Protozoa: Locomotion | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Protozoan Locomotion
Across the globe, we encounter a diverse array of creatures, some of which are so minuscule that they elude our naked eye's observation. These diminutive life forms are often found within a mere droplet of water. When we place a droplet of pond water under a microscope, it magnifies our perspective, revealing these otherwise imperceptible beings. Among them, some are single-celled eukaryotes that exhibit various forms of movement. Moreover, protozoa exhibit a range of locomotion methods.
Protozoans rely on locomotion to pursue sustenance, evade predators, access sunlight, navigate towards essential chemicals, or steer clear of toxic substances. Single-celled eukaryotes employ a spectrum of three or four distinct movement patterns, reflecting the diversity inherent in microscopic life. Protozoans are loosely categorized based on their specific movement styles. We shall delve further into the various locomotion types observed in protozoa.
Characteristics of Protozoan
- Protozoans refer to single-celled eukaryotes.
- These are also called “one-celled animals”.
- They show animal-like behaviour like locomotion and predation.
- They lack a cell wall, but it is surrounded by an elastic structure called the pellicle in some protozoans.
- E.g. Amoeba, Paramecium, and Trypanosoma.
- Its size ranges from 1μ to several MMS.
- Some protozoans are free-living, common and found in fresh and marine water bodies and other moist environments.
- Protozoans are generally parasitic and show heterotrophic modes of nutrition.
- They reproduce by asexual reproduction like binary fission or multiple fission.
- Sexually, they can reproduce by conjugation or formation of gametes.
Types of Locomotion in Protozoa
How many types of locomotion occur in protozoa? We have the answer here. Five modes of locomotion that can be seen in protozoa are:
Locomotion by pseudopodia
- This type of locomotion is seen in animals that do not have a set structure for mobility and are amorphous. This type of locomotion is seen in Amoeba, etc.
- It has a finger-shaped protoplasmic extension called pseudopodia or false feet. With these, they can creep over the substratum.
- These are temporary structures formed by the streaming flow of the cytoplasm.
- Finger-like pseudopodia are formed in those protozoans whose body is asymmetric or irregular, capable of changing their shape due to their formation and withdrawal.
- This type of movement is called amoeboid, which brings about locomotion and change in the body’s shape. This helps in food capture too.
- Locomotion is brought about by alternate changes in the colloidal state of the cytoplasm affected by sol-gel-sol transformations and the cytoplasmic streaming of plasmas into the pseudopodia.
- Pseudopodia are of four types:
- Lobopodia: They are lobe-like with broad and blunt ends. This type of pseudopodia is seen in Amoeba.
- Filopodia: They are fine thread-like, often with rounded ends, and slender, unsupported, and independent. Found in Euglypha.
- Axopodia: They are long and stiff with hard axial filament.
Example: Actinophrys. - Reticulopodia: They are slender, long and branched, forming a reticulate network. Example: Globigerina.
Locomotion by flagella
- These are found in flagellated protists.
- Flagella are thread-like projections on the cell surface and show whip-like movement.
- The external long whip-like part of the flagellum is called the shaft.
- Its length is about 2μ to 3mm , and its diameter is about 0.2μ .
- The internal structure of the flagellum consists of a 9+2 fibrillar arrangement.
- Undulating movement, i.e. movement of organisms in the opposite direction of the beat, is exhibited by most flagella.
- In some protozoans, there is one flagellum like in Euglena, while in some, more than one flagella are present, e.g. Giardia lamblia.
- Flagella is used for propulsion. It also helps bring food in by creating a current in the body.
Locomotion by Cilia
- Cilia are short, fine, hair-like structures present all over the body surface. Cilia bearing protozoans are called ciliates, and the movement produced by them is called ciliary movements.
- Cilia help in locomotion and food capture.
- They perform oar-like movements in a coordinated manner. It produces a progressive wave by beating in succession.
- Coordinated movement of cilia creates a vertex that allows the movement of the food into the cavity called the gullet.
Example: Paramecium shows ciliary movement that moves at the rate of 2mm per second.
Flagella | Cilia |
Larger in size | Smaller in size |
Commonly found at one end of the cell | Found throughout the body |
They beat whip-like | They beat oar-like |
Helps in locomotion | Helps in locomotion, aeration, feeding and circulation |
Few flagella are present in each cell, generally 1 to 4. | Numerous cilia, 300 to 1400, are present in the cell. |
Wriggling locomotion or Sporozoan movement
- This type of movement is slow and worm-like.
- Seen in non-flagellated protozoans performed with the help of waves of contraction and expansion of the body. E.g., Sporozoans.
- They do not possess organelles of locomotion (i.e. flagella, pseudopodia, cilia, etc.) and ingestion of food due to parasitic life.
We have explored the realm of protozoans and the diverse modes of locomotion exhibited by these microorganisms. Protozoans, which are members of the protist kingdom, are characterized as minute, single-celled eukaryotic organisms. Within the world of protozoa, various locomotory structures are found, including pseudopodia, flagella, and cilia, among others.
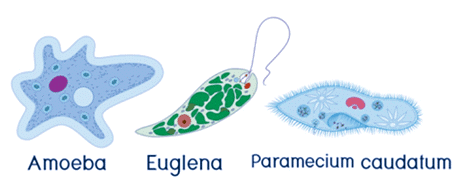
Amoeba utilizes pseudopodia for movement, while Euglena relies on flagella, and Paramecium employs cilia for locomotion. On the other hand, some parasitic protozoans, such as sporozoans, lack specialized locomotory organelles. Notably, flagella are relatively long and typically found in limited numbers within a cell, while cilia are numerous and densely distributed on the surface of a single cell.
|
181 videos|346 docs
|
FAQs on Protozoa: Locomotion - Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the characteristics of protozoa? |  |
| 2. What are the types of locomotion in protozoa? |  |
| 3. How do protozoa move using flagella? |  |
| 4. What is ciliary locomotion in protozoa? |  |
| 5. How do protozoa move using amoeboid locomotion? |  |


















