DC Pandey Solutions: Reflection of Light | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Introductory Exercise 27.1
Ques 1: Show that the unit of 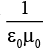 is m/s.
is m/s.
Sol: 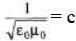 = Speed of light in vacuum.
= Speed of light in vacuum.
Ques 2: The magnetic field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given by (SI units)
By = (2 × 10-7 T) sin [500 x + 1.5 × 1011 t]
(a) What is the wavelength and frequency of the wave?
(b) Write an expression for the electric field vector.
Ans: 
= 0.0125 m= 1.25 cm
= 2.39 × 1010Hz
E0 = cB0
= (3 × 108)(2 × 10-7) = 60 V/m
kx and ωt have same sign. Therefore, electromagnetic wave is travelling along negative x direction.  are in mutually perpendicular direct ions. Hence oscillations
are in mutually perpendicular direct ions. Hence oscillations  of are along z-direction.
of are along z-direction.
Introductory Exercise 27.2
Ques 1: Prove that for any value of angle i, rays 1 and 2 are parallel.
Sol: 
PQ and MN are mutually parallel. Rays 1 and 2 are making equal angles (= ∠i) from PQ and MN. So, they are mutually parallel.
Ques 2: A man approaches a vertical plane mirror at speed of 2 m/s. At what rate does he approach his image?
Sol: 
Ques 3: A pole of height 4 m is kept in front of a vertical plane mirror of length 2 m. The lower end of the mirror is at a height of 6 m from the ground. The horizontal distance between the mirror and the pole is 2 m. Up to what minimum and maximum heights a man can see the image of top of the pole at a horizontal distance of 4 m (from the mirror) standing on the same horizontal line which is passing through the pole and the horizontal point below the mirror?
Sol:
PQ = Pole
MN = Image of pole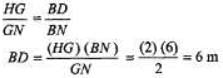
Minimum height required = AD = BD + AD = 10m
Further,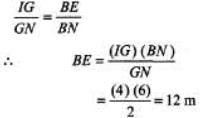
Maximum height required = AE = BE+ AB = 16 m
Introductory Exercise 27.3
Ques 1: Assume that a certain spherical mirror has a focal length of- 10.0 cm. Locate and describe the image for object distances of
(a) 25.0 cm (b) 10.0 cm (c) 5.0 cm.
Sol: Apply 
(a) f = -10 cm, u = - 25 cm Solving we get, v = -16.7cm
Since, v is negative, image is in front of mirror. So it is real. Similarly, we can solve for other parts.
Ques 2: A ball is dropped from rest 3.0 m directly above the vertex of a concave mirror that has a radius of 1.0 m and lies in a horizontal plane.
(a) Describe the motion of ball's image in the mirror.
(b) At what time do the ball and its image coincide?
Sol: (a) From O to F, image is real.
From F to P, image is virtual.
At O
∴ 
v = - 0.6 m
(b) When object is at C and P, image coincides with object. Using,
or 

Ques 3: A spherical mirror is to be used to form on a screen 5.0 m from the object an image five times the size of the object.
(a) Describe the type of mirror required.
(b) Where should the mirror be positioned relative to the object?
Sol: (a) Image has to be taken on a screen. So it should be real. Hence mirror should be concave.
Image is 5 times magnified. Hence, | v | = 5 | u |
or
(5 + x) = 5x
Solving we get, x = 1.25 cm
Now using, 
We have, 
Solving we get, R = - 2.08 m
Ques 4: Figure shows two rays P and Q being reflected by a mirror and going as F and Q'. State which type of mirror is this?
Sol: Reflected rays are neither converging nor diverging. Hence, mirror is plane.
Ques 5: The following table shows object distance, object size, and mirror focal length (all in centimeters) for various situations. Use ray tracing to determine the image size and location for each case.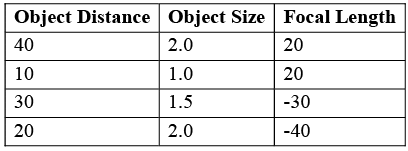
Sol: Let us draw the ray diagram for the first part.
In ΔO1O2P and ΔP I1I2 we have,
or
x = (20)(I1,I2) ...(i)
In ΔO1O2C and l1I2 C we have, 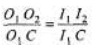
∴ 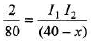
or (40 - x) = 40(I1I2) ....(ii)
Solving Eqs. (i) and (ii) we get, 
Ques 6: Complete the following table for spherical mirrors. All distances are in centrimeters.
| Mirror Type | Radius | Focal Length | Object Distance | Image Distance | Lateral Magnification | Real/Virtual Image |
| -25 | 40 | |||||
| 20 | -30 | |||||
| +15 | +30 | |||||
| 20 | -2.0 | |||||
| +20 | -40 | |||||
| -10 | +2.0 |
Sol: Negative focal length means concave mirror and positive focal length means convex mirror.
Apply, 
And 
Further, if v is negative then image is in front of mirror. So, it is real and inverted.
R = 2f
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions: Reflection of Light - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is reflection of light? |  |
| 2. How does reflection of light occur? |  |
| 3. What is the law of reflection? |  |
| 4. What are the types of reflection? |  |
| 5. How is reflection of light used in everyday life? |  |

















