Ramesh Singh Summary: Security Market in India- 3 | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Indian Depository Receipts
Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs) serve as a means for Indian investors to easily invest in foreign companies. Investors in India can use Indian rupees to invest in foreign companies through IDRs.
 Indian Depository Receipts
Indian Depository Receipts
In this process, a foreign company issues shares to an Indian depository, such as the National Security Depository Limited (NSDL). The Indian depository, in turn, issues depository receipts (IDRs) to investors in India, representing a stake in the foreign company. NSDL (National Security Depository Limited)
NSDL (National Security Depository Limited)
The actual shares of the foreign company are held by an Overseas Custodian, which authorizes the Indian depository to issue IDRs.
IDRs are priced in Indian Rupees and are tradable on Indian stock exchanges, similar to regular stocks.
In essence, IDRs provide a mechanism for Indians to invest in foreign companies using Indian currency, akin to how ADRs/GDRs enable foreigners to invest in Indian companies.
Regulatory Measures Amid COVID-19
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) implemented several measures to help pension funds and custodians.
 PFRDA(Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority)
PFRDA(Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority)
Here's a simplified explanation:
Extended Deadlines: The submission deadlines for various compliance requirements by Pension Funds and Custodians were extended.
Annual Accounts Extension: The time limit for submitting annual accounts and other yearly documents was given an extension.
Partial Withdrawal for COVID-19 Treatment: People with accounts in the National Pension System (NPS) were allowed to make partial withdrawals for treating COVID-19-related expenses.
Online Onboarding with Aadhaar: To make things easier, the NPS allowed online onboarding using Aadhaar-based offline paperless KYC verification. This streamlined the process of joining.
Atal Pension Yojana Registration Online:
 Subscribers of the Atal Pension Yojana could now register online through their bank's web portal without needing net-banking. This was particularly beneficial for savings bank customers.
Subscribers of the Atal Pension Yojana could now register online through their bank's web portal without needing net-banking. This was particularly beneficial for savings bank customers.
Hence, these measures aimed to provide flexibility and ease the procedures related to pension funds during the challenging times of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Financial Stability and Development Council
The Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) was created by the Indian government in December 2010 to deal with financial troubles worldwide caused by the 2007-08 crisis in the United States.
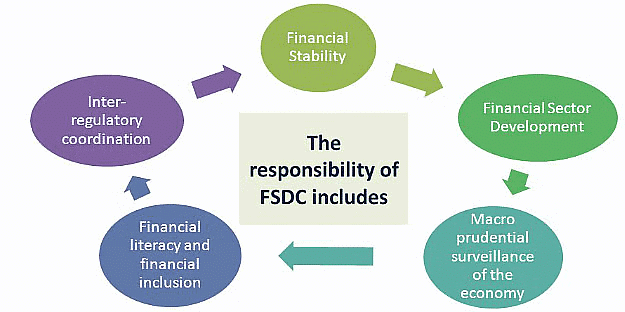 FSDC Responsibilities
FSDC Responsibilities - Keep Finances Stable: The FSDC works to make sure our country's money systems stay strong and stable.
- Help Different Money Groups Work Together: It tries to make sure that different groups that handle money in our country (regulators) talk to each other and work well together.
- Make Money System Better: The FSDC tries to make our money system better and more helpful for everyone.
The FSDC is led by the finance minister and includes other important people. While each group still does its own thing, the FSDC keeps an eye on three main things:
Making sure big money groups are doing well.
Helping different money groups work together better.
Making sure more people understand how money works and can use it.
So, it's like a team that watches over our money to keep it safe, helps different money groups work together, and tries to make our money system better for everyone.
Financial Stability Assessment Programme
In September 2010, the IMF Board decided to include 25 economically important countries, including India, in a program called the Financial Stability Assessment Programme (FSAP). This program is for countries with financially important sectors.
In January 2015, India underwent a joint assessment by the IMF and the World Bank under the Financial Stability Assessment Programme. This assessment checked how well India's financial system followed international standards. The assessment found that India's financial system was generally stable because of good rules and supervision.
However, the assessment pointed out a few areas where India could improve:
Sharing Information: There's room to improve how India shares information internationally and domestically for supervision.
Supervising Big Financial Groups: India could do better at keeping an eye on big financial groups to make sure they follow all the rules.
Regulatory Independence: Some rules limit the independence of certain regulators (like RBI and IRDA).
In simple terms, the assessment acknowledged that India's financial system is mostly stable due to good regulations. But, it also suggested that India could work on sharing information better, supervising big financial groups more effectively, and ensuring regulatory independence.
