Revision Notes: Sound | Physics Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Sound Waves |

|
| Echo |

|
| Free (or Natural) Vibrations |

|
| Damped Vibrations |

|
| Forced Vibrations |

|
| Resonance |

|
| Examples of Resonance |

|
| Characteristics of Sound |

|
| Music and Noise |

|
Sound Waves
- Sound is produced and is heard when a body vibrates in a medium.
- When the vibrations reach our ear, a sound is heard.
- Our ears are sensitive only to a limited range of frequencies, from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
- Sound of frequency above 20,000 Hz is called ultrasonic, while sound of frequency below 20 Hz is called infrasonic.
- The wave velocity V, frequency f and wavelength λ are related as V = fλ. The time period and frequency of a wave are related as f = 1/T.
- Sound is a mechanical wave and needs a material medium to propagate. It cannot travel through vacuum.
- Sound waves are of two kinds—longitudinal waves and transverse waves.
- When the vibrations of medium particles are along the direction of propagation of the wave, the wave is called a longitudinal wave, which has compressions and rarefactions in the medium. The longitudinal waves travel in solid, liquid and gas.
- On the other hand, if the medium particles vibrate normal to the direction of propagation of the wave, forming crests and troughs, the wave is called a transverse wave.
Echo
- The repetition of sound caused by the reflection of sound waves from an obstacle after the original sound has ceased is known as echo.
Condition for forming an echo
- The sensation of sound persists in our brain for about 0.1 s. To hear a distinct echo, the time interval between the original sound and the reflected one must be at least 0.1 s.
- If d is the distance between the observer and the obstacle and V is the speed of sound, then the total distance travelled by the sound to reach the obstacle and then to come back is 2 d and the time taken is
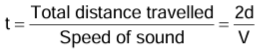
∴ d = Vt/2 - For hearing distinct echoes, the minimum distance of the obstacle from the source of sound must be 17 m.
- The speed of sound on a hot day is more than that on a cold day. Thus, the echo will reach sooner on a hot day.
Use of echoes
Bats, dolphins and fisherman:
- The sounds produced by flying bats get reflected from an obstacle in front of it. By hearing the echoes, bats are able to detect obstacles in the dark. Hence, they can fly safely without colliding with the obstacles. This process of detecting obstacles is called sound ranging.
- Dolphins detect their enemy and obstacles by emitting ultrasonic waves and hearing their echo. They use ultrasonic waves for hunting their prey.
- A fisherman sends a pulse of ultrasonic waves from a source into the sea and receives the waves reflected from the shoal of fish via a detector.
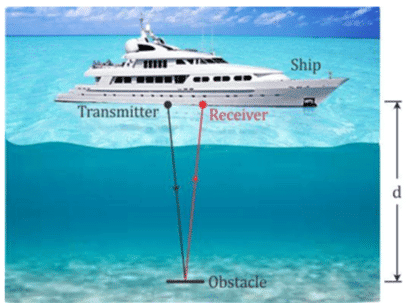
By sonar:
- SONAR stands for sound navigation and ranging.
- It consists of a transmitter and detector. The transmitter transmits the ultrasonic sound. These waves travel through water, and after striking an underwater object (e.g. submarine, iceberg, sunken ship), reflect and are detected by a detector.
In medicine:
- Ultrasonic waves are made to reflect from various parts of the heart and form the image of the heart. This technique is called Echocardiography.
- Ultrasonography is used to obtain the images of patient’s organs such as the liver, kidneys etc. It helps to detect stones in the kidneys.
Free (or Natural) Vibrations
- Free vibrations are the periodic vibrations of a body of constant amplitude in the absence of any external force on it.
- The time period of a freely vibrating body is called free (or natural) period, and the frequency of the freely vibrating body is called its natural frequency.
- The amplitude of an isolated, freely vibrating body remains constant.
- The free vibrations of a body actually occur only in vacuum because the presence of a medium offers some resistance due to which the amplitude of vibration does not remain constant and decreases continuously.
Examples of Free or Natural Vibrations
- When the bob of a simple pendulum is displaced slightly from its mean (or resting) position, it starts vibrating with its natural frequency which is determined by the length of the pendulum and the acceleration due to gravity at that place.
- When a tuning fork is struck against a hard rubber pad, it vibrates with its natural frequency.
- When we strike the keys of a piano, various strings are set in vibration at their natural frequencies.
- When the strings of instruments such as the sitar, guitar and violin are plucked, transverse vibrations of a definite natural frequency are produced in the string.
Nature of Free Vibrations
- The amplitude and frequency of a freely vibrating body should remain constant. When a body starts vibrating, it should continue with the same amplitude and same frequency forever.
