Ramesh Singh Summary: Micro & Macro Economies, Different Economic Systems | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is Economics? |

|
| Macroeconomics vs. Microeconomics |

|
| Economic Systems |

|
| Market Economic System |

|
| Command Economic System |

|
In This Chapter
► Meaning and Scope of economics.
► Branches of economics viz., Macroeconomics and Microeconomics.
► Meaning, salient features of Economic systems viz., Market Economy, Socialist Economy, Communist Economy and Mixed Economy.
► Advantages and disadvantages of different economic systems.
► Sectors of an economy.
Introduction
- Economics is one of the oldest and most influential of intellectual disciplines.
- Practically all the great thinkers, from Aristotle to Einstein, have tried their hand at it, and the great economists like Adam Smith, Thomas Malthus, David Ricardo, John Maynard Keynes and Milton Friedman rank among the most influential minds in our history.
- The word economics comes from two Greek words- “Oikos” and “Nomos” which literally means “rule or law of the household”.
- Economic thought goes as far back as the ancient Greeks, and is known to have been an important topic in the ancient Middle East. However, Scottish thinker Adam Smith is widely credited for creating the field of economics. He is considered as the father of modern Economics.
- In 1776, Adam Smith’s book- "An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations", commonly referred as "The Wealth of Nations" was first published. It is considered by many as the seminal work on modern day economics.
 Adam Smith’s The Wealth of Nations
Adam Smith’s The Wealth of Nations
What is Economics?
 Definition of Economics
Definition of Economics
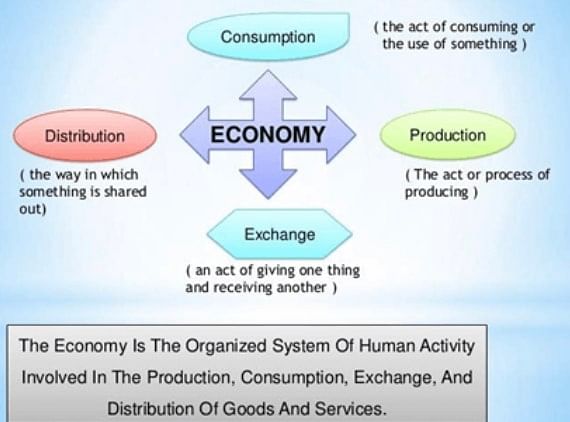
- In simple words, economics studies the economic activities undertaken by humans. Economics studies how goods and services are produced, distributed and consumed in a society.
- Economics is the study of the ways in which people use resources to satisfy their wants.
- All of us want food, clothing and shelter to stay alive. But most of us want much more. We want cars, television sets, vacation etc—in fact, our wants are unlimited.
- In contrast, resources available to satisfy our wants are limited. Even in a wealthy country like the United States there is never enough of everything to satisfy all the wants of every person in the country.
- Economics is thus the study of how societies use scarce resources to produce valuable commodities and distribute them among different people. It studies how individuals, firms, governments and other organizations within our society make choices and how these choices determine the society’s use of its resources.
- Economics is the study of ‘how a society uses its scarce resources to fulfill unlimited needs and wants of its members’.
- As resources are always in short supply, British economist Lionel Robbins described economics as ‘the science of scarcity’.
Branches of Economics
- The two main branches of economics are macroeconomics and microeconomics.
 Two main branches of Economics
Two main branches of Economics
Macro and Micro are Greek words which mean ‘Big ‘and ‘small’ respectively.
Macroeconomics:
- Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that studies how an overall economy behaves.
- Macroeconomics looks at the overall, big-picture scenario of the economy. It focuses on the way the economy performs as a whole
- Macroeconomics studies larger phenomena such as inflation, price levels, rate of economic growth, national income, gross domestic product (GDP), and changes in unemployment.
- Some of the key questions addressed by macroeconomics include: What causes unemployment? What causes inflation? What creates or stimulates economic growth? Macroeconomics attempts to measure how well an economy is performing, to understand what forces drive it, and to project how performance can improve.