Despite having some concerns, Indian authorities recognize certain reservations.
Significant Role of FSAP:
Indian authorities expect the FSAP exercise to play a key role in shaping post-COVID initiatives. Despite some reservations on specific issues, there is an overall positive outlook.
The focus is on strengthening the regulatory and supervisory framework based on evolving international consensus.
- Careful examination is being done to assess its relevance in the Indian context.
- India, through representatives like Tudia in ISE BOEBSTM and IME, actively participates in shaping global regulatory frameworks under the G-20.
- The commitment is to adopt international standards and best practices gradually.
- Adoption will be phased, considering the complexity and diversity of socio-political and economic conditions in India.
- Flexibility is maintained to align with local conditions wherever necessary.
Financial Action Task Force
The FATF (Financial Action Task Force) is a collaborative group of governments working together. FATF (Financial Action Task Force)
FATF (Financial Action Task Force)
- Its primary goal is to establish rules aimed at preventing illegal money transactions, commonly known as money laundering, and to combat the financing of terrorism.
- In June 2010, India became the 34th member of the FATF.
- Currently, the FATF comprises 36 members, consisting of 34 countries and 2 organizations—the European Union and the GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council).
- Member countries, including India, adhere to these rules collectively to ensure the legal use of money and to thwart activities like terrorism financing.
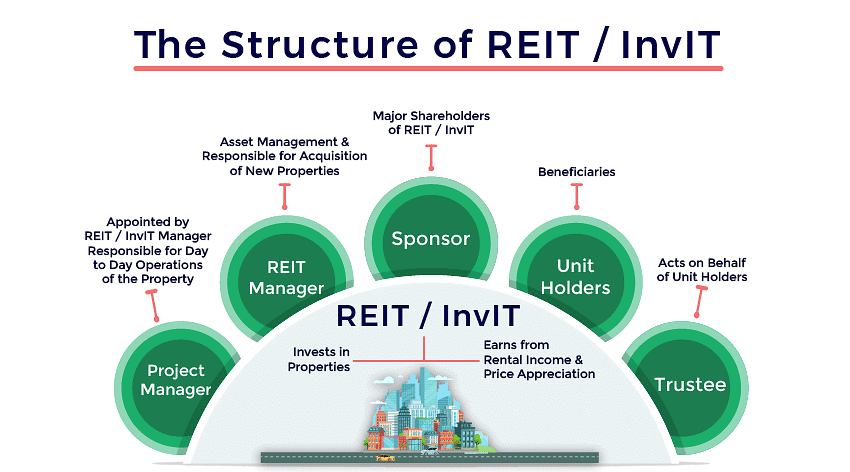
Real Estate and Infrastructure Investment Trusts(REITs)
SEBI has finalized rules for governing REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts) and Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs). These trusts, proposed in 2008, aim to help real estate and infrastructure developers who are facing financial challenges to easily access funds. They provide a new way for institutions, high-net-worth individuals, and other investors to invest their money. 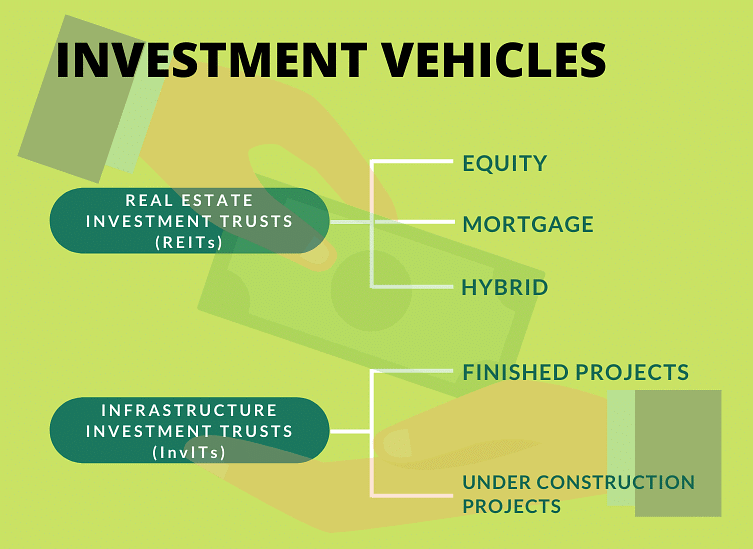 REITs and InvITs
REITs and InvITs
REITS
The SEBI has made some important rules for REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts), and here are the key points explained in simpler terms:
- Nature of REITs: REITs will be close-ended real estate investment schemes. Their main goal is to invest in properties and provide returns to unit holders.
