Revision Notes: Goods and Services Tax | Mathematics Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Important Terms
- Direct Taxes are levies on the income of individuals or organisations, including income tax and corporate tax.
- Indirect Taxes are charges added to the price of goods or services, collected by sellers from consumers.
- A Dealer is an individual or entity that buys goods or services with the intention of reselling them.
- The Cost Price (C.P) is the amount a trader pays to acquire goods, representing the purchase expenditure.
- The Marked Price (M.P.) is the price displayed on a product, also known as the list price, printed price, or quoted price.
- Shopkeepers may offer a Percentage Discount on the list price to clear old stock or for other reasons. This discount is always calculated based on the list price.
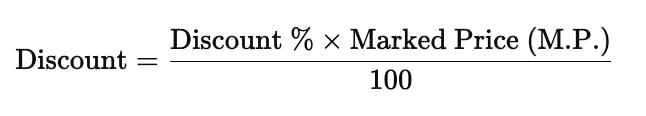
- The Selling Price (S.P.) is the amount at which a trader sells their goods, including any discounts. It is also referred to as the sale price.
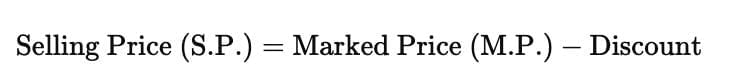 If no discount is applied, the selling price equals the list price.
If no discount is applied, the selling price equals the list price.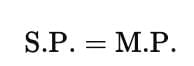
- The formula for calculating tax is:
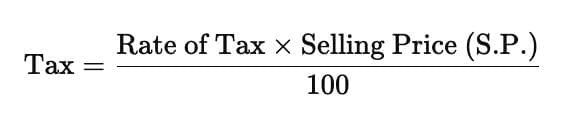

Goods and Services Tax (GST)
- GST is a tax on consumption, applied when purchasing or transferring goods or services.
- It is levied at every sale or transfer of goods or services.

- GST has replaced all previous indirect taxes imposed by central and state authorities.
- It is implemented across India, including Jammu and Kashmir.
Important
- A consumer (the end user) cannot reclaim the GST they have paid.
- Only individuals or organisations registered with GST can charge and collect it on sales or transfers.
- Those who charge GST must include their GST registration number on the invoice.
- GST applies to all types of movement of goods and services.
- GST consists of:
1. Central-GST (CGST). Collected by the central government for transactions within a state.
2. State-GST (SGST). Union Territory GST (UGST). Collected by the state or union territory for transactions within that region.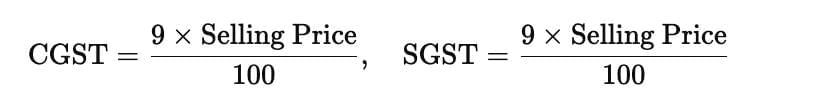 3. Integrated-GST (IGST). Imposed on transactions between states and on imports of goods and services.
3. Integrated-GST (IGST). Imposed on transactions between states and on imports of goods and services.
Note:
- For transactions within a state, the seller collects both CGST and SGST from the buyer, paying CGST to the central government and SGST to the state government.
- The tax from intra-state movements of goods and services is shared equally between the central and state governments.
- GST rates are 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%, as applicable.
- GST is calculated on the sale price after deducting any discounts from the listed price.
- For intra-state sales with a GST rate of 18%: CGST and SGST are each 9% of the sale price; IGST is 0.
- For inter-state sales with a GST rate of 18%: IGST is 18% of the sale price.
- Discounts are not allowed on the amount that includes GST.