Macroeconomics
Microeconomics:
Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of individual units in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individual units.- Microeconomics is more focused on the choices made by individual actors in the economy (like people, households, industries, etc.).
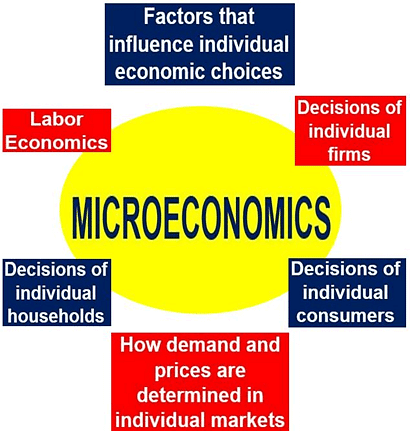 Microeconomics
Microeconomics
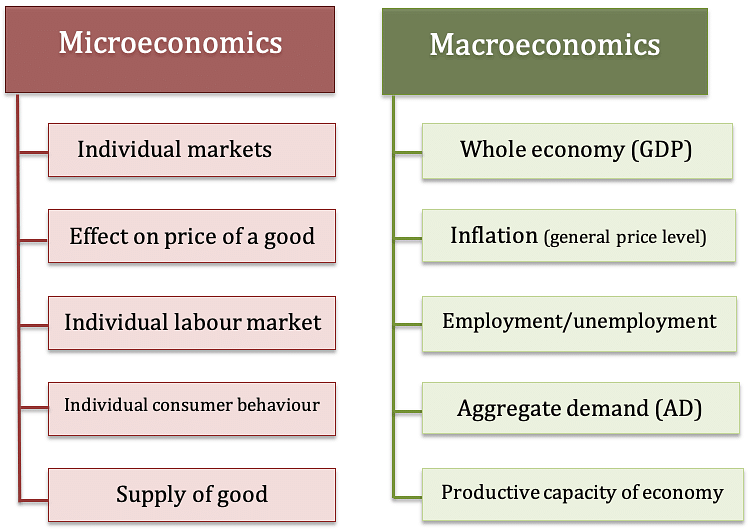
Macroeconomics vs. Microeconomics
Though macroeconomics and micro economics appear to be different, actually they are interdependent and complementary to each other. There are many overlapping issues between them.
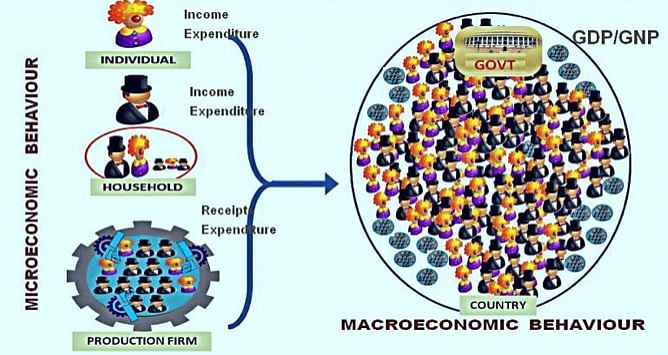 Microeconomic and Macroeconomic Behaviour
Microeconomic and Macroeconomic Behaviour
- Macroeconomics is overall study of microeconomic units. For example, employment of the country is the sum of all individual employment in different sectors. National income and national output is the sum of income and output of thousands of person and firms. Price level shows the average price, which comes through the appropriate calculation of prices of all transected commodities in the country in a fiscal year.
- Likewise, Microeconomics matters deeply depend upon the macroeconomic activity. For example, price, rate of interest, rate of profit, wages etc all are known as microeconomic topics. But they depend upon macroeconomic behavior. Price, rate of interest, wage are determined by their demand and supply in country not by individual demand and supply. Same way, profit of any firm depends upon the nature of market, aggregate demand, national income, and general price level in economy. Aggregate demand, price level, national income, employment etc are deeply affected by macroeconomic fluctuations. Thus, change in macroeconomic indicators brings the change in microeconomic activities.
- Simply put, if macroeconomics is study about the forest than microeconomics is study about the trees.
- While macroeconomics deals with the big picture (the forest), microeconomics deals with the details (the trees) which make up the forest.
- Macroeconomics follows a top-down approach while microeconomics follows a bottom-up approach.
Economic Systems
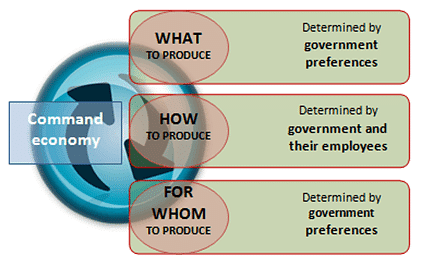
Every society has to answer some important questions regarding production of goods and services viz,
- What kind of goods and services should be produced in the society?
- What mode of production should be adopted?
- How will the produced goods and services be distributed among people?
- Who will own the Factors of production?
- Who will control/regulate the economic activities and how much should be the control?
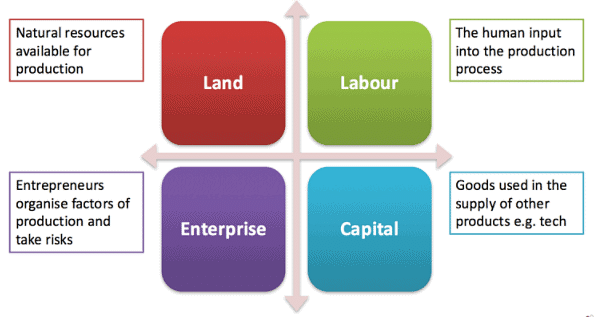 Factors of Production
Factors of Production
➤ Factors of Production
- As an answer to the above questions, different types of economic systems took birth. Each of the economic system has its own way of organizing the economy.
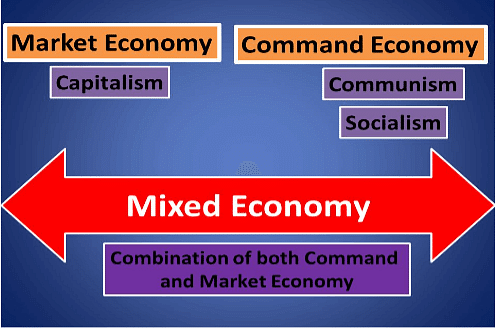
- Important economic systems found in the contemporaneous world can be classified as:
 Economics Systems
Economics Systems
Market Economic System
- Market economic system is considered as the first formal economic system emerging out of the traditional economic system.
- It is also known as Capitalist economy, free market economy, laissez faire economy etc.
- The origin of market economic system can be traced back to teachings of Adam Smith in his seminal book – Wealth of the nations.
- The free market economic system was first tried in the USA from 1777 onwards from where it spread to other parts of the world especially Western Europe and North America. The countries those adopted free market economic system enjoyed high prosperity and operated well till 1929 when they were hit by the Great American depression. The Great American Depression was caused due to the drawbacks of the free market economy.
