SWOT Analysis | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
A valuable planning tool, the SWOT analysis combines an assessment of Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats within a project or business. By identifying the objectives and recognizing internal and external factors, this analysis aids in strategic planning. Often integrated into the strategic planning process, SWOT provides guidance for organizations to discern positive and negative aspects (S-W) internally and in the external environment (O-T). Moreover, it highlights the time-limited nature of corresponding competencies with opportunities. Following a general policy, organizations aim to maximize strengths and opportunities while minimizing weaknesses and threats (Nadine Pahl, 2009).
Component of SWOT analysis
History of SWOT Analysis
Originator: Albert Humphrey developed the SWOT analysis in the 1960s and 1970s at Stanford University.
Research Purpose: Humphrey's research aimed to understand why corporate planning failed by studying data from top companies.
Original Name: Initially called "SOFT analysis," it identified critical areas using categories: Satisfactory, Opportunity, Fault, and Threat.
Categories Defined: "What is good now is Satisfactory; good in the future is an Opportunity; bad now is a Fault; and bad in the future is a Threat."
Expansion to Various Fields: Originally designed for business, SWOT (or TOWS) is now applied in community health, development, education, and personal growth.
SWOT Analysis Framework:
Telescopic Observations: In 2003, Panagiotou introduced a strategic framework that aligns strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats with the acronym "telescopic observations."
Versatility: SWOT is widely used for company assessments and can be compared with other tools to find the most suitable approach.
Strengths of SWOT:
- Straightforwardness
- Applicability to various operational levels
SWOT in Management:
Audit Mechanism: In management reviews, SWOT serves as an auditing tool for both the organization and its environment.
Planning Stage: It is the initial stage of planning, helping to focus on key issues.
Role of SWOT:
- Separates information into internal and external issues
- Determines if information supports objectives or indicates obstacles that need overcoming for desired results.
Elements of a SWOT Analysis
SWOT Elements:
Purpose of SWOT:
- Reveals positive forces and potential problems in a project or business.
- A diagnostic tool for identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Graphic Format:
- Companies use varied graphic formats based on the depth and complexity of their SWOT analysis efforts.
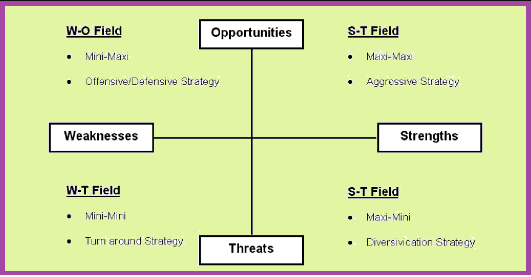
SWOT Matrix for strategy formulation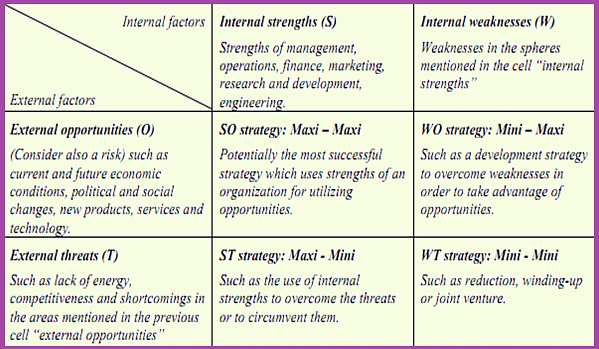
SWOT Elements Explained
Strengths:
- Positive attributes, tangible and intangible, internal to the organization.
- In areas like marketing, finance, manufacturing, and organizational structure.
- Includes knowledge, backgrounds, education, credentials, equipment, and other tangible assets.
Weaknesses:
- Factors within the company's control that detract from a competitive edge.
- Areas for improvement, such as lack of expertise, limited resources, or poor location.
- Identifying weaknesses helps in effective marketing objective accomplishment.
Opportunities:
- External factors that represent reasons for the business to flourish.
- Result from market growth, lifestyle changes, or positive market perceptions.
- Realizing opportunities enhances internal strengths and control.
Threats:
- Factors beyond the company's control that could risk the business.
- External challenges like competition, price increases, regulations, or economic downturns.
- Contingency plans may be needed to address potential threats.
Implications of SWOT:
- Internal strengths and weaknesses, compared to external opportunities and threats, provide insights into the business's condition and potential.
- SWOT analysis helps prioritize opportunities and address critical issues.
Aim of SWOT Analysis:
- Reveals competitive advantages.
- Analyzes prospects for sales, profitability, and product development.
- Prepares the company for potential problems and aids in developing contingency plans.
Steps to Perform SWOT Analysis
Data Collection and Evaluation:
- Collect and analyze authentic data, including demographics, funding sources, and technology status.
- Assess the organization's capabilities in these areas.
Sorting Data into SWOT Categories:
- Categorize data into strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors; opportunities and threats are external.
SWOT Matrix Development:
- Develop a SWOT matrix for each business alternative under consideration.
Incorporating SWOT into Decision-Making:
- Use the SWOT analysis in the decision-making process to align with the organization's overall strategic plan.
