Refraction of Light & Total Internal Refraction | Science Class 10 PDF Download
What is Refraction of Light?
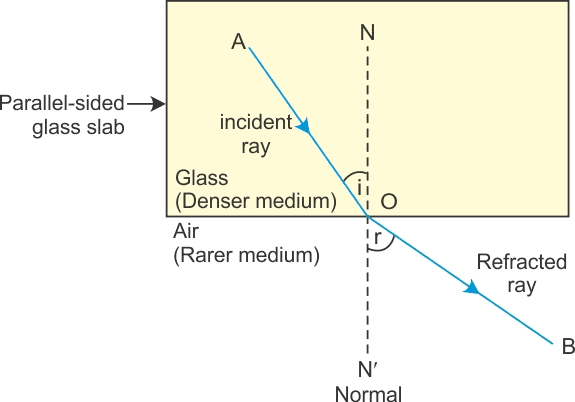
The bending of a ray of light as it passes from one medium to another is called refraction.
It is due to a change in the velocity of light while travelling from one medium to another.
- The maximum velocity of light is 3 x 108 m/sec in a vacuum or air.
- The velocity is less in the denser medium.
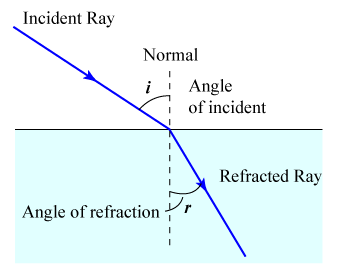 Refraction of Light
Refraction of Light
Why do stars twinkle?
Did you know that the twinkling effect of stars is due to atmospheric refraction? The starlight undergoes several refractions while reaching the Earth. This atmospheric refraction occurs in a medium of gradually changing refractive index.
Causes of Refraction
- Change of Speed Results in Change in Direction
A light ray refracts whenever it travels at an angle into a medium of different refractive index. This change in speed results in a change in direction. As an example, consider air travelling into water. The speed of light decreases as it continues to travel at a different angle.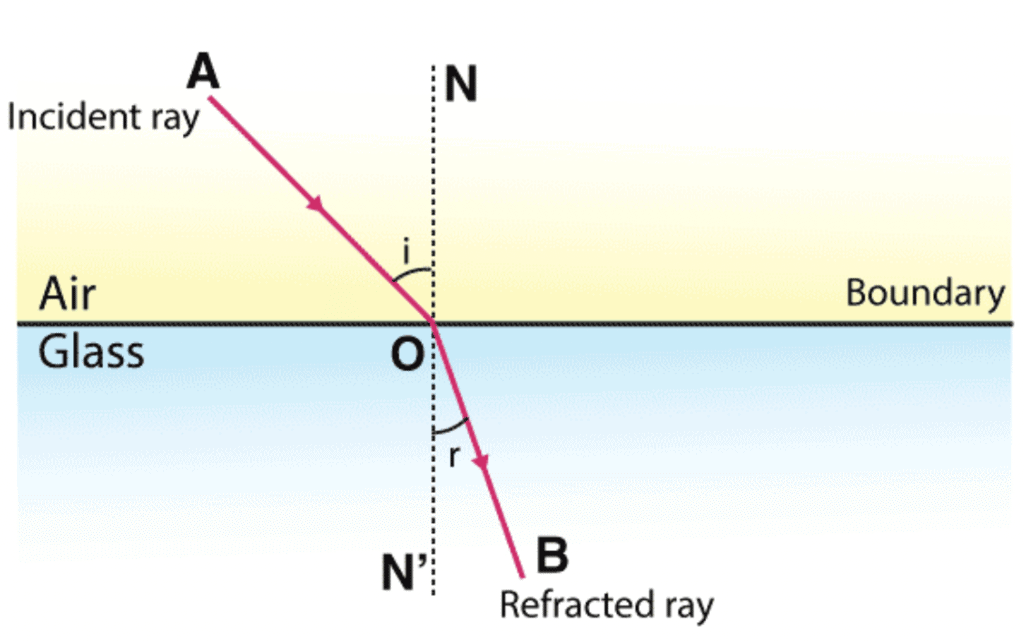 The refraction of light in glass is shown in the figure above. When light travels from air into glass, the light slows down and changes direction slightly. When light travels from a less dense substance to a denser substance, the refracted light bends more towards the normal line. If the light wave approaches the boundary in a direction that is perpendicular to it, the light ray doesn’t refract in spite of the change in speed.
