Role of Public and Private Sectors in Seed Production | Agriculture Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Private and Public Sector Contribution in Seed Production
In recent years, the private sector has expanded its role in the seed market, with approximately 400 to 500 companies now involved in seed production and trade.
Private seed companies have primarily focused on producing high-value, low-volume seeds and entering the market for low-value, high-volume seeds. Public seed firms still maintain control over seeds of cereals, pulses, and oilseeds. However, for crops like maize, sunflower, and cotton, the private sector plays a significant role.
The private sector takes the lead in producing vegetable seeds and planting supplies for horticulture crops.
For high-volume, low-margin crops such as wheat, paddy, other cereals, oilseeds, and pulses, the private sector has been hesitant to enter the seed business. Therefore, public seed companies will continue to dominate the cereals, pulses, and oilseeds sectors for many more years.
Currently, there are 15 state seed corporations and two national seed corporations in India. The National Seeds Corporation of India and the State Farms Corporation of India are both operational. In areas where State Seeds businesses do not exist, State Departments of Agriculture play a significant role in seed production.
The following table illustrates the contribution of private sector seed companies to the overall seed production in the country: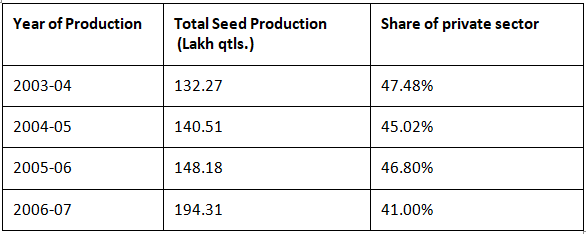
The following map depicts the major seed production states.
Here is a list of Indian states and their major crops:
- Odisha: Paddy
- Andhra Pradesh: Paddy, Groundnut, Sunflower, Jute, Corn, Pigeon Pea
- Tamil Nadu: Paddy, Cotton, Green Gram, Black Gram
- Karnataka: Paddy, Groundnut, Sunflower, Jute, Corn, Pigeon Pea, Vegetable
- Maharashtra: Paddy, Groundnut, Sunflower, Jute, Corn, Pigeon Pea, Soybean, Vegetable, Cotton
- Gujarat: Groundnut, Cotton, Castor
- Rajasthan: Wheat, Mustard, Gram
- Uttar Pradesh: Wheat, Mustard, Gram, Paddy, Green Gram, Black Gram
- Madhya Pradesh (Bhopal): Wheat, Soybean, Red Gram, Gram
- Punjab: Wheat, Paddy
- Haryana: Wheat, Paddy, Mustard
- Uttarakhand: Wheat, Paddy
FAQs on Role of Public and Private Sectors in Seed Production - Agriculture Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the role of the private sector in seed production? |  |
| 2. How does the public sector contribute to seed production? |  |
| 3. What are the benefits of private sector involvement in seed production? |  |
| 4. How does the public sector ensure the availability of quality seeds to farmers? |  |
| 5. What is the role of the government in promoting a conducive environment for seed production? |  |

