➤ Features of Market Economic System
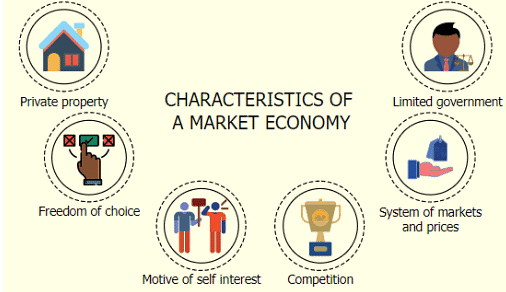 Characteristics of a Market Economy
Characteristics of a Market Economy- Market led: A market economy is a type of economic system where forces of supply and demand regulate the economy. Production, utilization of resources, pricing, employment level etc are according to demand and supply of goods and services. Only the goods demanded are produced. Wage and employment level too are determined by demand and supply of labor. Rent and interest rate are determined by demand and supply of land and capital respectively.
- No governmental intervention: One of the most important characteristics of a market economy is Laissez faire or limited role or non intervention of the government in economic activities. Most economic decisions are made by buyers and sellers, not the government. In market economy, government is facilitator not doer. It does not make the investment. It does not decide about Production, utilization of resources, determination of prices, employment, distribution of benefits etc.
- Private Ownership: All the resources/factors of production are owned by Private Sector (private individuals and businesses). The decisions about the allocation of those resources are made by individuals without government intervention.
- Motive of self interest: A market economy is driven by the motive of self-interest. Consumers have the motive of trying to get the greatest benefits. Entrepreneurs try to get the highest profits for their businesses. Workers try to get the highest possible wages and salaries. Owners of capital resources try to get the highest possible prices from the rent or sale of their resources. This "invisible hand" of self-interest is the driving force of a market economy.
- Competition: is another major characteristic of a market economy.
Everybody is allowed to participate in the economic activities and compete according to their capabilities. Instead of government regulation, competition limits abuse of economic power by one business or individual against another. - Freedom of choice: Since there is no governmental intervention in the activities of people and business organizations, each of them has freedom to choose occupations, subject of interest and way of life. Each of them performs activities according to their own motives. The government just facilitates them.
➤ Advantages of Market economy
- More choice for consumers: In a market system, producers compete with each other by offering wider variety and better quality of goods and services, therefore consumers have more choice, and this may even lead to lower prices.
- Efficiency: A market economy rewards the most efficient producers since efficient producers will earn more money than inefficient producers.
- Rewards innovation: New, exciting products will satisfy consumer demand better than existing products. This often gives great push to innovate or create new and exciting products which gives fillip to innovation and creativity.
- Investment: Market economies encourage successful businesses to invest in up-and-coming companies, thus increasing the quality of production.
- Faster economic growth: Due to more freedom, higher competition and efficiency in a market economy, countries that adopts market economy often experiences rapid economic growth and prosperity.
➤ Disadvantages of Market economy
- Free market economy increases the gap between the rich and the poor: When firms and individuals are able to produce and consume freely, it makes the rich even richer because they have more decision making power, and the poor may become poorer because they have less decision making power in the market. The market system allocates more goods and services to those consumers who have more money than others.