SWOT Matrix for health care industry:
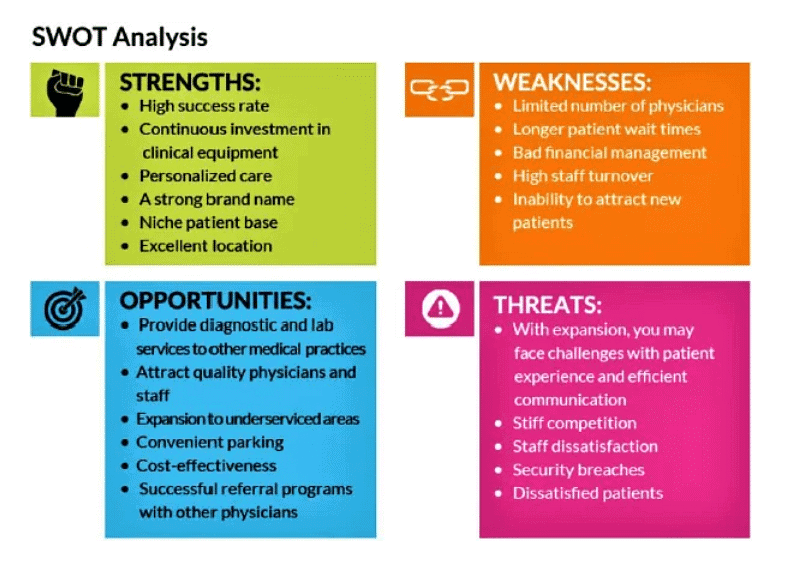
Applications of SWOT analysis:
Business Organizations:
- Helps business organizations assess their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Useful for crisis prevention and resolution.
Non-Profit Organizations:
- Applicable in decision-making situations for non-profit organizations.
- Aids in planning, problem-solving, and crisis management.
Governmental Organizations:
- Governmental organizations can utilize SWOT analysis for decision-making.
- Helps in crisis avoidance and resolution.
Individuals:
- Individuals can apply SWOT analysis in personal development planning.
- Useful for self-assessment and decision-making.
SWOT Applications in Various Situations:
Workshop Sessions:
- SWOT analysis can be effectively employed in workshop sessions.
- Facilitates collaborative assessment and planning.
Brainstorm Meetings:
- Useful during brainstorm meetings to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Enhances team collaboration and problem-solving.
Problem Solving:
- SWOT is a valuable tool for systematic problem-solving.
- Helps in identifying and addressing challenges.
Planning:
- Essential for planning purposes, aiding organizations in strategic decision-making.
- Guides future actions based on a comprehensive assessment.
Product Evaluation:
- Companies can use SWOT analysis to evaluate their products.
- Assesses the product's strengths, weaknesses, market opportunities, and potential threats.
Competitor Evaluation:
- Businesses can analyze competitors using SWOT.
- Identifies competitor strengths and weaknesses for strategic advantage.
Personal Development Planning:
- Individuals can use SWOT for personal development planning.
- Identifies personal strengths and areas for improvement.
Decision Making (with Force Field Analysis):
- Integrates with force field analysis for decision-making.
- Considers internal and external factors before making informed decisions.
Merits and Demerits of SWOT Analysis
Proactive Thinking:
- Encourages forward-thinking instead of relying on personal opinions.
- Provides a framework to review a company's strategy, position, and direction.
Versatile Applications:
- Useful for various purposes like business planning, strategic marketing, competitor analysis, and research reports.
Strengths and Weaknesses Recognition:
- Helps organizations identify their strengths and weaknesses.
- Supports strategic thinking by focusing on strengths and leveraging opportunities.
Opportunity Utilization:
- Enables the identification and utilization of opportunities for the company's advantage.
- Helps predict and mitigate potential threats.
Brief Overview:
- Offers a quick overview of internal assets and market conditions through analysis.
- Exploits strategic windows to increase profit potential.
Flexible and Modifiable:
- Adaptable and can be modified to suit specific circumstances.
- No rigid structure, making it a straightforward and flexible model.
Integration with Other Models:
- Implementable in various theoretical models like the balanced scorecard or Boston Consulting Group portfolio.
- Proven to be scalable, simple, low-cost, flexible, collaborative, quick, and integratable.
Alignment of Resources:
- Assists in synchronizing a firm's resources and capabilities with its competitive environment.
SWOT analysis framework:
Drawbacks of SWOT Analysis:
Subjectivity and Lack of Quantification:
- Relies on subjective instincts and lacks quantification, which can impact performance.
Difficulty in Element Identification:
- Doesn't guide organizations in recognizing elements specific to their company.
- Some officials may struggle to identify these elements.
Risk of Unintentional Mistakes:
- Risk of unintentional use of wrong assumptions or generalizing data.
- Time-consuming for complex situations involving large amounts of data.
Lack of Detailed Structure:
- Lacks a detailed structure, leading to potential oversight of crucial information.
- Consistency may be doubtful if not used carefully.
Success Factors for SWOT Analysis:
Realism and Precision:
- Must be realistic, precise, short, and simple.
- Avoid including too much or too little information.
Avoid Over-Analysis:
- Refrain from over-analyzing data to prevent information distortion.
- Focus on generating valuable strategies to achieve objectives.
Summary
- SWOT analysis is a beneficial decision-making tool.
- Examines strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for a new endeavor.
- Allows users to consider the company's direction for the future.
FAQs on SWOT Analysis - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is a SWOT analysis? |  |
| 2. What are the elements of a SWOT analysis? |  |
| 3. What are the merits of conducting a SWOT analysis? |  |
| 4. What are the demerits of using a SWOT analysis? |  |
| 5. How can a SWOT analysis be beneficial for UPSC exam preparation? |  |