- In actual practice, this does not happen because the surrounding medium offers resistance (or friction) to the motion. Thus, the vibrating body continuously loses energy due to which the amplitude of motion gradually decreases.
Damped Vibrations
- Damped vibrations are the periodic vibrations of a body of decreasing amplitude in the presence of resistive force.
- The amplitude of motion decreases due to the frictional (or resistive) force which the surrounding medium exerts on the body vibrating in it. The frictional force at any instant is proportional to the velocity of the vibrating body and it has the tendency to resist the motion.
- The rate at which the energy is lost to the surroundings (or the rate of decrease of amplitude) depends on the nature (i.e. viscosity, density etc.) of the surrounding medium and also on the shape and size of the vibrating body.
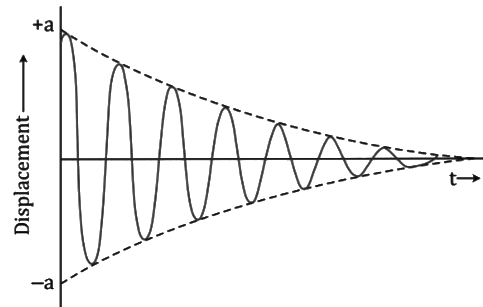
Examples of Damped Vibrations
- When a slim branch of a tree is pulled and then released, it produces damped vibrations.
- A tuning fork vibrating in air produces damped vibrations as its prongs stop vibrating after some time.
- A simple pendulum oscillating in air produces damped vibrations.
Forced Vibrations
- Forced vibrations are the vibrations of a body which occur under the influence of external periodic force acting on it.
- When an external periodic force is applied on a vibrating body, the body no longer vibrates with its own natural frequency, but it gradually acquires the frequency of the applied periodic force.
- The external applied force is called the driving force.
- When the frequency of the external force is different from the natural frequency of the body, the body oscillates with small amplitude. However, when the frequency of the external force is exactly equal to the natural frequency of the vibrating body, the body oscillates with large amplitude.
Examples of Forced Vibrations
- The vibrations produced in the diaphragm of a microphone sound box with frequencies corresponding to the speech of the speaker are forced vibrations.
- When a guitar is played, the artist forces the strings of the guitar to produce forced vibrations.
- All stringed instruments are provided with a hollow sound box which contains air. In these instruments, when the strings are made to vibrate by plucking, vibrations are produced in the air present in the sound box which are forced vibrations. Because the surface area of the air in the sound box is large, the forced vibrations of air cause a loud sound.
Resonance
- When the frequency of an externally applied periodic force on a body is equal to its natural frequency, the body readily begins to vibrate with increased amplitude. This phenomenon is known as resonance.
- The vibrations of large amplitude are called resonant vibrations.
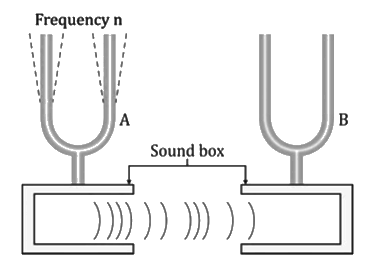
Experiment 1: Resonance with Tuning Forks
- When the prong of one of the tuning forks is struck on a rubber pad, it starts vibrating. On putting the tuning fork A on its sound box, we find that the other tuning fork B also starts vibrating and a loud sound is heard. The vibrations produced in the second tuning fork B are forced vibrations, and the sound is loud due to resonance.
Experiment 2: Forced and resonant vibrations of pendulums
- When the pendulum A is set into vibration by displacing it to one side normal to its length, pendulum B also starts vibrating initially with small amplitude and in some time it acquires the same amplitude as A. When the amplitude of pendulum B becomes maximum, the amplitude of pendulum A becomes minimum because the total energy is constant. After some time, the amplitude of pendulum B decreases and that of pendulum A increases.
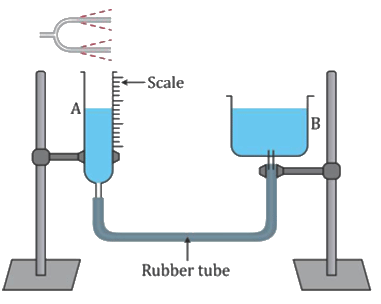
Experiment 3: Resonance in air column
- The vibrating source (i.e. tuning fork) is kept at the mouth of tube A so that it works as a closed end air pipe with the water surface in it forming the closed end (i.e. the reflecting surface). Thus, an air column is formed in the tube A between the water surface and its mouth. When this air column is made to vibrate, it will vibrate with its natural frequency which depends on the length of the air column.
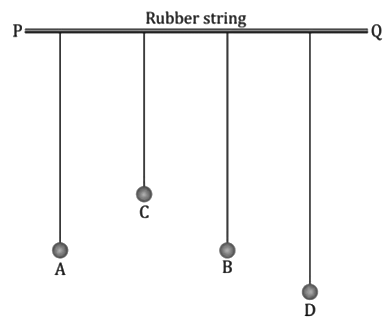
Examples of Resonance
- When two pendulums of same lengths are suspended from a rubber string and one pendulum is made to vibrate, the other pendulum also starts vibrating with the large amplitude and in the same phase because of resonance.
- When a vehicle is driven, the piston of the engine moves in and out at a frequency depending on the speed of the vehicle. Some parts of the vehicle may have natural frequency of vibration equal to the frequency of the to-and-fro movement of the piston. The part of the vehicle starts vibrating vigorously due to resonance, and a rattling sound is heard.
- When a troop crosses a suspension bridge, the soldiers are asked to break steps.

