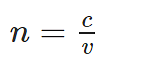Refraction of Light & Total Internal Reflection | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Refraction? |

|
| What is Total Internal Reflection? |

|
| Formula of Total Internal Reflection |

|
| Applications of Total Internal Reflection |

|
| Important Questions for Exam |

|
What is Refraction?
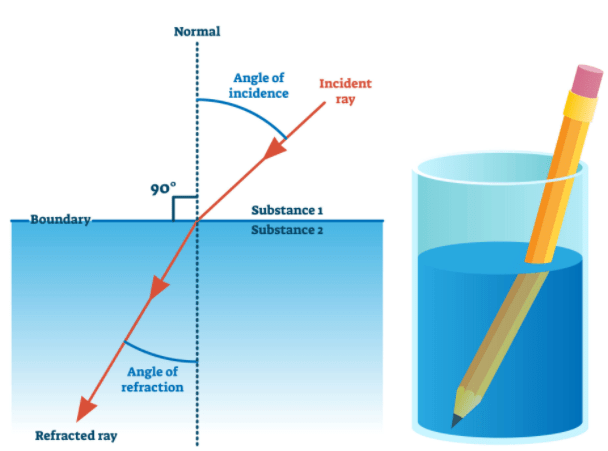
- Refraction is the bending of a wave when it passes from one medium to another. The bending is caused due to the differences in density between the two substances.
 Refraction
Refraction - Refraction of light is one of the most commonly observed phenomena, but other waves like sound waves and water waves also experience refraction.
- Refraction makes it possible for us to have optical instruments such as magnifying glasses, lenses and prisms. It is also because of the refraction of light that we are able to focus light on to our retina.
Why do stars twinkle?
Did you know that the twinkling effect of stars is due to atmospheric refraction? The starlight undergoes several refractions while reaching the Earth. This atmospheric refraction occurs in a medium of gradually changing refractive index.
Causes of Refraction
- A light ray refracts whenever it travels at an angle into a medium of different refractive index. This change in speed results in a change in direction. As an example, consider air travelling into water. The speed of light decreases as it continues to travel at a different angle.

- The refraction of light in glass is shown in the figure above. When light travels from air into glass, the light slows down and changes direction slightly. When light travels from a less dense substance to a denser substance, the refracted light bends more towards the normal line.
- If the light wave approaches the boundary in a direction that is perpendicular to it, the light ray doesn’t refract in spite of the change in speed.
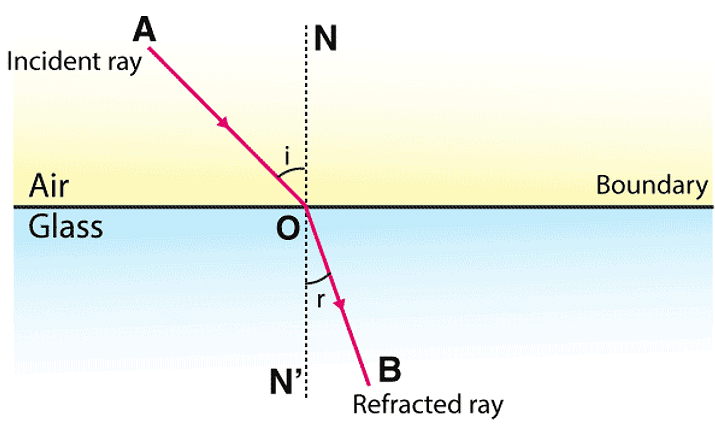
Laws of Refraction of Light
Laws of refraction state that:
- The incident ray refracted ray, and the normal to the interface of two media at the point of incidence all lie on the same plane.
- The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant. This is also known as Snell’s law of refraction.

What is Refractive Index?
- The Refractive index, also called the index of refraction describes how fast light travels through the material.
- Refractive Index is dimensionless. For a given material, the refractive index is the ratio between the speed of light in a vacuum (c) and the speed of light in the medium (v). If the refractive index for a medium is represented by n, then it is given by the following formula:

