Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Pyramids of Energy
Pyramids of Energy | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Pyramids of Energy
Energy Flow in Ecosystems
- In ecosystems, energy flow is a crucial process that sustains life. Let's delve into the key concepts:
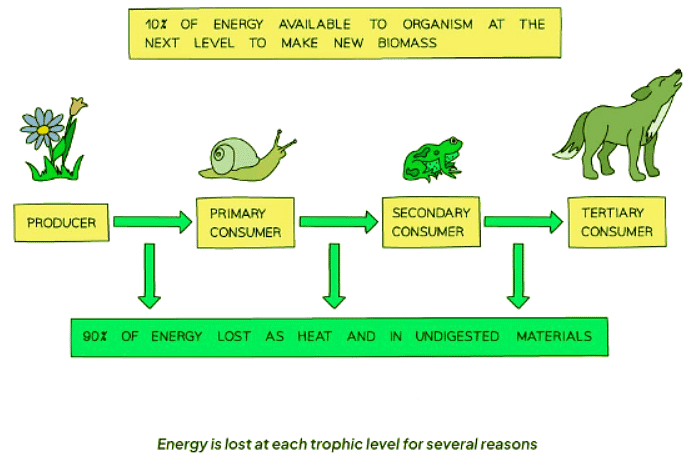
- Energy Consumption and Transfer: In order for energy to move through an ecosystem, it must be consumed. However, not all the energy an organism receives is passed on. For instance, when a vole consumes grass, only a portion of the energy is retained in new cells.
- Energy Loss in Trophic Levels: Energy is lost as it moves through trophic levels due to various factors:
- Waste Production: Organisms produce waste products like urine, which removes energy from the system.
- Heat Generation: Mammals and birds release energy as heat, especially those maintaining a constant body temperature.
- Undigested Waste: Undigested waste, such as faeces, provides food for decomposers but represents lost energy from the ecosystem.
- Energy Efficiency and Food Chains: The inefficiency of energy transfer explains why food chains are limited in length. Energy loss at each trophic level restricts the number of organisms in a chain. For instance, predators consuming barn owls would need to consume many to meet their energy needs due to the low energy transfer efficiency.
Energy Loss in Food Chains
- Energy Inefficiency: Energy loss occurs at each trophic level, limiting food chains to about 5 organisms due to inefficiencies.
- Energy Transfer Example: When an organism preys on another, like a barn owl, it only gains a small fraction (0.1J) of energy from each owl consumed.
- Survival Challenges: To survive, the predator must consume a large number of owls daily and expend minimal energy in hunting.
- Requirement for Survival: The predator needs to consume numerous owls daily to meet its energy needs.
- Energy Efficiency in Hunting: The predator must conserve energy during the hunting process to sustain itself.
A typical pyramid of energy would look like this: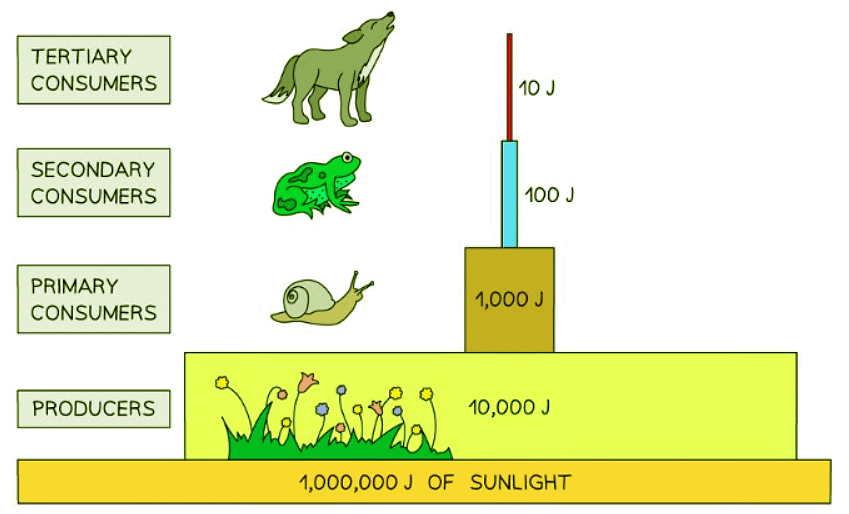
Impact of Human Food Choices
- Humans are omnivores, obtaining energy from both plants and animals, allowing a choice in diet.
- These dietary choices influence agriculture and ecosystem usage.
- Consider different food chains involving humans:
- Wheat → Cow → Human
- Wheat → Human
- Considering energy transfer in food chains, it becomes evident that consuming wheat directly provides humans with more available energy compared to consuming cows that feed on wheat.
- This is due to the energy loss as it moves up the trophic levels, resulting in less energy available for humans if they consume cows.
- Thus, within a crop food chain, it is more energy efficient for humans to act as herbivores rather than carnivores.
- In practice, humans often feed animals with plants that are unsuitable for human consumption, such as grass, or are too widespread for direct collection, like algae in the ocean, which indirectly contribute to the food chain.
Question for Pyramids of EnergyTry yourself: Which of the following factors contributes to the loss of energy in ecosystems?View Solution
The document Pyramids of Energy | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
101 videos|193 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Pyramids of Energy - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is a pyramid of energy? |  |
Ans. A pyramid of energy is a graphical representation of the flow of energy through different trophic levels in an ecosystem. It shows the amount of energy transferred from one trophic level to the next, with each level representing a decrease in energy as it moves up the food chain.
| 2. How are pyramids of energy different from pyramids of biomass? |  |
Ans. Pyramids of energy show the flow of energy through trophic levels, while pyramids of biomass represent the total amount of living material at each trophic level. Energy pyramids focus on the transfer of energy, while biomass pyramids focus on the amount of living organisms.
| 3. Why is the shape of a pyramid of energy always pyramid-shaped? |  |
Ans. A pyramid of energy is always pyramid-shaped because energy is lost as heat at each trophic level, resulting in a decrease in available energy as it moves up the food chain. This loss of energy leads to a decrease in the amount of energy available at higher trophic levels, creating the pyramid shape.
| 4. How do pyramids of energy help us understand ecosystem dynamics? |  |
Ans. Pyramids of energy provide a visual representation of how energy flows through an ecosystem, showing the transfer of energy from producers to consumers. By analyzing these pyramids, we can understand the efficiency of energy transfer, the importance of different trophic levels, and the overall stability of an ecosystem.
| 5. What are some limitations of using pyramids of energy to represent ecosystems? |  |
Ans. One limitation of pyramids of energy is that they do not account for the recycling of nutrients within an ecosystem. Additionally, they may not accurately represent all ecosystems, as some food chains may have more complex interactions that do not fit neatly into a pyramid structure.
Related Searches