The refraction of light in glass is shown in the figure above. When light travels from air into glass, the light slows down and changes direction slightly. When light travels from a less dense substance to a denser substance, the refracted light bends more towards the normal line. If the light wave approaches the boundary in a direction that is perpendicular to it, the light ray doesn’t refract in spite of the change in speed.
Laws of Refraction of Light
Laws of refraction state that:
- The incident ray refracted ray, and the normal to the interface of two media at the point of incidence all lie on the same plane.
- The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant. This is also known as Snell’s law of refraction.
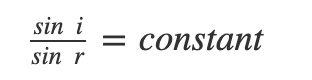
Bending of Light Ray
According to Snell's law, μ1 sin i = μ2 sin r
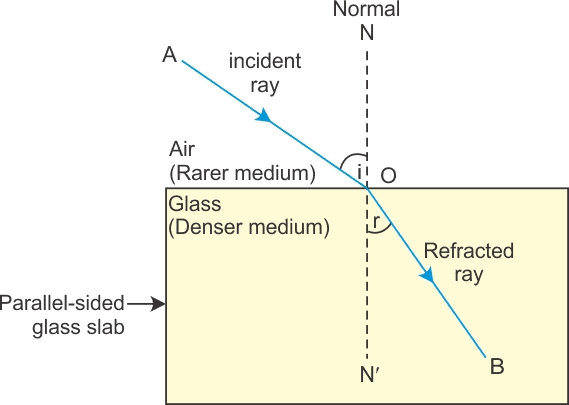
(i) If light passes from rarer to the denser medium:
μ1 = μR and μ2 = μD
so that,
⇒ ∠i > ∠r
In passing from rarer to a denser medium, the ray bends towards the normal.
(ii) If light passes from denser to rarer medium μ1= μD and μ2 = μR
⇒ ∠ i < ∠r
In passing from denser to rarer medium, the ray bends away from the normal.
Refractive index depends on nature and density of medium and colour of light refractive index is maximum for violet and minimum for the red light.
What is Refractive Index?
Refractive index, also called the index of refraction describes how fast light travels through the material.
Refractive Index is dimensionless. For a given material, the refractive index is the ratio between the speed of light in a vacuum (c) and the speed of light in the medium (v). If the refractive index for a medium is represented by n, then it is given by the following formula: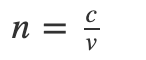
Based on the refractive index of the medium, the light ray changes its direction, or it bends at the junction separating the two media. If the light ray travels from a medium to another of a higher refractive index, it bends towards the normal, else it bends away from the normal.
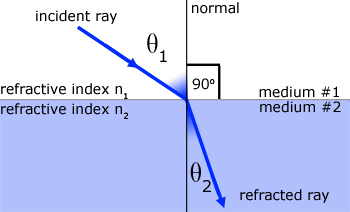
When light passes from one medium to the other, the refractive index of medium 2 relative to 1 is written as 1μ2 and is defined as μ21 or 1μ2 or 1m 2
Refraction of Light in Real Life
- Mirage and looming are optical illusions that are a result of the refraction of light.
- A swimming pool always looks shallower than it really is because the light coming from the bottom of the pool bends at the surface due to the refraction of light.
- The formation of a rainbow is an example of refraction as the sun rays bend through the raindrops resulting in the rainbow.
- When white light passes through a prism it is split into its component colours – red, orange, yellow, green, blue and violet due to the refraction of light.
Applications of Refraction of Light
Refraction has many applications in optics and technology. A few of the prominent applications are listed below:
- A lens uses refraction to form an image of an object for various purposes, such as magnification.
- Spectacles worn by people with defective vision use the principle of refraction.
- Refraction is used in peepholes of house doors, cameras, movie projectors and telescopes.
What is Total Internal Reflection (TIR)?
The phenomenon which occurs when the light rays travel from a more optically denser medium to a less optically denser medium.
- When light ray travel from denser to rarer medium it bends away from the normal if the angle of incidence is increased angle of refraction will also increase.
- At a particular value of angle of incidence the refracted ray subtends 90º angle with the normal, this angle of incidence is known as critical angle (θC).
- If the angle of incidence further increases, the ray comes back in the same medium this phenomenon is known as total internal reflection.
Formula of Total Internal Reflection

Conditions of Total Internal Reflection
Following are the two conditions of total internal reflection:
- The light ray moves from a more dense medium to a less dense medium.
- The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle.
Some Illustrations of Total Internal Reflection
- Sparkling of diamond: The sparkling of diamond is due to total internal reflection inside it. As refractive index for a diamond is 2.5, so θC = 24. Now the cutting of diamond is such that i > θC. So TIR will take place again and again inside it. The light which beams out from a few places in some specific directions makes it sparkle.
