UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC > Pyrrole, Furan and Thiophene Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
Pyrrole, Furan and Thiophene Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Nucleophilic Substitutions in Pyrrole, Furan and Thiophene |

|
| Furans |

|
| Condensed Five-Membered Heterocycles |

|
| Vilsmeier–Haack Formylation with N,N-Dimethylformamide. |

|
Introduction
- Electron-withdrawing substituents (W) at the position “α” to the heteroatom generally cause substitution at the 4- and / or 5-position.

- Electron-donating substituents (D) at the position “α” to the heteroatom tend to cause substitution at both the remaining “α” position (C-5) and at the (3-position).

- Electron-withdrawing substituents (W) at the position “β” to the heteroatom facilitate substitution
at position 5.

Electron-donating substituents (D) at the position “β” to the heteroatom generally cause substitution to take place at the 2-position.

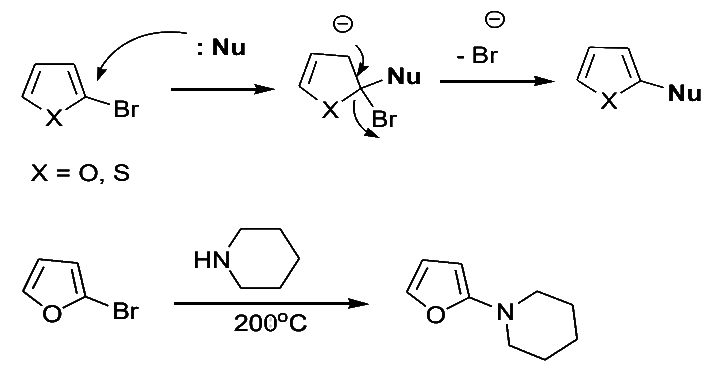
Nucleophilic Substitutions in Pyrrole, Furan and Thiophene
- We have seen that the reactivity of pyrrole, furan and thiophene towards electrophilic substitution is in the following order

- The reactivity of these rings towards nucleophilic substitution is in the opposite order

- Pyrroles: the pyrrole ring is the least reactive and both 2-haloand 3-halopyrroles behave like-aryl halides in nucleophilic displacement. Thus, 2-chloropyrrole does not react with potassium tert-butoxide or with lithium aluminum hydride

Furans
- Furns are more reactive towards nucleophilic displacement than pyrrole. 2-bromo- and 2-chloro react with piperidine at 200oC as follows:

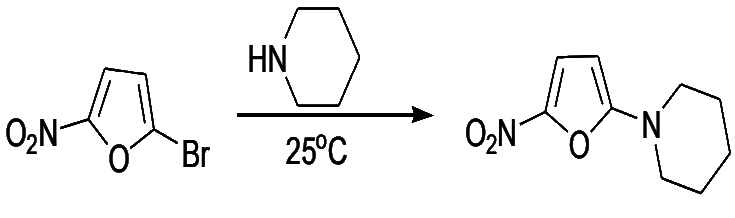
- The presence of electron-withdrawing groups on the furan ring facilitates nucleophilic displacement. Thus, 2-bromo-5-nitrofuran and methyl 2-bromo-5-carboxylate react readily with nucleophiles


- It is of considerable interest that in these reactions the furans react about 10 times faster than the corresponding benzene analogues. This strong behavior has also been observed in theiophene series
Question for Pyrrole, Furan and Thiophene Nucleophilic Substitution ReactionsTry yourself: Which of the following statements is true regarding the reactivity of pyrrole, furan, and thiophene towards nucleophilic substitution?View Solution
Thiophenes
- Nucleophilic substitution occurs much more readily within the thiophene series than it does for the corresponding benzene compounds. The thiophenes are at least 1000 times more reactive than corresponding benzene analogues (This increased reactivity has also been noticed in the electrophilic substitution of thiophenes compared to the corresponding benzene analogues).
- The increased reactivity of thiophene ring nucleophilic substitution can be explained by Wheland intermediates involved in nucleophilic substitution of bromine in 2-bromo-5- nitrothiophene.

- It is suggested that the sulfur atom causes additional stabilization by involvement of its d-orbitals "Structure III"
- It must be noted that the lone pair of the sulphur atom also enters into resonance with the π electrons. X-ray studies indicate that the valency angle of C-S-C in thiophene is nearly 91o and not 105o as expected. This can be explained by assuming that the 3d orbital of sulphur are also used in resonance and following additional contributing structures may be written.