Characteristics of Sound
Two sounds are distinguished by the following characteristics:
- Loudness
- Pitch or shrillness
- Quality or timbre
1. Loudness
- Loudness is the property by which a loud sound can be distinguished from a faint one, both having the same pitch and quality.
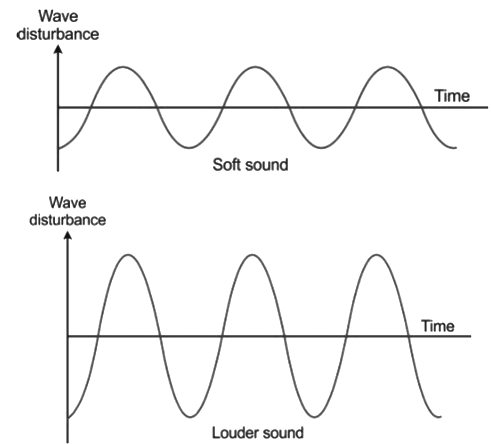
- The loudness or softness of a sound is determined by the amplitude (or intensity) of the wave.
- However, loudness is not the same as intensity. Intensity is a measurable quantity, while loudness is a sensation.
- The intensity at any point of the medium is measured as the amount of sound energy passing per second normally through the unit area at that point. Its unit is microwatt per metre squared.
- The intensity of a sound wave in air is proportional to (i) the square of the amplitude of vibration, (ii) the square of the frequency of vibration and (iii) the density of air.
Factors affecting the loudness of sound
The loudness of sound heard at a place
- Is proportional to the square of the amplitude.
- Varies inversely as the square of the distance.
- Depends on the surface area of the vibrating body.
- Depends on the density of the medium.
- Depends on the presence of resonant bodies.
Units of loudness and sound level
The unit of loudness is phon. The loudness of a sound in phon is the loudness in decibel (dB) of an equally loud pure sound of frequency 1 kHz. The sound level is usually expressed in decibel (dB).
The difference in loudness is
L = L1 - L0
= K(log10I1 - L1 = Klog10I0)
= Klog10(I1/I0)
L = 10log10(I1/I0) decibel
- Now, if then we have
I1 /I0 = 1.26 - Thus, we can define 1 dB as the change in level of loudness when the intensity of sound is changed by 26%.
Noise Pollution
The disturbance produced in the environment due to undesirable loud and harsh sound of level above 120 dB from various sources such as loudspeakers, sirens, moving vehicles etc. is called noise pollution. A constant hearing of sound of level above 120 dB can cause headache and permanent damage to the ear/hearing in a listener. The sound of level 10 dB to 30 dB has a soothing sensation, while the level 0 dB of loudness of sound represents the limit of hearing.
2. Pitch or Shrillness
- How our brain interprets the frequency of an emitted sound is called its pitch. The faster the vibration of the source of sound, higher is the frequency and higher is the pitch.
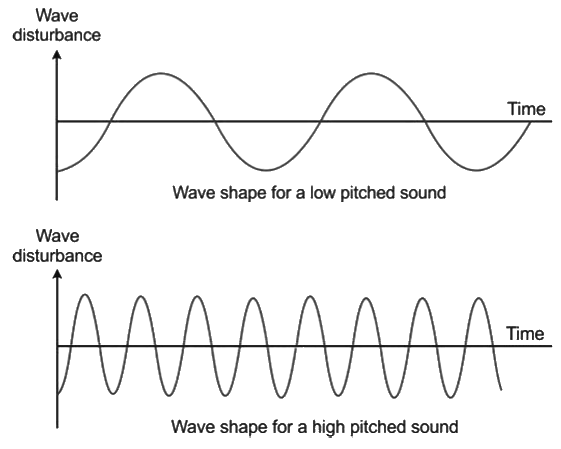
- Pitch is that characteristic of sound by which an acute (or shrill) note can be distinguished from a grave or flat note.
- Pitch refers only to musical sounds, and each musical note has a definite pitch. If the pitch is higher, then the sound is said to be shrill, and if the pitch is lower, then the sound is flat.
- The pitch of a note depends on the wavelength or frequency of wave.