- Source of Income: The primary income for REITs will come from rental income or capital gains from real estate.
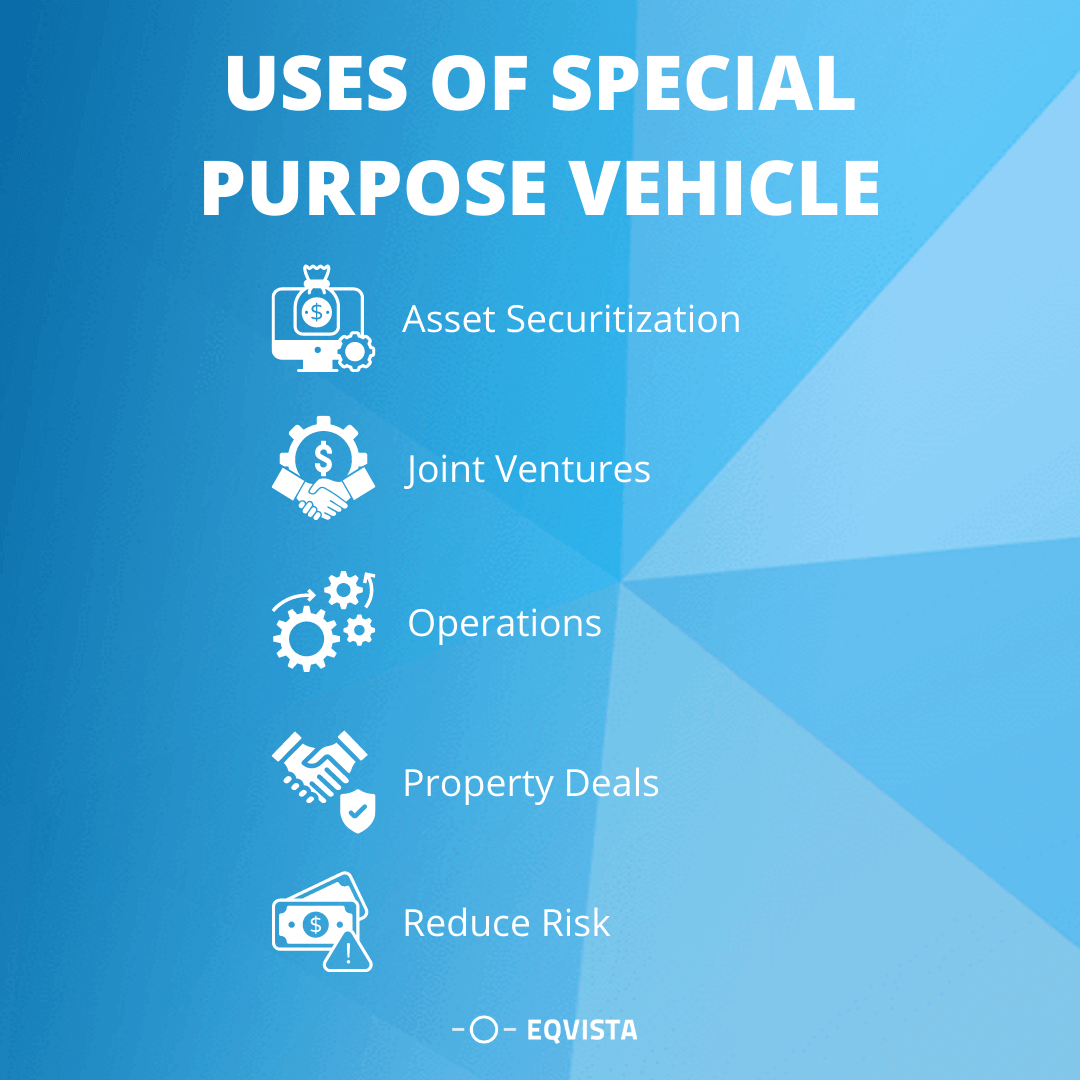
- Investment Scope: REITs are allowed to invest in commercial real estate assets, either directly or through special purpose vehicles (SPVs). In SPVs, an REIT must control at least 50% of the share capital and hold at least 80% of their assets directly in properties.
- Funding and Listing: REITs can raise funds only through an initial offering, and their units must be listed on a stock exchange, similar to IPOs and listing for equity shares. The assets of the REIT must be worth at least ₹500 crore at the time of the initial offer, with a minimum issue size of ₹230 crore. The minimum subscription size for units of a REIT on offer will be ₹2 lakh, and at least 25% of the units must be offered to the public.
InvITs
SEBI has introduced InvITs (Infrastructure Investment Trusts), similar to REITs but with some differences. Here are the key points explained in simpler terms:
Investment Focus: InvITs can invest in infrastructure projects directly or through a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV). For Public-Private Partnership (PPP) projects, investments will be made only through an SPV.
 SPV Uses
SPV UsesSponsor Holding: During listing, the collective holding of sponsors of an InvIT must be at least 25% for a minimum of three years.
Asset Requirement: InvITs must have a holding worth at least ₹500 crore in the underlying assets, and the initial offer size has to be at least ₹250 crore.
Fundraising Methods: InvITs looking to invest at least 80% of their assets in completed and revenue-generating infrastructure assets must raise funds through a public issue of units. This requires a minimum 25% public float and at least 20 investors.
Subscription Size and Trading Lot: The minimum subscription size and trading lot for a listed InvIT must be ₹10 lakh and ₹5 lakh, respectively. A publicly offered InvIT can invest the remaining 20% in under-construction infrastructure projects and other permissible investments.
Private Placement
InvITs planning to invest more than 10% of their assets in under-construction projects can raise funds only through private placement from qualified institutional buyers, with a minimum investment and trading lot of ₹1 crore, and from at least five investors, with no single holding exceeding 25%.
Regarding recent developments, the government introduced a more favorable tax regime for real estate and infrastructure trusts starting April 2022. However, attracting investors for new projects or trusts has been challenging due to market conditions. To promote trusts, SEBI allowed Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) in 2019-20. The success of these trusts depends on future interest from FPIs and a potential economic upturn.
ESG Investment
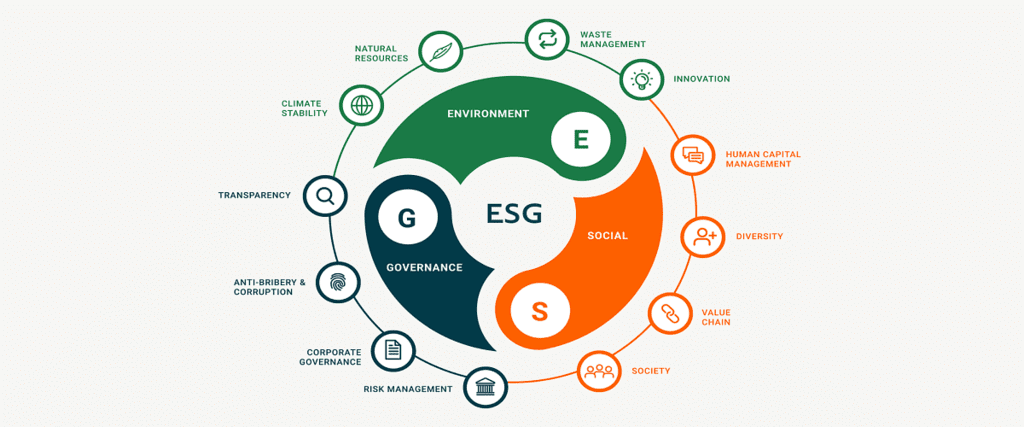
In recent years, a new idea has emerged in stock markets worldwide - a set of criteria known as ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) for listed companies. Let's break down what these criteria mean:
Environmental Criteria: This looks at how a company deals with nature, including aspects like energy usage, pollution control, waste disposal, conservation of resources, and treatment of animals.
Social Criteria: This examines a company's relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, as well as its stance on privacy, data protection, and its impact on communities.
Governance: This focuses on a company's management, covering leadership, executive pay, audit practices, internal controls, and the rights of shareholders.
 ESG Components
ESG Components
Socially conscious investors, especially in Western countries, are increasingly considering these criteria before deciding where to invest. ESG investing, also known as impact investing, is seen as a sustainable and socially responsible way of investing that can positively influence not just the environment but also investment trends.
Investors using ESG criteria believe they can support companies that share their values. This approach helps them avoid investing in companies with risky practices, as seen in cases like the 2010 BP oil spill and the 2015 Volkswagen emission scandal, where both companies faced significant share price drops due to investor backlash.
As companies become more aware of these criteria, investment firms are keeping a closer eye on how well businesses perform in terms of ESG.
In 2020, big financial service companies like JPMorgan Chase, Wells Fargo, and Goldman Sachs extensively talked about their performance in their yearly reports.
Case with India
In India, the stock market regulator, SEBI, noticed an increased focus on ESG, following the global trend. Investors in India also showed more interest in ESG investment during 2020-21. As a result, in April 2021, SEBI committed to announcing relevant guidelines soon.
