Evolution Class 12 Notes Biology Chapter 6
(i) Ancient theories of origin of life: Various theories have been put forward to explain the phenomenon of origin of life. A few of them were only speculations while others were based on scientific grounds. These theories are –
(a) Theory of special creation.
(b) Theory of spontaneous generation or Abiogenesis.
(c) Biogenesis
(d) Cosmozoic theory
(e) Theory of sudden creation from inorganic material.
(f) Naturalistic theory
(ii) Oparin's Modern Theory:
(a) Oparin (1924) proposed that “life could have originated from non-living organic molecules.”
(b) He believed in Biochemical origin of life. Haldane (1929) also stated similar views. Oparin greatly expanded his ideas and presented them as a book “The origin of life” in 1936.
(c) According to this theory, the Earth originated about 4,500 million years ago. When the earth was cooling down, it had a reduced atmosphere. In this primitive atmosphere nitrogen, hydrogen, ammonia, methane, carbon mono-oxide and water were present. Energy was available in the form of electric discharges by lightening and ultraviolet rays. As soon as the earth crust was formed, it was very much folded. Torrential rains poured over the earth for centuries and were deposited in deep places.
(d) Miller's Experiment: An American scientist (Biologist) Stanley Miller (1953) performed an experiment under support Oparin's theory of origin of life. He believed that basic compounds which are essential for life can be synthesised in the laboratory by creation in the laboratory, on a small scale, the conditions which must have existed at the time of origin of life on earth.
(e) Miller took a flask and filled it with methane, ammonia and hydrogen in proportion of 2:1:2 respectively at 0°C. This proportion of gases probably existed in the environment at time of origin of life. This flask was connected with a smaller flask, that was filled with water, with the help of glass tubes. In the bigger flask, two electrodes of tungsten were fitted. Then a current of 60,000 volts was passes, through gases containing bigger flask for seven days. At the end of seven days, when the vapours condensed, a red substance was found in the U-tube. When this red substance was analyzed, it was found to contain amino acids, Glycine and nitrogenous bases which are found in the nucleus of a cell.
(f) The entire process of the origin of life, as proposed by Oparin, can be summarised as under –
(i) The Chemical Evolution:
(1) Step 1: Formation of simple molecules
(2) Step 2: Formation of Simple organic compounds
(3) Step 3: Formation of complex organic compounds
(4) Step 4: Formation of nucleic acids and nucleoproteins
(ii) Organic Evolution:
(1) Step 5: Formation of Coacervates
(2) Step 6: Formation of Primitive cell
(3) Step 7: Origin of autotrophism
(4) Step 8: Origin of Eukaryotic cells
Evidences of Organic Evolution
The following are the evidences in favour of Organic Evolution:
(i) Evidences from Classification
(ii) Evidences from Comparative Anatomy
(a) Analogy and Homology
(b) Vestigeal organs
(iii) Evidences from Physiology
(iv) Evidences from Serology
(v) Evidences from Embryology
(vi) Evidences from Palaeontology
(vii) Evidences from geographic distribution
(viii) Evidences from Genetics
(i) Evidences from Classification: All the known living animals and plants have been classified into various species, genera, families, order, classes, phyla and kingdoms. The classification of a particular animal is attempted only after its extensive study.
(ii) Evidences from Comparative Anatomy: In all the living animals, the basic substance of life is Protoplasm. If the species had been created separately, then there should be no relationship in the various organs and systems of animals. But on the contrary, we see that large number of animals although unlike in appearance show most of the systems and organs made on the same plan. The resemblance is very close in the members of the same group.
(iii) Evidences from Physiology: Various types of chemical tests exhibit many basic similarities in physiological and chemical properties that show a physiological relationship among animals.
(iv) Evidences from Serology: This is a method by which the reactions of blood serum are observed. From the blood are also extracted the crystals of Oxyhaemoglobin. The structure differs in different vertebrates, but in a definite order. The reaction is nearly identical in man and anthropoid monkeys, but slightly less identical with other mammals.
(v) Evidences from Embryology: With the exception of a few, every multi-cellular animal originates from a zygote. The development from zygote to adult shows many similarities in various organisms. The development is termed as ontogeny
(vi) Evidences from Palaeontology: The study of fossils and their interpretation forms one of the great evidences of evolution. An Italian scientist, Leonardo da Vinci, was the first person to recognize their importance and said they were either remains of organisms of their impressions on some sort of clay or rock.
Important living fossils
(vii) Evidences from geographic distribution: If the study of horizontal distribution of animals on the face of this earth is made, it would be seen that animals are not evenly distributed. Two identical places with the same climate and vegetation may not have same sort of animal fauna
(viii) Evidences from Genetics: Johan Gregor Mendel in 1866 published his work on experimental breeding. He bred two individuals differing in certain well-defined characters, and observed the ratio in which various contrasting parental characters appeared in successive generations.
(c) Connecting links: Intermediate or intergrading forms between two groups of organisms:
Theories of organic evolution
(i) Lamarckism: Lamarck (1744 –1829) was one of the most brilliant stars on the horizon of the history of evolution. He was the first naturalist to put forward a general theory of evolution in his famous book. Philosophic Zoologique published in 1809. His evolutionary theory may be summarised in the form of following laws:
(a) The internal forces of life tend to increase the size of an organism.
(b) The necessity in animals to produce new structures.
(c) The effect of use and disuse.
(d) Inheritance of acquired characters.
Difference between Lamarckism and Neo–Lamarckism
(iii) Darwinism: Charles Robert Darwin was undoubtedly the first naturalist who put the idea of organic evolution on sound footing. His statements and theories were based upon practical experiences and large number of proofs which he collected directly from the nature.
His main ideas about the evolution are given below –
(a) Over – production of offspring
(b) Limited supply of food and shelter
(c) Struggle for existence:
(i) Intra –specific
(ii) Inter –specific
(iii) Environment
(d) Survival of the fittest
(e) Universal occurrence of variations
(f) Inheritance
(g) Natural selection
Difference between Darwinism and Neo–Darwinism
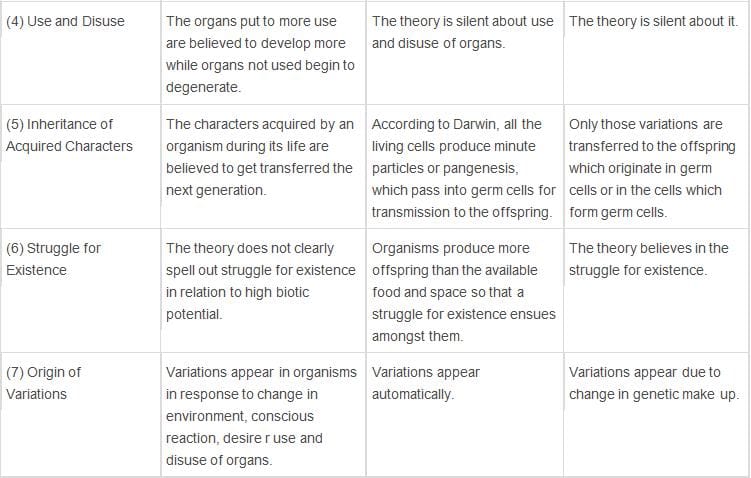
Difference Amongst Lamarckism, Darwinism and Mutation Theory

FAQs on Evolution Class 12 Notes Biology Chapter 6
| 1. What is the theory of evolution? |  |
| 2. How does natural selection contribute to evolution? |  |
| 3. What is genetic mutation and its role in evolution? |  |
| 4. Is evolution a fact or a theory? |  |
| 5. Are humans still evolving? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|

