- Optical Fibre: In it, light through multiple total internal reflections is propagated along the axis of a glass fibre of radius of few microns in which the index of refraction of the core is greater than that of surroundings.
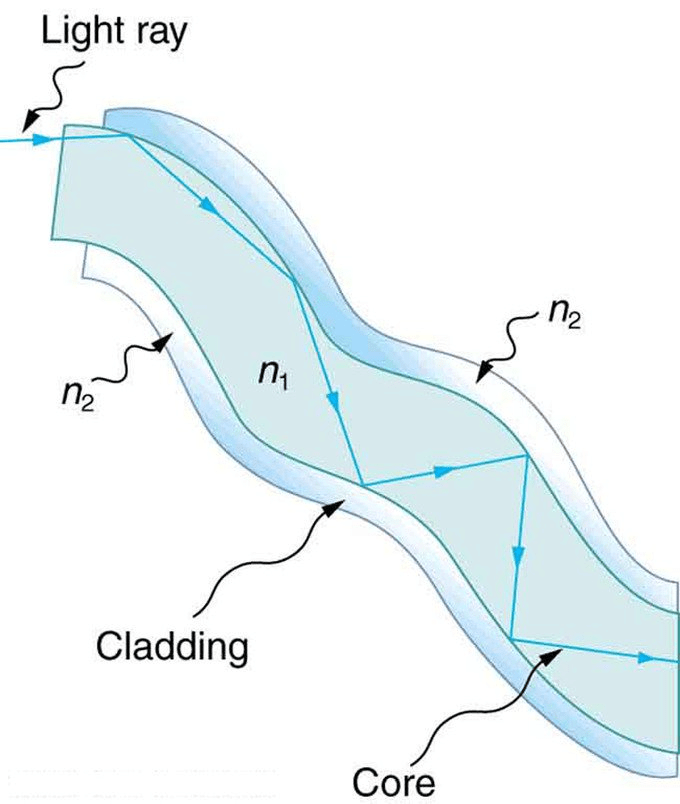 Optical Fibre
Optical Fibre - Mirage and looming: It is an optical illusion that is responsible for the appearance of the water layer at short distances in a desert or on the road. Mirage is an example of total internal reflection which occurs due to atmospheric refraction.
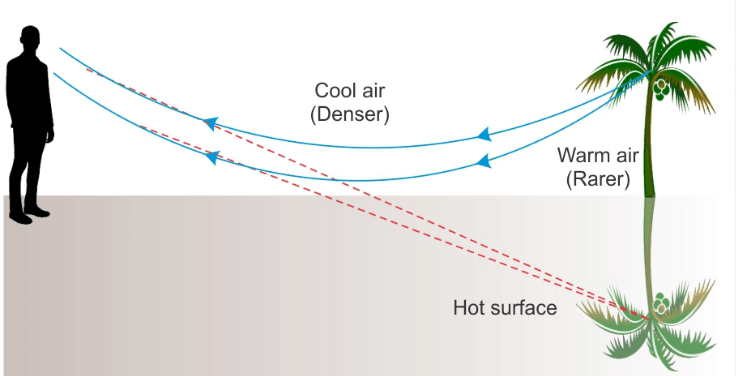 Mirage
Mirage
Golden Key Points
- A diver in water at a depth d sees the world outside through a horizontal circle of radius.
- r = d tanθC
- For total internal reflection to take place light must be propagating from denser to rarer medium.
- In the case of total internal reflection, as all (i.e. 100%) incident light is reflected back into the same medium there is no loss of intensity while in the case of reflection from a mirror or refraction from lenses there is some drop in intensity as all light can never be reflected or refracted. This is why images formed by TIR are much brighter than those formed by mirrors or lenses.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1: What do you mean by the term refraction?
Ans: Refraction is the bending of light at the surface of separation, which takes when it passes from one optical medium to another optical medium with different optical densities.
Q.2: Does reflection also take place with the refraction?
Ans: Yes, reflection also takes place with the refraction.
Q.3: For which colour of white light, is the refractive index of glass the most?
Ans: Violet colour of white light has highest refractive index.
|
80 videos|565 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Refraction of Light & Total Internal Refraction - Science Class 10
| 1. What is the definition of refraction of light? |  |
| 2. What are the causes of refraction of light? |  |
| 3. What are the laws of refraction of light? |  |
| 4. What is the refractive index? |  |
| 5. What are some real-life applications of refraction of light? |  |























