Revision Notes: Central Banking | Economics Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Meaning of Central Bank
A central bank is the highest authority in a country’s banking system. It has the exclusive power to issue currency notes and regulate the money supply. The central bank also acts as the government’s banker and advisor on monetary matters.
Differences Between Central Bank and Commercial Bank
- Authority and Control: The Central Bank is the topmost authority in the banking system, often referred to as the "bank of all banks." In contrast, Commercial Banks operate under the regulations and control of the Central Bank.
- Objectives: The Central Bank aims for social welfare and economic stability, while Commercial Banks focus on maximizing profits.
- Deposit Acceptance: The Central Bank does not accept public deposits. In contrast, Commercial Banks accept deposits from the public and provide loans to individuals and households.
- Currency Issuance: Only the Central Bank has the authority to issue currency. Commercial Banks do not have this power.=
- Government Advisory Role: The Central Bank advises the government on monetary policy and economic issues. Commercial Banks do not have this advisory role.
Functions of the Reserve Bank of India
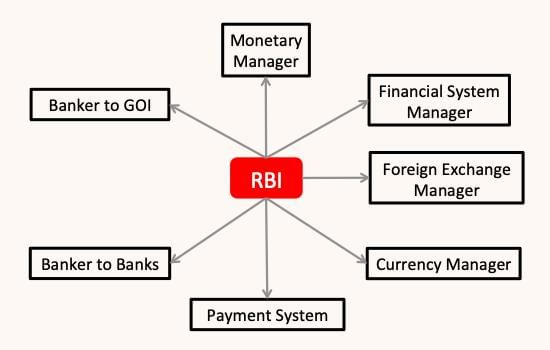
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was established on April 1, 1935, under the RBI Act of 1934, with a share capital of Rs 5 crore. Initially a joint stock bank, the RBI was nationalized on January 1, 1949, and has since functioned as the Central Bank of India.
- Issuing of Notes: The RBI has the exclusive right to issue currency notes. Initially, notes were issued based on a proportional reserve system. Currently, the RBI can issue any volume of currency notes, backed by a gold reserve of Rs 115 crore and foreign exchange reserves of Rs 85 crore.
- Banker to the Government: The RBI acts as a banker, agent, and financial advisor to the government. It manages government accounts, buys and sells securities on behalf of the government, and advises on money market regulations.
- Lender of Last Resort: The RBI provides financial assistance to commercial banks by rediscounting eligible bills of exchange. It serves as a last resort for banks in need of loans, advancing funds against approved securities.
- Custodian of Cash Reserves: The RBI safeguards India’s foreign exchange reserves and maintains the external value of the Indian Rupee. It conducts foreign exchange transactions on its own and the government’s behalf, intervening in the market as needed.
- Controlling Credit: The RBI regulates the money supply by controlling the credit creation of commercial banks. This is crucial for preventing economic fluctuations and ensuring stability in both internal prices and foreign exchange rates, which is essential for economic growth.
- Other Functions: The RBI maintains relationships with international organizations like the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank. It also engages in various developmental and promotional activities and is responsible for collecting and compiling statistical information related to the banking and financial sectors.
Methods of Credit Control
Credit control refers to the measures taken by the Central Bank to regulate the flow of credit in the economy. The Central Bank adopts various methods to control credit depending on the situation. There are two types of credit control:
- Quantitative Credit Control
- Qualitative Credit Control
Quantitative Credit Control
Quantitative credit control measures impact the overall money supply in the economy without targeting specific sectors.
- Bank Rate Policy: The bank rate policy is a key tool for monetary control, especially during inflation. When the Central Bank raises the bank rate, it signals a dear money policy. This increase in the bank rate raises the cost of borrowing, leading to a reduction in commercial banks' borrowing from the Central Bank. As a result, the flow of money from commercial banks to the public decreases, helping to control inflation caused by bank credit.
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): The CRR is the minimum percentage of a bank's total deposits that must be kept with the Central Bank. According to the RBI Act of 1934, commercial banks are required to maintain a certain percentage of their deposits as cash reserves with the Central Bank. An amendment in 1962 allowed the Central Bank to vary the CRR between 3% and 15% of the total deposits of commercial banks. During inflation, the Central Bank may increase the CRR, reducing the funds available for commercial banks to provide loans. This decrease in credit flow helps to curb inflation. Conversely, the RBI can lower the CRR to address deflationary situations.
- Open Market Operation: Open market operations involve the sale and purchase of government securities and bonds by the Central Bank. To control inflation, the Central Bank may sell government securities to the public through banks. This process transfers a portion of bank deposits to the Central Bank, reducing the credit creation capacity of commercial banks.
- Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR): The SLR is the mandated percentage of assets, such as cash or other liquid assets, that a bank must maintain with the Central Bank. The Central Bank has the authority to vary the SLR between 20% and 40%.
Qualitative Credit Control
Qualitative credit control measures focus on regulating the flow of credit to specific areas of economic activity. These measures aim to influence the alternative uses of credit within the economy.
- Margin Money: Margin money refers to the minimum margins that borrowers must maintain when borrowing money against specific securities from commercial banks. This practice helps ensure that borrowers have a financial buffer in place, reducing the risk for lenders.
- Credit Authorisation Scheme: This scheme sets a limit on the amount of credit that can be extended for specific purposes and requires prior approval from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Moral Suasion: Moral suasion involves persuading or pressuring commercial banks to adhere to the RBI's monetary policy directives. If persuasion fails, the RBI may resort to direct action, such as non-recognition of a bank.
- Rationing of Credit: Introduced in 1960, this system involves the RBI fixing credit quotas for member banks. If a bank seeks to borrow beyond its allocated quota, it must pay a higher interest rate.
|
18 videos|88 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Central Banking - Economics Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is the meaning of a Central Bank? |  |
| 2. What are the main functions of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)? |  |
| 3. How does the Reserve Bank of India control credit in the economy? |  |
| 4. Why is the role of a Central Bank important for an economy? |  |
| 5. What are the tools used by the Reserve Bank of India for credit control? |  |
