- Based on the refractive index of the medium, the light ray changes its direction, or it bends at the junction separating the two media. If the light ray travels from a medium to another of a higher refractive index, it bends towards the normal, else it bends away from the normal.
Refraction of Light in Real Life
- Mirage and looming are optical illusions which are a result of refraction of light.
- A swimming pool always looks shallower than it really is because the light coming from the bottom of the pool bends at the surface due to refraction of light.
- Formation of a rainbow is an example of refraction as the sun rays bend through the raindrops resulting in the rainbow.
- When white light passes through a prism it is split into its component colours – red, orange, yellow, green, blue and violet due to refraction of light.
Applications of Refraction of Light
Refraction has many applications in optics and technology. A few of the prominent applications are listed below:
- A lens uses refraction to form an image of an object for various purposes, such as magnification.
- Spectacles worn by people with defective vision use the principle of refraction.
- Refraction is used in peepholes of house doors, cameras, movie projectors and telescopes.
Solved Examples
Q.1. Light travelling in air enters into an optical fibre of refractive index 1.44.
a) In which direction does the light bend?
b) If the angle of incidence on one end of the fibre is 22o, then what is the angle of refraction?
Solution:
a) The light travels from rarer medium(air) to denser medium(optical fibre), hence the refracted ray will bend towards the normal.
b) The angle of refraction can be calculated as follows:
Let air be medium 1 and optical fibre be medium 2. Therefore, n1 = 1.00, n2 = 1.44, and θ1= 22o.
Now, substituting the values in the equation as follows:
(1.00) sin 22o = 1.44 sin θ2.
sin θ2 = (1.00/1.44) sin 22o = 0.260
θ2 = sin-1 (0.260) = 15o
Q.2. The light travelling through the optical fibre reaches the end of the optical fibre and exits into the air. If the angle of incidence at the end of the tube is 30o. Then what would the angle of refraction outside the fibre be?
Solution: Let the fibre be medium 1 and air medium 2. Therefore, n1 = 1.44, n2 = 1.00, and θ,1 = 30o. Substituting the values in the equation, we get
(1.44) sin 30o = 1.00 sin θ2
sin θ2 = (1.44/1.00) sin 30o = 1.44 (0.500) = 0.720
θ2 = sin-1 (0.720) = 46o
This time we notice that the angle of refraction is larger than the angle of incidence. This indicates that the light is bending away from the normal as it enters a rarer material.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q.1. Define Refraction.
The change in the direction of a wave when it passes from one medium to another is known as refraction.
Q.2. When does refraction of waves occur?
The refraction of light occurs when a light wave, incident at an angle away from the normal, passes a boundary from one medium into another in which there is a change in velocity of the light.
Q.3. When is the refraction of light not possible?
When the incident light is perpendicular to the boundary, refraction of light is not possible.
Q.4. What is the difference between reflection and refraction in the light?
Reflection of light is when the light bounces off a medium. If the medium has a smooth surface, then the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Refraction of light is the change in the direction of light as it passes from one medium to another.
Q.5. State an example of refraction of light.
An example of refraction is the rainbow. The light rays bend as they enter water drops in the atmosphere forming a rainbow.
What is Total Internal Reflection?
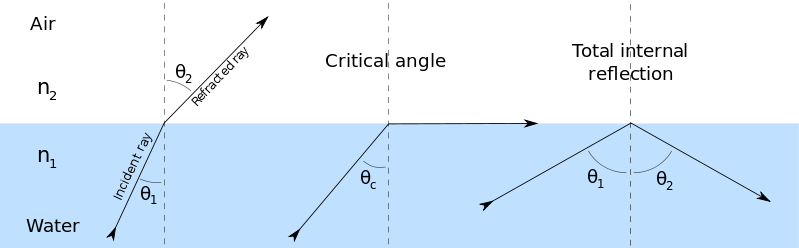
When a light ray travelling from a denser medium towards a rarer medium is incident at the interface at an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle, then light rays get reflected back into the denser medium. This phenomenon is called Total Internal Reflection.
 Total Internal Reflection
Total Internal Reflection
[Question: 907154]
- Consider the following situation. A ray of light passes from a medium of water to that of air. Light rays will be refracted at the junction separating the two media.
- Since it passes from a medium with a higher refractive index to that having a lower refractive index, the refracted light ray bends away from the normal.
