Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Proton Transfer, Strong and Weak Acid
Proton Transfer, Strong and Weak Acid | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Proton transfer |

|
| Acids |

|
| Bases |

|
| Strong Acids |

|
| Weak Acids |

|
| Effect of Concentration on Strong and Weak Acids |

|
Proton transfer
- The previous definitions of acids and bases can be expanded upon. When we consider proton transfer, we delve deeper into how each substance interacts with protons.
- In the context of proton transfer, we can elaborate on how substances behave regarding proton interactions.
Acids
- Acids act as proton donors by ionizing in a solution, releasing protons (H⁺ ions). These H⁺ ions contribute to the acidic nature of the solution.
- Proton donors supply H⁺ ions, thereby increasing the acidity of the solution.
Bases
- Bases function as proton acceptors; they receive protons donated by acids.
- Proton acceptors take in protons provided by acids, playing a crucial role in chemical reactions.
- Diagram showing the role of acids and bases in the transfer of protons - here water acts as a base as it accepts a proton:
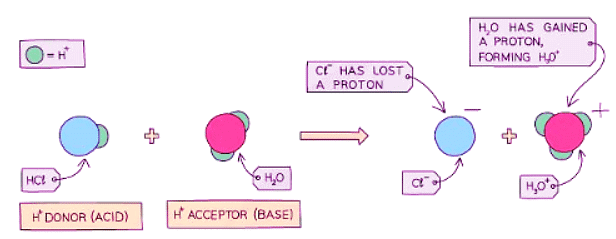
Strong Acids
- Acids can be categorized as strong or weak based on the number of H+ ions they release in water.
- Strong acids completely dissociate in water, resulting in solutions with very low pH levels.
- Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
- For instance, when hydrochloric acid dissolves in water, it ionizes into H+ and Cl- ions: HCl (aq) → H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq).
Weak Acids
- Weak acids only partially dissociate in water, leading to pH values closer to the middle of the pH scale, below 7.
- Organic acids like ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) are examples of weak acids.
- When weak acids are added to water, an equilibrium is established between the molecules and their ions.
- For example, propanoic acid undergoes partial ionization in water: CH3CH2COOH ⇌ H+ + CH3CH2COO-.
- The equilibrium favors the left side, indicating a high concentration of intact acid molecules with a low concentration of H+ ions in the solution.
Effect of Concentration on Strong and Weak Acids
- A concentrated acid solution has a higher number of acid molecules per dm3 of solution. It does not necessarily denote strength, as it could be from a weak acid that doesn't fully dissociate.
- For instance, a dilute HCl solution can be more acidic than a concentrated ethanoic acid solution, as most HCl molecules dissociate compared to CH3COOH.
Question for Proton Transfer, Strong and Weak AcidTry yourself: What is the role of bases in proton transfer?View Solution
The document Proton Transfer, Strong and Weak Acid | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
71 videos|147 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Proton Transfer, Strong and Weak Acid - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid? |  |
Ans. A strong acid completely dissociates in water to release all its protons, while a weak acid only partially dissociates, resulting in fewer protons being released.
| 2. How does proton transfer occur in acids? |  |
Ans. Proton transfer in acids involves the transfer of a hydrogen ion (proton) from the acid to a base, forming the conjugate base of the acid and the conjugate acid of the base.
| 3. Can you provide an example of a strong acid and a weak acid? |  |
Ans. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is an example of a strong acid, while acetic acid (CH3COOH) is a weak acid.
| 4. Why are strong acids considered to be more corrosive than weak acids? |  |
Ans. Strong acids release more protons, leading to a higher concentration of H+ ions in solution, which can cause more severe chemical burns and corrosion compared to weak acids.
| 5. How does the equilibrium expression change for a weak acid compared to a strong acid? |  |
Ans. For a weak acid, the equilibrium expression includes both the dissociation of the acid and the recombination of the ions formed, while for a strong acid, the equilibrium expression only considers the dissociation of the acid.
Related Searches