Examples of Change in Pitch
- Instruments such as a piano, violin and guitar have several strings of different thickness under different tensions which vibrate to produce notes.
- In a flute, a lower note is obtained by closing some more holes so that the length of the vibrating air column increases.
- As the water level in a pitcher kept under a water tap rises, the height of the air column decreases, so the frequency of sound produced increases, i.e. the sound becomes shriller. Thus, by hearing the sound from a distance, one can get the idea of water level in the pitcher.
- The voice of women is usually of higher pitch than that of men.
3. Quality or Timbre
- Quality or timbre of a sound is a characteristic which distinguishes two sounds of the same loudness and same pitch but emitted by two different instruments.
- The sound from an instrument does not contain a note of single frequency, but it contains a combination of vibrations of different frequencies and different amplitudes. The vibration of lowest frequency and maximum amplitude is called the principal (or fundamental) vibration and vibrations of frequency integer multiples of it are called subsidiary (or secondary) vibrations.
- The resultant vibration obtained by the superposition of all these vibrations gives the wave form of sound which we hear.
- A note played on a piano has a large number of subsidiary notes, while the same note when played on a flute contains only a few subsidiary notes. Thus, we can easily distinguish between the sounds of a piano and a flute by their different wave forms, though they may be of exactly the same loudness and same pitch.
Music and Noise
- All sounds, which produce the sensation of hearing, can be roughly divided into two categories music and noise.
- Music: It is a pleasant, continuous and uniform sound produced by regular and periodic vibrations. For example, the sounds produced by a violin, piano, flute, tuning fork etc. are musical sounds. Their sound level is usually between 10 dB and 30 dB.
- Noise: Sounds other than musical sounds are called noise. It is a sound produced by an irregular succession of disturbances, and it is a discontinuous sound. For example, the sound produced when a stone is thrown on a tin sheet is noise. Usually all sounds above 120 dB are termed noise.
|
28 videos|121 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Sound - Physics Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What are sound waves and how do they travel? |  |
| 2. What is resonance and why is it important? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between music and noise? |  |
| 4. What are damped vibrations and how do they differ from free vibrations? |  |
| 5. Can you give examples of resonance in everyday life? |  |




