- Copper-meditated nucleophilic substitutions of halo thiophenes are also of great synthetic utility. Examples of some transformation follow

Condensed Five-Membered Heterocycles
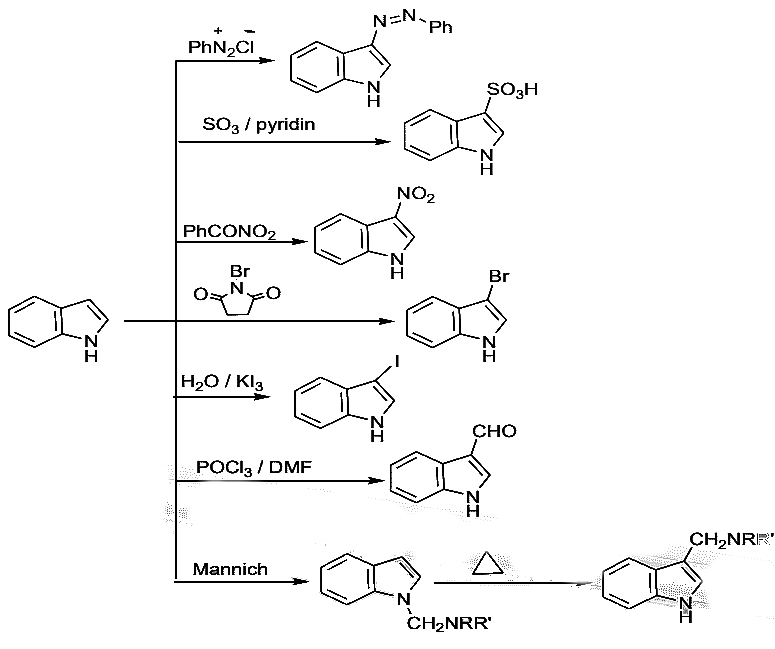
Fusing benzene ring with 2,3-positions of furan, pyrrole and thiophene leading to benzo[b]furan, indole and benzo[b]thiophene, respectively.
- The molecular orbital description of benzofused heterocycles with one heteroatom is very similar to that furan, pyrrole and thiophene, the only added feature being distribution of π- electrons. The reactivity of these fused heterocycles is lower than that of the parent heterocycle but still higher than that of benzene.
- Position 3- is preferred position for electrophilic attack in indole, since it results in two more stable resonance structures in the aromatic sixtet of the benzene ring is preserved, which attack at position 2-yield one structure only in which the aromatic sixtet is preserved.

- Attack at position 2-

- Attack at position 3-

Vilsmeier–Haack Formylation with N,N-Dimethylformamide.
- The mechanism of the reaction involves first the phosphorylation of the carbonyl oxygen of the formamide with POCl3 to form a dichlorophosphate. Chloride ion then displaces the phosphate group, which forms the electrophilic species that attacks the ring. Hydrolysis of the imino group restores the carbonyl group.

- Electrophilic substitution in benzo[b]furan occurs mainly at C-2.

- Both C-2 and C-3 of benzo[b]thiophene are involved as the intermediates are of comparable stability

The document Pyrrole, Furan and Thiophene Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
FAQs on Pyrrole, Furan and Thiophene Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions - Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are nucleophilic substitutions in pyrrole, furan, and thiophene? |  |
Ans. Nucleophilic substitutions in pyrrole, furan, and thiophene are chemical reactions in which a nucleophile replaces a leaving group in these heterocyclic compounds. These reactions are commonly used in organic synthesis to introduce functional groups into these compounds.
| 2. How do nucleophilic substitutions in furans occur? |  |
Ans. Nucleophilic substitutions in furans occur when a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic carbon atom in the furan ring, displacing a leaving group. This can lead to the formation of various substituted furan derivatives with different functional groups.
| 3. What are condensed five-membered heterocycles? |  |
Ans. Condensed five-membered heterocycles are compounds that contain two or more fused five-membered rings. These rings can be heterocyclic, meaning they contain atoms other than carbon, such as nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur. Examples of condensed five-membered heterocycles include indoles, benzofurans, and benzothiophenes.
| 4. What is Vilsmeier-Haack formylation with N,N-dimethylformamide? |  |
Ans. Vilsmeier-Haack formylation with N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) is a chemical reaction used to introduce a formyl group (-CHO) into aromatic compounds. In this reaction, DMF reacts with a strong electrophile, such as phosphorus oxychloride (POCl3), to form a reactive intermediate that can then react with an aromatic compound to form a formylated product.
| 5. How do pyrrole, furan, and thiophene undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions? |  |
Ans. Pyrrole, furan, and thiophene can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions when a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic carbon atom in the heterocyclic ring, displacing a leaving group. The nucleophile can be a wide range of compounds, such as amines, alkoxides, or thiolates. These reactions can lead to the formation of various substituted derivatives of pyrrole, furan, and thiophene with different functional groups.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches