Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE > Rounding & Estimation
Rounding & Estimation | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Rounding & Estimation
How do I round numbers to a given place value?
- Identify the digit in the required place value and circle the number to the right to determine whether to round up or round off.
- For example, to round 1294 to the nearest 100, locate the 2 digit and use the 9 to decide how to round
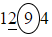 .
.
- For example, to round 1294 to the nearest 100, locate the 2 digit and use the 9 to decide how to round
- Find the two options that the number could round to. For example, the two nearest 100's to 1294 are 1200 and 1300.
- Be cautious when the digit is 9, as rounding up may affect higher place values. For instance, the nearest 2 decimal places to 3.497 are 3.49 and 3.50.
- Rounding Rules: If the digit following the specified decimal place is 5 or greater, round up to the next higher number. If it is less than 5, round down to the lower number.
- Adding Zeroes: When rounding, ensure that you include any necessary zero placeholders after the decimal point. For example, rounding 1297 to the nearest 100 gives 1300.
- Rounding to Nearest 100th: Consider rounding 3.497 to two decimal places. Since the digit after the hundredth place is 5, we round up to get 3.50, maintaining exactly two decimal places in the answer.
How do I round to significant figures?
- Rounding to significant figures is akin to rounding to place value but with a focus on significant digits.
- To round to significant figures, identify the first significant figure and the relevant place value.
- For instance, the first significant figure of 3097 is 3, and for 0.006207, it is 6.
- Start with this number and count along to the right
- You do count the following zeros, for example:
- 0 is the second significant figure of 3.097
- 9 is the third significant figure of 30.97
- Use the normal rules for rounding:
- Circle the number to the right
- Use this to determine whether the given significant figure rounds up or rounds off
- You do count the following zeros, for example:
Why do we use estimation?
- We estimate to find approximations for difficult sums
- Or to check if our answers are about the correct size (right order of magnitude)
How do I estimate?
- We usually round numbers to a sensible value before performing calculations.
- General Rule
- Round numbers to 1 significant figure:
- 7.8 → 8,
- 18 → 20,
- 3.65 × 10-4 → 4 × 10-4,
- 1080 → 1000
- Exceptions
- It can be more practical to round to a convenient value like
- 16.2 → 15,
- 9.1 → 10,
- 1180 → 1200
- Round numbers to 1 significant figure:
How do I know if I have underestimated or overestimated?
- Rounding for addition:
- Rounding both numbers up leads to an overestimation
- Rounding both numbers down leads to an underestimation
- Rounding for multiplication:
- Rounding both numbers up results in an overestimation
- Rounding both numbers down results in an underestimation
- Subtraction and division complexities:
- For subtraction (a - b):
- Increasing 'a' and/or decreasing 'b' leads to an overestimated result.
- Decreasing 'a' and/or increasing 'b' leads to an underestimated result.
- If both numbers are increased or decreased, it's challenging to determine if it's an overestimate or underestimate.
- For division (a ÷ b):
- Increasing 'a' and/or decreasing 'b' results in an overestimated answer.
- Decreasing 'a' and/or increasing 'b' results in an underestimated answer.
- If both numbers are increased or decreased, determining overestimation or underestimation becomes complex.
- For subtraction (a - b):
Question for Rounding & EstimationTry yourself: How do you round a number to the nearest hundred?View Solution
The document Rounding & Estimation | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
38 videos|413 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Rounding & Estimation - Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How can rounding and estimation help in simplifying complex calculations? |  |
Ans. Rounding and estimation can help simplify complex calculations by providing approximate values that are easier to work with. By rounding numbers to the nearest whole number or a specific decimal place, calculations become more manageable and less prone to errors.
| 2. What are the advantages of using bounds in mathematical problems involving rounding and estimation? |  |
Ans. Bounds in mathematical problems involving rounding and estimation help provide a range within which the actual value lies. This can be useful in determining the level of accuracy or uncertainty in a calculation, especially when dealing with real-world scenarios where exact values may not be known.
| 3. How can rounding and estimation be applied in everyday situations outside of mathematics? |  |
Ans. Rounding and estimation techniques are commonly used in everyday situations such as budgeting, grocery shopping, and time management. For example, estimating the total cost of items in a shopping cart or rounding off the time needed to complete a task can help make quick decisions without the need for precise calculations.
| 4. What are some common pitfalls to avoid when using rounding and estimation in calculations? |  |
Ans. One common pitfall when using rounding and estimation is rounding too early in a calculation, which can lead to significant errors in the final result. It is important to only round at the end of a series of calculations to minimize inaccuracies.
| 5. How can technology assist in improving the accuracy of rounding and estimation in mathematical calculations? |  |
Ans. Technology such as calculators and spreadsheet software can assist in improving the accuracy of rounding and estimation by providing tools for precise calculations and automatic rounding functions. These tools can help ensure that calculations are performed consistently and efficiently.
Related Searches
















