Regional Synthesis | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
- Regional Synthesis is a sophisticated approach to Areal Differentiation, which is supported by its proponents. It is a part of the Areal Differentiation process and focuses on the methodology for studying a region.
- In Areal Differentiation, the emphasis is on the examination of a specific region, while Regional Synthesis concentrates on the process of studying that region. The term "synthesis" refers to the formation of a complex whole by combining various parts in a unified manner.
- Therefore, Regional Synthesis involves the analysis of integration and interrelationships among various phenomena, such as physio-cultural, socio-economic, and geopolitical factors within a region. This approach aims to provide a comprehensive and accurate representation of the region being studied.
Region
A region can be described as a distinct segment of the Earth's surface, as suggested by Whittlesey. The concept of a region is dynamic and has been defined in various ways, with its boundaries constantly changing over time. For example, areas like the National Capital Region (NCR), rural, and urban areas experience shifts in their boundaries.
Vidal de la Blache referred to areas with similar physical and cultural characteristics as "pays." For instance, climatic regions like the equatorial areas, which include the Amazon and Congo basins, share similar physical features. In a broader sense, a region can be described as an area that is distinct from other areas based on specific criteria. Examples include the differentiation between equatorial, savannah, and tundra regions based on climate and vegetation, or wheat and rice regions based on rainfall, water availability, and soil conditions.
Regions possess various attributes, such as:
- Location: Regions can be identified by their specific locations, such as wheat, industrial, or climatic regions.
- Spatial extent: Regions have a definite area that they cover.
- Boundaries: Regions have limits, like the NCR.
- Formal or functional nature: Regions can be classified as either formal or functional.
- Hierarchical arrangement: Regions are organized in a hierarchical manner.
- Transitional boundaries: Regions often have unclear demarcation lines, like the zone between the equatorial region and the savannah in Africa.
Regions can be classified into two main types:
- Physical Regions: These include landform regions, climatic regions, air masses, and ecosystems.
- Cultural Regions: These encompass population regions (e.g., Uttar Pradesh), linguistic regions (e.g., the Kannada-speaking region), and religious regions (e.g., Hindu communities).
What is Regional Synthesis?
Regional Synthesis is a method used in regionalization, which involves bringing together various variables and integrating them to create a new, coherent picture of a particular region. This approach is essential in studying specific regions because it takes into account multiple factors that contribute to the overall understanding of the area.
- For instance, to identify a backward area – a region with lower development or resources – one cannot rely on a single variable such as literacy or health. Instead, a regional synthesis of multiple variables, including per capita income, literacy rate, mortality rate, and health facilities, is required to form a comprehensive picture of the region's development status.
- Similarly, in defining a cultural region, various factors such as language, ethnicity, customs, rituals, and religion need to be analyzed, synthesized, and integrated to provide an accurate representation of the area's unique culture.
- The development of regional synthesis requires expertise in different aspects of geography, as it involves the study of relationships between human society and the environment. For example, when studying the Indo-Gangetic plains, attributes such as rainfall, soil, topography, and culture must be considered to gain a thorough understanding of the region.
- Regional synthesis is based on a multidisciplinary approach, examining diverse physical and cultural phenomena and their interactions with each other. Fenneman, a geographer, emphasized that geography deals with the overall interaction between various subjects, highlighting the importance of regional synthesis in understanding the complexities of a region.
In summary, regional synthesis is a crucial approach in geography that involves the integration of multiple variables to form a comprehensive understanding of a particular region. This method provides a more accurate representation of the region by considering various factors and their interactions, offering valuable insights into the area's characteristics and development.
