The Origin and Evolution of the Earth Class 11 Geography
| Table of contents |

|
| Early Theories |

|
| Modern Theories |

|
| Evolution of Earth |

|
| Origin of The Life |

|
Early Theories
Origin of the Earth

- A large number of hypotheses were put forth by different philosophers and scientists regarding the origin of the earth.
- One of the earlier and popular arguments was by German philosopher Immanuel Kant.
- Mathematician Laplace revised it in 1796.
- It is known as Nebular Hypothesis.
- The hypothesis considered that the planets were formed out of a cloud of material associated with a youthful sun, which was slowly rotating.
- In 1950, Otto Schmidt in Russia and Carl Weizascar in Germany somewhat revised the 'nebular hypothesis', though differing in details.
- They considered that the sun was surrounded by solar nebula containing mostly the hydrogen and helium along with what may be termed as dust.
- The friction and collision of particles led to formation of a disk-shaped cloud and the planets were formed through the process of accretion.
- However, scientists in later period took up the problems of origin of universe rather than that of just the earth or the planets.
Modern Theories
The Origin of The Universe- The Big Bang Theory stands as a contemporary explanation for the origin and evolution of the Earth.
- Edwin Hubble introduced this theory in 1920, and it is also recognized as the Expanding Universe Hypothesis.
- This theory posits that the universe is in a constant state of expansion.
- According to the theory, all the matter in the universe was concentrated at its center, occupying a minute space with incredibly high temperatures and densities.
- Approximately 13.7 billion years ago, a significant explosion occurred, leading to the formation of atoms, and over time, the conversion of energy into matter took place.
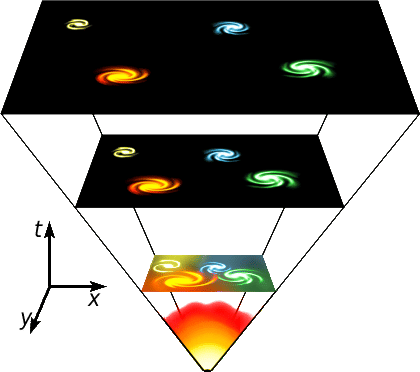
Stages of the Big Bang Theory
1. Singularity:
- All matter and energy existed in a "tiny ball" (singular atom) with infinite temperature and density.
2. Big Bang Explosion:
- The "tiny ball" exploded violently 13.7 billion years ago, leading to rapid expansion.
- Some energy converted into matter.
- Rapid expansion within fractions of a second; first atoms formed within three minutes.
3. Cooling and Atomic Matter Formation:
- 300,000 years after the Big Bang, temperature dropped to 4,500K.
- Atomic matter formed, and the universe became transparent.
The Star Formation
- The distribution of matter and energy was not even in the early universe. These initial density differences gave rise to differences in gravitational forces and it caused the matter to get drawn together.
- These formed the bases for development of galaxies.
- A galaxy contains a large number of stars.
- A galaxy starts to form by accumulation of hydrogen gas in the form of a very large cloud called nebula.
- Eventually, growing nebula develops localised clumps of gas.
- These clumps continue to grow into even denser gaseous bodies, giving rise to formation of stars.
- The formation of stars is believed to have taken place some 5-6 billion years ago.
Formation of Planets
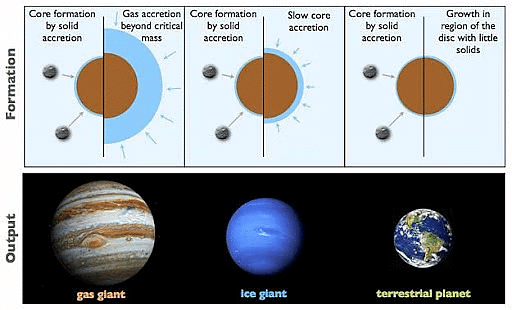 Formation of Planets
Formation of Planets
Formation of Core and Rotating Disc
- Stars form as localized lumps of gas within a nebula.
- Gravitational forces create a core in the gas cloud.
- A rotating disc of gas and dust develops around this core.
Condensation and Planetesimals Formation
- The gas cloud condenses, forming small-rounded objects around the core.
- These small objects, through cohesion, become planetesimals.
- Larger bodies form through collisions and gravitational attraction, sticking together.
Accretion into Planets
- Numerous small planetesimals accrete to form fewer, larger bodies.
- These larger bodies become planets.