- Neglects negative externalities: When firms are always trying to maximize their profits, they may ignore external costs like damages to the environment, labor welfare etc.
- Free market may encourage harmful and sin goods: If there are people in the market who wish to buy dangerous goods like narcotic drugs, the market will be ready to sell it since private firms will be willing to provide anything that is profitable.
- Lack of safety net for the needy: The key mechanism of a market economy is competition. As a result, it has no system to care for those who are at an inherent competitive disadvantage. That includes the elderly, children, and people with mental or physical disabilities.
- Neglects social needs: Because market economy is mainly oriented towards profit maximization, many goods and services which are very important for the society as a whole, but which are not very profitable may be produced in lesser number. A market economy may produce private jets for some while others starve and are homeless.
- Negligible welfare role of the State: The role of the state in a market economy is very negligible and hence it reduces the capacity of the state in providing welfare activities to its citizens.
- Monopoly: Lack of government intervention in market economy can lead to creation of cartels and monopolies which in turn will lead to exploitation of the customers.
Command Economic System
- The Command economic system also known as State economy, nonmarket economy, planned economy etc. evolved as a reaction to the negative aspects of Market economy.
- The ideals of command economic system are rooted in the teachings of German philosopher Karl Marx.
 Karl Marx
Karl Marx
➤ Features of Command economy
- In a command economy, State /government takes the decisions regarding all economic activities. The government creates an economic plan. The central plan sets the priorities for the production of all goods and services. The government allocates all resources according to the central plan.

Command Economy
- Government owns (Public ownership) all the factors of production and business enterprises. All economic roles will be played by government only. Private property rights are not allowed in a command economy.
- There is complete state monopoly in the economic sphere. The idea of competition does not exist in a command economy.
- Government fixes the prices of goods and services. Supply and demand are determined by the government not by consumers and producers.
- In a command economy, people play economic roles according to their abilities and in return get facilities from the government as per their needs.
➤ Types of Command Economy
- There are 2 main types of command economy namely:
- Socialist economy - It took birth in 1919 in the USSR after the Russian Revolution or the Bolshevik Revolution under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin.
- Communist economy - It took birth in the People’s Republic of China in 1949. It is the purest form of non market economy or command economy.
|
110 videos|315 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Ramesh Singh Summary: Micro & Macro Economies, Different Economic Systems - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the difference between macroeconomics and microeconomics? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of economic systems? |  |
| 3. How does a market economic system work? |  |
| 4. What are the characteristics of a command economic system? |  |
| 5. How do different economic systems impact individual consumers and businesses? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|