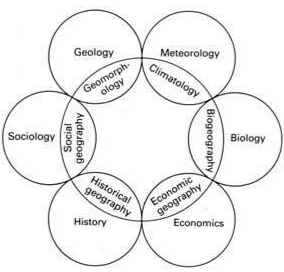
- This circumference of Geography contains interactions such as
- Geology and Physiography/Geomorphology consisting of Volcanoes, Earthquakes, Rock types, etc
- Biology and Bio-Geography consisting of Flora, Fauna, etc
- Economics and Commercial/Economic Geography consisting of economic resources, industry, trade, etc
- A multidisciplinary approach is being followed to study any particular region with the attributes of the circumference
- Regional Synthesis implies that geography is an integration of various sister disciplines like Geology, meteorology, etc
- All parameters are studied in an integrated way and values are deciphered from sister disciplines of geography
An American Geographer, J.L Berry, explains the regional synthesis through the geographical matrix. In Geographical Matrix, there are three dimensions:
- 1st: Rows represent attributes
- 2nd: Columns represent locations
- 3rd: Time
In this matrix, each cell has a geographical fact.
The following diagram shows the basic features of the Berry geographical matrix of the Delhi Region (in this matrix we considered matura location as part of the Delhi region).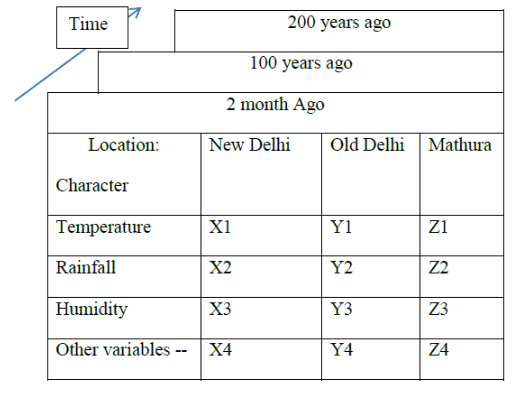
As per Berry geographical matrix, there are ten approaches to do regional analysis and same are listed below:
- Cells within rows show the spatial distributions of geographical features. In the above geographical matrix, the first geographical feature is temperature.
- Cells within the column show the localized geographical features. In the above geographical matrix, New Delhi localized regional analysis variables are temperature, rainfall, and humidity.
- Spatial variation can be studied by comparing two rows
- Areal differentiation can be studied by comparing two column
- Study of sub-matrix
- Study of spatial variation by comparing the same row through time which is temporal-spatial covariation. Example caparison of the present-day temperature of New Delhi with 100 years ago temperature.
- We can get sequence occupancy of a particular location by comparing the same column through time.
- Comparing a row with another row across the time dimension.
- Comparing a column with other columns across the time dimension.
- The comparison and study of sub-matrix across the time dimension.
Importance of Regional Synthesis is the current time
The importance of regional synthesis in the current era cannot be understated, as global temperature rise is an ongoing and non-uniform phenomenon. By employing regional synthesis analysis, trends in temperature rise can be observed on a region-by-region basis, enabling better understanding and management of the issue.
- Regional synthesis is also crucial for studying the sequence occupancy of a region and analyzing disparities within and between regions by comparing economic variables over time.
- The concept of geography as a regional synthesis was first proposed by Fenneman in 1919 and later supported by Richard Hartshorne and his followers, as it is a part of areal differentiation. Hartshorne argued that geography is an integrative and synthetic science.
- According to the Oxford Human Geography Dictionary, synthesis refers to "a complex whole made up of a number of parts unified." James Cunant further explained that every science is an integrated whole resulting from the interconnections between various concepts, experiments, field surveys, and observations. Geographers, like other scientists, are identified not only by the phenomena they study but also by the integrating concepts and processes they emphasize.
- The concept of regional synthesis is relatively recent, having been developed through the efforts of American, British, and German geographers to define the philosophy, scope, and methodology of their discipline. The goal of these philosophical discussions was to delineate the subject matter of geography, determine its scope and areas of focus, and suggest appropriate methodologies for geographical research.
- Geography shares its subject matter with numerous related disciplines, such as anthropology for tribal studies, meteorology, geology, ocean sciences, and biology, among others. As such, the importance of regional synthesis lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive, integrated understanding of a region's various aspects, allowing for better analysis and management of issues like climate change and economic disparities.