- At a specific angle of incidence, the incident ray of light is refracted in such a way that it passes along the surface of the water. This particular angle of incidence is called the critical angle. Here the angle of refraction is 90 degrees.
- When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, the incident ray is reflected back to the medium. We call this phenomenon total internal reflection.
- The refractive index is maximum for the violet colour of light and minimum for the red colour of light. i.e., μv > μ R therefore, the critical angle is maximum for the red colour of light and minimum for the violet colour of light, i.e., Cv < CR
The following are the two conditions of total internal reflection:
- The light ray moves from a more dense medium to a less dense medium.
- The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle.
Note: The critical angle increases with temperature.
[Question: 907156]
Formula of Total Internal Reflection
Total Internal Reflection: 
Critical Angle, θ: sinθ = n2/n1 (n1 > n2)
- r is the angle of refraction
- i is the angle of incidence
- n1 is the refractive index in medium 1
- n2 is the refractive index in medium 2
- θ is the critical angle
Applications of Total Internal Reflection
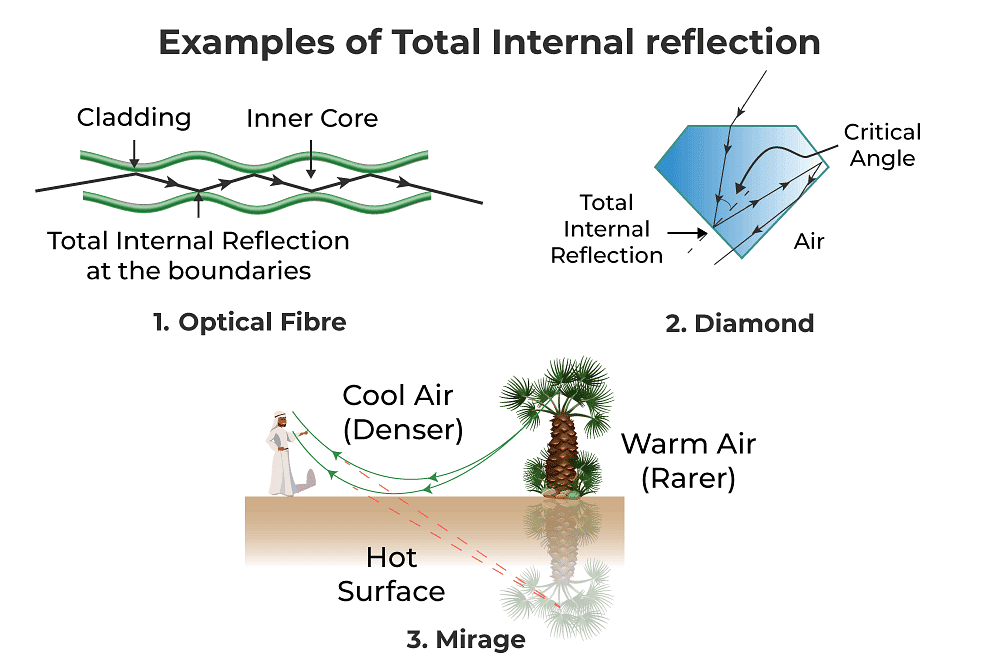 Applications of Total Internal Reflection
Applications of Total Internal Reflection
➢ Optical Fibre
- When the incident ray falls on the cladding, it suffers total internal reflection as the angle formed by the ray is greater than the critical angle.
- Optical fibres have revolutionised the speed with which signals are transferred, not only across cities but across countries and continents making telecommunication one of the fastest modes of information transfer.
- Optical fibres are also used in endoscopy.
➢ Diamond
- When the incident ray falls on every face of the diamond such that the angle formed, the ray is greater than the critical angle. The critical value of the diamond is 23°.
- This condition is responsible for the total internal reflection in a diamond which makes it shine.
➢ Mirage
- It is an optical illusion that is responsible for the appearance of the water layer at short distances in a desert or on the road.
- Mirage is an example of total internal reflection which occurs due to atmospheric refraction.
Important Questions for Exam
Q1: An optical fibre made up of glass with a refractive index of n1 = 1.5 which is surrounded by another glass with refractive index n2. Find the refractive index n2 of the cladding such that the critical angle between the two cladding is 80°.
Solution.
Critical angle, θ = 80°
Refractive index, n1 = 1.5
Refractive index n2 =?
Using the below formula, we can calculate n2:
sinθ = n2/n1
sin80∘ = (n2 / 1.5)
n2 = 1.5 * sin80∘
n2 = 1.48
Q2: Find the refractive index of the medium whose critical angle is 40°.
Solution.
Critical angle, θ = 40°
The refractive index of the medium, μ =?
μ = 1/sinθ
μ = 1/sin40∘
μ =1/0.65
µ = 1.6
Q3: Which of the following is an example of total internal reflection?
1. Mirror
2. Twinkling of stars
3. Mirage
4. Thin film of soap bubble
Answer: Option 3: Mirage
Explanation: Mirage is an example of total internal reflection.On hot summer days, the air near the ground becomes hotter than the air at higher levels. Due to this, there is a difference in the refractive index of the air in different layers.
- To a distant observer, the light appears to be coming from somewhere below the ground. The observer naturally assumes that light is being reflected from the ground, say, by a pool of water near the tall object.
- Such inverted images of distant tall objects cause an optical illusion to the observer. This phenomenon is called a mirage.
Q4: A scuba diver is wearing a head lamp and looking up at the surface of the water. If the minimum angle to the vertical resulting in total internal reflection is 25∘, what is the index of refraction of the water?
θair=1
a) 2.37
b) 0.85
c) 0.49
d) 1.12
Answer: 2.37
Solution: 
|
97 videos|336 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on Refraction of Light & Total Internal Reflection - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is refraction and how does it occur? |  |
| 2. What conditions are necessary for total internal reflection to occur? |  |
| 3. What is the formula for calculating the critical angle in total internal reflection? |  |
| 4. What are some practical applications of total internal reflection? |  |
| 5. How does the refractive index affect the refraction and total internal reflection of light? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|