Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Resistance
Resistance | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Ohm's Law
- Resistance is the opposition to current.
- For a given potential difference, the higher the resistance, the lower the current.
- Therefore, resistors are used in circuits to control the current.
- The unit of resistance is the ohm, represented by the Greek symbol omega (Ω).
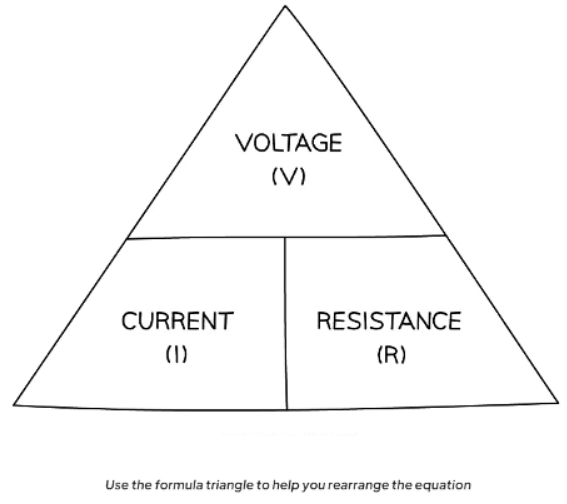
- It can be calculated using the formula
R = V/I,
- where,
- R = resistance (ohms, Ω)
- V = potential difference (volts, V)
- I = current (amperes, A)
- Ohm's Law: According to Ohm's Law, the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference applied across it, as long as the temperature remains constant.
Consequences of Ohm's Law
- Resistors serve the purpose of regulating either:
- The current flowing through specific components in the circuit.
- The potential difference (voltage) across particular components.
- Resistors are crucial due to the implications of Ohm's Law:
- When the resistance of an electrical conductor increases (with a constant voltage), the current flowing through it decreases.
- When the resistance of an electrical conductor increases (with a constant current), the voltage across it increases.
- Specifically, resistors help in controlling:
- The current in branches of the circuit, directing it through specific components.
- The potential difference across certain components, modulating the voltage they experience.
I-V Graphs for Ohmic Resistors, Filament Lamps & Diodes
- When the voltage across a component increases, the current through it also increases. This relationship is depicted by an I-V graph.
- The I-V graph illustrates the varying relationship between voltage and current for different components.
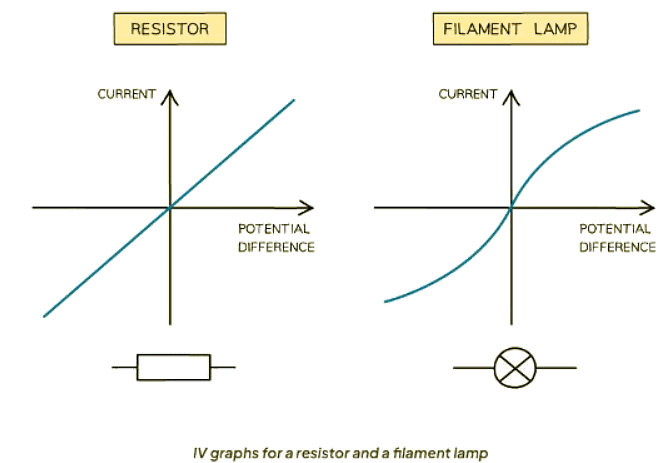
- The current-voltage (IV) graph of a resistor is straightforward: current is directly proportional to the potential difference across it.
- This proportionality arises because the resistor maintains a constant resistance.
- In contrast, the relationship for a lamp is more intricate:
- The current's growth is proportionally subdued compared to the potential difference.
- The reason behind this lies in the following:
- Electrical current heats the lamp's filament.
- As the filament temperature rises, its resistance also increases.
- This resistance increment opposes the current flow, resulting in a slower rate of increase in current.
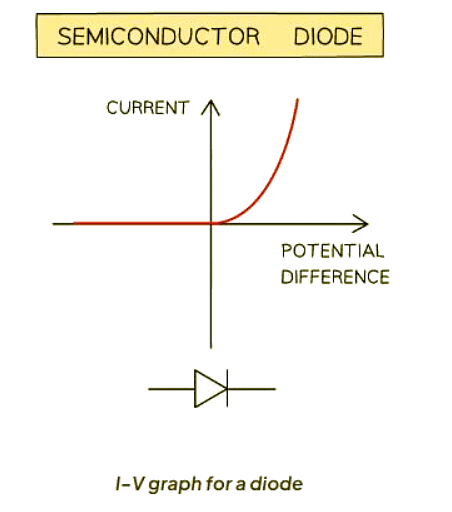
- A diode functions as a non-ohmic conductor, permitting the flow of current exclusively in one direction. This unidirectional conductive property is visually represented by a triangular arrow within the diode symbol, denoting forward bias.
- Forward bias in a diode indicates the condition where current flows easily due to the low resistance in that direction.
- Conversely, in reverse bias, the diode presents high resistance, impeding the flow of current significantly.
- The I–V (current-voltage) graph of a diode exhibits a distinctive shape. When the diode operates in forward bias, the graph displays a sharp incline in both voltage and current on the right side. In contrast, during reverse bias, the graph maintains a flat line, signifying zero current across all voltage levels on the left side.
Question for ResistanceTry yourself: What is the purpose of using resistors in circuits?View Solution
The document Resistance | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
126 videos|182 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Resistance - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is Ohm's Law and how is it represented mathematically? |  |
Ans. Ohm's Law states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it, given a constant temperature. Mathematically, Ohm's Law is represented as V = IR, where V is the voltage, I is the current, and R is the resistance.
| 2. What do the I-V graphs for Ohmic resistors, filament lamps, and diodes look like? |  |
Ans. The I-V graph for an Ohmic resistor is a straight line passing through the origin, representing a constant resistance. The I-V graph for a filament lamp is a curved line showing a non-linear relationship between current and voltage. The I-V graph for a diode is non-linear and shows that the current only flows in one direction.
| 3. How does resistance affect the I-V graph of a component? |  |
Ans. The resistance of a component determines the slope of its I-V graph. A higher resistance will result in a steeper slope, indicating that more voltage is required to achieve the same current flow. Conversely, a lower resistance will result in a shallower slope.
| 4. What is the significance of the slope of an I-V graph in relation to Ohm's Law? |  |
Ans. The slope of an I-V graph represents the resistance of a component. According to Ohm's Law, resistance is equal to the ratio of voltage to current. Therefore, the slope of an I-V graph can be used to calculate the resistance of a component.
| 5. How does the behavior of a diode differ from that of an Ohmic resistor on an I-V graph? |  |
Ans. Unlike an Ohmic resistor, a diode has a non-linear I-V graph that shows current flowing in only one direction. This behavior is due to the diode's property of allowing current to flow freely in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction.
Related Searches