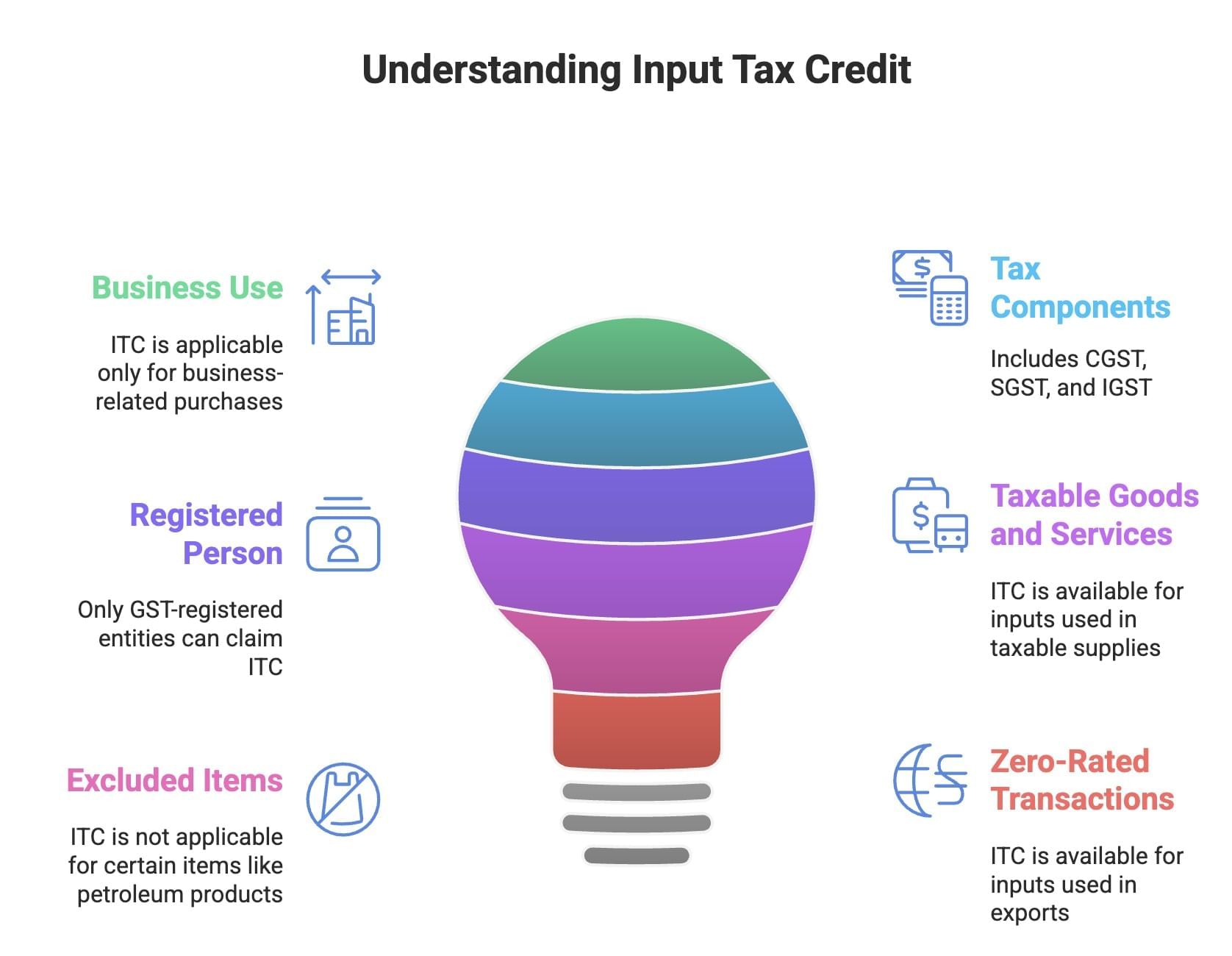
Input Tax Credit (ITC)
- Input Tax Credit (ITC) is a provision that allows businesses to deduct the tax paid on their purchases (input tax) from the tax they owe on their sales (output tax). This means you only pay the difference to the government.

- ITC can only be claimed on goods and services used for business purposes, not for personal use.
- Input tax includes various components like CGST (Central Goods and Services Tax), SGST (State Goods and Services Tax), and IGST (Integrated Goods and Services Tax) paid on input goods and services.
- Only a registered person under GST can claim credit for input tax charged on the supply of goods and services.
- Credit is available for tax paid on every input used for supplying taxable goods or services under GST.
- However, input tax credit is not available for purchases of certain items like petroleum products, liquor, petrol, diesel, and motor spirit.
- For exports of goods and services, GST does not apply, and businesses can claim input tax credit on inputs used for these supplies. These transactions are referred to as zero-rated transactions under GST.
Revision Questions
Q1: A shopkeeper buy goods worth ₹ 4000 and sells these at a profit of 20% to a consumer in the same state. If GST is charged at 5%, find:
(i) the selling price (excluding tax) of the goods.
(ii) CGST paid by the consumer.
(iii) SGST paid by the consumer.
(iv) the total amount paid by the consumer.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Solution:
(i) Actual price of the goods = ₹4000
When sold at a profit of 20%
Profit = (20/100) x ₹4000 = ₹800
Thus, the selling price (excluding tax) of the goods will be
= Actual price + profit
= ₹4000 + ₹800
= ₹4800
The GST charged is 5%
(ii) CGST paid by the consumer = 2.5% of the selling price
= (2.5/100) x ₹4800
= ₹120
(iii) SGST paid by the consumer = 2.5% of the selling price
= (2.5/100) x ₹4800
= ₹120
(iv) Thus, the total amount paid by the consumer = selling price + CGST + SGST
= ₹4800 + ₹120 + ₹120
= ₹5040
Q2: A shopkeeper in Delhi buys an article at the printed price of Rs 24000 from a wholesaler in Mumbai. The shopkeeper sells the article to a consumer in Delhi at a profit of 15% on the basic cost price. if the rate of GST is 12%, find:
(i) The price inclusive of tax (under GST) at which the wholesaler bought the article.