Evolution of Earth
Initially, Earth existed in a scorching state, devoid of life, and characterized by rocky desolation. Its atmosphere primarily comprised hydrogen and helium. Over time, the processes of lithosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere formation gradually transformed the planet.
Evolution of Lithosphere
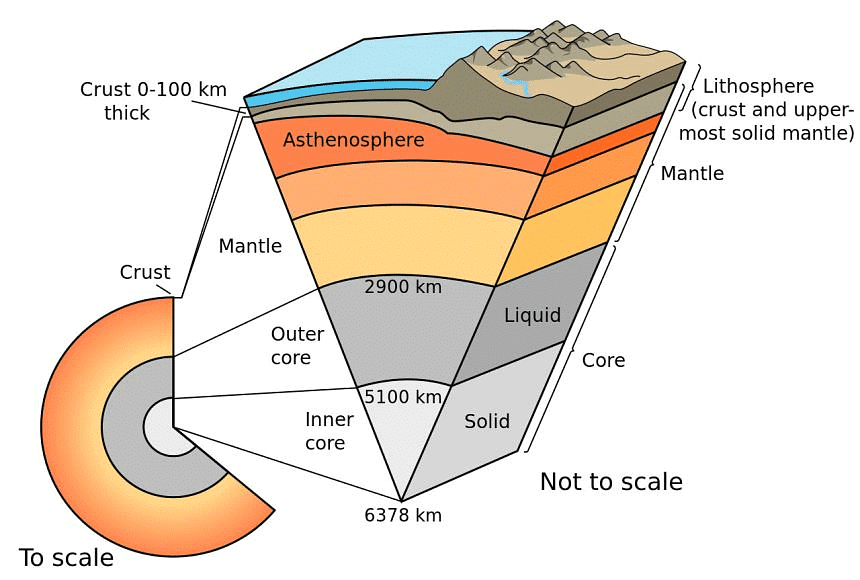 Evolution of Lithosphere
Evolution of Lithosphere
- During its primordial stage, the Earth was mostly in a volatile state with increasing internal temperature.
- Due to the gradual increase in density and temperature, materials inside the Earth began to separate based on their densities. Heavier materials, such as iron, sank towards the center, while lighter materials moved towards the surface.
- As time passed, the Earth cooled, solidified, and condensed into a smaller size. This cooling process led to the development of the outer surface in the form of a crust.
- During the formation of the moon, a giant impact further heated the Earth.
- Through the process of differentiation, the Earth-forming materials separated into different layers. These layers, from the surface to the center, include the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. The density of the materials increases from the crust to the core.
Evolution of Atmosphere and Hydrosphere
Three Stages of Atmosphere Evolution
- The early atmosphere, composed of hydrogen and helium, was stripped off by solar winds. This phenomenon occurred not only on Earth but also on other terrestrial planets.
- During the cooling of the Earth, gases and water vapor were released from the interior solid Earth, initiating the evolution of the present atmosphere. The early atmosphere largely contained water vapor, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, methane, ammonia, and very little free oxygen. Continuous volcanic eruptions contributed water vapor and gases to the atmosphere.
- The composition of the atmosphere was significantly modified by the process of photosynthesis. This process, carried out by early life forms, increased the oxygen levels in the atmosphere.
Formation of Oceans
- As the Earth cooled, the water vapor in the atmosphere began to condense, leading to rain.
- The rainwater collected in depressions on the Earth's surface, giving rise to oceans.
- The Earth's oceans were formed within 500 million years from its formation, making them approximately 4,000 million years old.
Origin of The Life
- Life emerged on Earth approximately 3.8 billion years ago, with blue algae representing the earliest life form.
- These life forms evolved from chemical reactions that gave rise to molecules capable of replication and transformation into living entities.
- Two primary theories include the Nebular Hypothesis and the modern Big Bang Theory.
- Earth's early state was characterized by solid rockiness and desolation, eventually leading to the formation of its distinct layers: the crust, mantle, and core.
- Initially, Earth's atmosphere lacked oxygen, but the emergence of life and the process of photosynthesis subsequently raised oxygen levels while reducing carbon dioxide.
- The evolution of life on Earth can be traced back to the presence of blue algae.
|
70 videos|340 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on The Origin and Evolution of the Earth Class 11 Geography
| 1. What are some early theories about the origin and evolution of the Earth? |  |
| 2. What are some modern theories explaining the origin and evolution of the Earth? |  |
| 3. How has the Earth evolved over time? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the origin of life in the context of the Earth's evolution? |  |
| 5. How does the study of the humanities and arts contribute to our understanding of the origin and evolution of the Earth? |  |
















