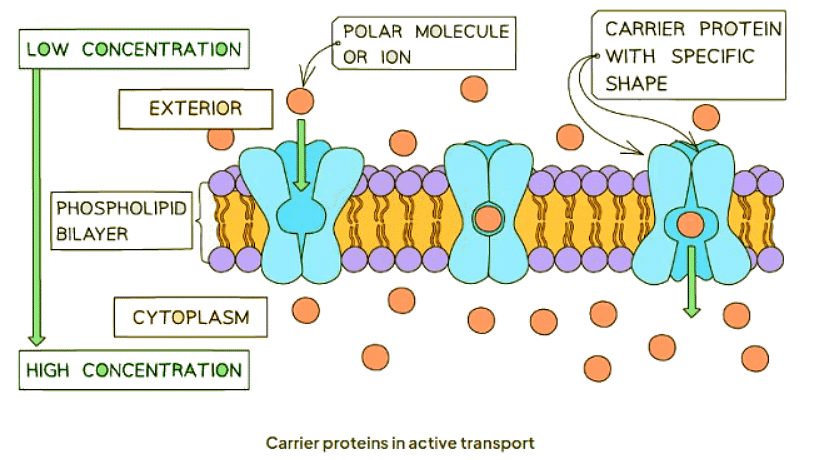
Protein Carriers
Active transport mechanisms rely on carrier proteins embedded within the cell membrane to facilitate the movement of specific molecules against their concentration gradient:
- Initially, the substance binds with a carrier protein molecule located in the cell membrane.
- The carrier protein undergoes a shape change, powered by the energy derived from cellular respiration, enabling it to transport the substance across the membrane.
- Subsequently, the substance is released into the cell, completing the transport process.
Question for Proteins & Active TransportTry yourself: What is the role of protein carriers in active transport?View Solution
The document Proteins & Active Transport | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
101 videos|193 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Proteins & Active Transport - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the role of protein carriers in active transport? |  |
Ans. Protein carriers play a crucial role in active transport by facilitating the movement of molecules across the cell membrane against their concentration gradient. These carriers undergo conformational changes to transport specific molecules into or out of the cell.
| 2. How do protein carriers differ from other transport proteins? |  |
Ans. Protein carriers are specific to certain molecules and undergo conformational changes to transport them, while other transport proteins like channel proteins facilitate the passive movement of molecules down their concentration gradient without the need for energy.
| 3. Why is active transport important for cellular functions? |  |
Ans. Active transport is essential for maintaining proper ion concentrations inside and outside the cell, facilitating nutrient uptake, and removing waste products. It also helps in maintaining cell volume and creating a suitable environment for various cellular processes.
| 4. Can active transport be inhibited? |  |
Ans. Yes, active transport can be inhibited by certain drugs or molecules that interfere with the activity of protein carriers, disrupting the transport of specific molecules across the cell membrane. This can lead to various cellular dysfunctions.
| 5. How do cells regulate the activity of protein carriers in active transport? |  |
Ans. Cells regulate the activity of protein carriers through various mechanisms such as phosphorylation, allosteric regulation, and the expression of different types of carriers based on the cell's needs. This ensures efficient and controlled transport of molecules across the cell membrane.
Related Searches




