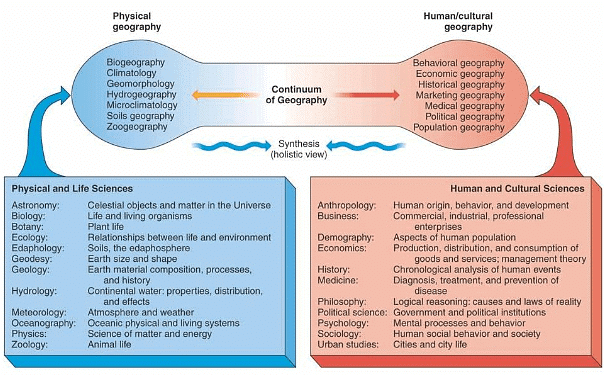
- Some geographers believe that their primary task is to examine and analyze various regions and places with the goal of understanding their unique characteristics and synthesizing new regional knowledge.
- For example, they might study the distinct features of equatorial climates, such as rainfall patterns, dense vegetation, and wildlife diversity. While geologists focus on lithology and rock structures, geographers concentrate on geomorphology. Similarly, biologists examine the taxonomy of plants and animals, whereas geographers investigate the spatial distribution of biogeography through mapping techniques.
- This means that geographers tackle numerous phenomena simultaneously, with the overarching aim of synthesizing a comprehensive understanding of how the atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere interact.
- For instance, theorists like Koppen utilized vegetation and precipitation data to develop their climatic classifications. Similarly, soil classifications are often based on humidity and aridity levels. Geographers are concerned with the overall interplay between biotic and abiotic phenomena, both spatially and temporally, within the biosphere.
The importance of regional synthesis lies in its dynamic approach to understanding the various interconnected phenomena related to the physical and human aspects of Earth. This comprehensive perspective aids demographic and regional planners, geomorphologists, and climatologists in combining their knowledge for the betterment of human society and overall prosperity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, regional synthesis is a vital approach in geography, as it integrates multiple variables to form a comprehensive understanding of a particular region. By considering various factors and their interactions, regional synthesis offers valuable insights into the area's characteristics and development. This multidisciplinary approach enables better analysis and management of issues like climate change and economic disparities, contributing to the overall betterment of human society and prosperity.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Regional Synthesis
What is the main goal of regional synthesis in geography?
The main goal of regional synthesis is to provide a comprehensive, integrated understanding of a region's various aspects, such as physical, cultural, socio-economic, and geopolitical factors. This approach allows for a more accurate representation of the region and offers valuable insights into the area's characteristics and development.
What are the two main types of regions in geography?
Regions can be classified into two main types: physical regions and cultural regions. Physical regions include landform regions, climatic regions, air masses, and ecosystems. Cultural regions encompass population regions, linguistic regions, and religious regions.
How does regional synthesis differ from areal differentiation?
Areal differentiation focuses on the examination of a specific region, while regional synthesis concentrates on the process of studying that region. Regional synthesis involves the analysis of integration and interrelationships among various phenomena within a region, providing a comprehensive and accurate representation of the region being studied.
What is the significance of the Berry geographical matrix in regional synthesis?
The Berry geographical matrix is a method used to analyze a region by considering its attributes, locations, and time. This matrix provides a framework for studying various geographical facts and helps in understanding the spatial distributions, localized geographical features, areal differentiation, and sequence occupancy of a particular region.
Why is regional synthesis important in the current era?
Regional synthesis is crucial in the current era for issues like climate change and economic disparities. By employing regional synthesis analysis, trends in temperature rise, economic variables, and other factors can be observed on a region-by-region basis, enabling better understanding and management of these issues.
|
303 videos|635 docs|253 tests
|
FAQs on Regional Synthesis - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is Regional Synthesis? |  |
| 2. How does Regional Synthesis help in UPSC exam preparation? |  |
| 3. What are the key steps involved in Regional Synthesis? |  |
| 4. How can one develop the skill of Regional Synthesis? |  |
| 5. Can you provide some examples of Regional Synthesis in the context of UPSC exam? |  |






