(ii) The amount which the consumer pays for the article.
(iii) The amount of tax (under GST) received by the State Government of Delhi.
(iv) The amount of tax (under GST) received by the Central Government.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Solution:
Given:
(i) The price inclusive of tax (under GST) at which the wholesaler bought the article.
CP of an article for shopkeeper = ₹24000
Rate of GST = 12%
IGST collected by wholesaler from shopkeeper = 12% of ₹24000
= (12/100) × 24000
= ₹2880
The price inclusive of tax (under GST) at which the wholesaler bought the article =
CP of article for shopkeeper + IGST paid by shopkeeper to wholesaler = ₹24000 + ₹2880
= ₹26880
(ii) The amount which the consumer pays for the article.
CP of an article for shopkeeper = ₹24000
Profit on CP of article = 15% of CP
SP of an article by the shopkeeper to consumer = CP + Profit
= ₹24000 + 15% of ₹24000
= ₹24000 + (15/100) × 24000
= ₹24000 + 3600
= ₹27600
The amount which the consumer pays for the article = CP of article for consumer + CGST paid by the consumer + SGST paid by consumer =
₹27600 + 6% of ₹27600 + 6% of ₹27600 =
₹27600 + (6/100) × ₹27600 + (6/100) × ₹27600 = ₹27600 + ₹1656 + ₹1656
= ₹30912
(iii) The amount of tax (under GST) received by the State Government of Delhi.
Amount of IGST for shopkeeper = ₹2880
SP of an article to consumer = CP of article for shopkeeper + profit on basic CP
= ₹24000 + 15% of ₹24000
= ₹24000 + (15/100) × ₹24000
= ₹24000 + ₹3600
= ₹27600
As the shopkeeper sells an article to consumer in Delhi; so this sales is Intra-state sales.
Amount of GST collected by shopkeeper from consumer,
CGST = SGST = 6% of ₹27600
= (6/100) × ₹27600
= ₹1656
Amount of tax paid by shopkeeper to state govt. = ₹2880 – ₹1656 = ₹1224
The amount of tax (under GST) received by the State Government of Delhi =
₹1656 – ₹1224 = ₹432
(iv) The amount of tax (under GST) received by the Central Government.
The amount of tax (under GST) received by the Central Government = IGST received from wholesaler + CGST received from shopkeeper = ₹ 2880 + NIL = ₹ 2880
Q3: A retailer buys an article at a discount of 15% on the printed price from a wholesaler. He marks up the price by 10% on the printed price but due to competition in the market, he allows a discount of 5% on the marked price to a buyer. If the rate of GST is 12% and the buyer pays ₹468.16 for the article inclusive of tax (under GST), find
(i) the printed price of the article
(ii) the profit percentage of the retailer
 View Answer
View Answer 
Solution:
(i) Let the printed price of the article be ₹x
The retailer marks up the price by 10% on the printed price
So, the marked price by the retailer = ₹x + 10% of ₹x
= ₹x + ₹0.1x
= ₹1.1x
Due to competition the retailer allows discount of 5% on the marked price, then
The selling price of the article = ₹1.1x – discount
Discount = 5% of ₹1.1x
= ₹ (5/100) x 1.1x
= ₹0.055x
The rate of GST = 12%
The tax (under GST) for the purchase = 12% of the selling price set by the retailer
= 12% of ₹ (1.1x – 0.055x)
= ₹ (12/100) x (1.045x)
Thus, the price of the article inclusive of GST = ₹1.045x + ₹ (12/100) x (1.045x)
Given, the buyer pays ₹468.16 for the article inclusive of tax (under GST)
So,
1.045x + (12/100) x (1.045x) = 468.16
1.045x + 0.1254x = 468.16
1.1704x = 468.16
x = 468.16/1.1704
x = ₹400
Therefore, the printed price of the article is ₹400
(ii) The retailer buys at 15% discount on the printed price and sells at 5% discount for the marked price of 10% on the printed price
So,
Bought at = 400 – 15% of ₹400 = ₹400 – ₹60 = ₹340
Sold at = (₹400 + 10% of ₹400) – 5% of (₹400 + 10% of ₹400)
= ₹(400 + 40) – [(5/100) x ₹400 + 40)]
= ₹440 – ₹ (0.05 x 440)
= ₹440 – ₹22
= ₹418
So, profit = Selling price – cost price = ₹418 – ₹340 = ₹78
Hence, the profit percentage = (78/340) x 100 = 22.94%
|
74 videos|198 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Goods and Services Tax - Mathematics Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is Goods and Services Tax (GST) and how does it work? |  |
| 2. Who is liable to pay GST? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of GST? |  |
| 4. How can I file GST returns? |  |
| 5. What are the penalties for non-compliance with GST regulations? |  |
