Social Stock Exchange
The Social Stock Exchange (SSE) is a platform where social enterprises, both non-profit and for-profit, can get listed to raise funds.
These exchanges operate in various countries like the United Kingdom, Canada, Singapore, South Africa, Kenya, and Brazil. In India, social enterprises take different forms:
Non-Profit Organizations (NPOs): These are usually set up as non-governmental organizations (NGOs) under structures like Section 8 Companies, Trusts, or Societies.
For-Profit Enterprises (FPEs): These operate as private limited companies, partnerships, or sole proprietorships.
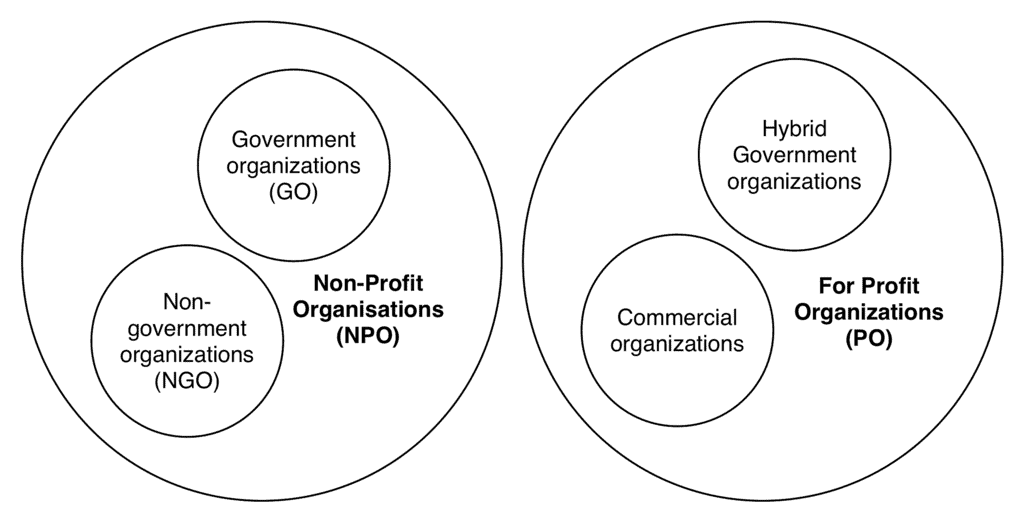 NGO vs FPE
NGO vs FPE
Social enterprises primarily rely on philanthropic funds from governments, international donors, or corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Shift Towards Socially Responsible Development: Due to the sustainable development goals of the UNO, India recognizes the importance of inclusive and socially responsible development.
Corporate Adoption of ESG Framework: The corporate sector is adopting measures to ensure their activities don't harm society or the environment, shifting towards an Environmental Social Governance (ESG) framework in investing.
Introduction of Social Stock Exchange (SSE): In the Union Budget 2019-20, the Indian government proposed the creation of an SSE under SEBI for social enterprises to raise capital through equity, debt, or units like a Mutual Fund.
SEBI Guidelines for SSE: Following recommendations from a Working Group chaired by Ishaat Hussain, SEBI announced guidelines in June 2020 for setting up the SSE.
Leveraging Existing Stock Exchanges: According to SEBI, the SSE can be housed within existing stock exchanges (e.g., BSE and/or NSE) to leverage their infrastructure and client relationships.
Onboarding Investors, Donors, and Social Enterprises: This approach helps the SSE onboard investors, donors, and both for-profit and non-profit social enterprises, creating a platform for socially responsible investments.
The Social Stock Exchange (SSE), serving both for-profit and non-profit social enterprises, will play two key roles:
- Facilitating Fundraising:
- For For-Profit Enterprises (FPEs), it will enable fundraising through equity and Social Venture Funds (SVFs).
- Non-Profit Organizations (NPOs) can use fundraising instruments like Zero coupon zero principal bonds, SVFs, Mutual Funds (MFs), pay-for-success structures, and other evolving securities and units.

- Section 8 Companies can access funding through equity and debt.
- Sector Development Support: Establishing a capacity-building unit with responsibilities including:
 SRO
SRO- Implementing reporting standards for all social enterprises benefiting from the SSE.
- Encouraging the formation of a self-regulatory organization (SRO) that brings together existing information repositories for immediate support to the SSE.
- Operating a capacity-building fund to enhance reporting capabilities for NPOs, especially smaller ones, and creating awareness among NPOs, philanthropists, and donors.
- Actively promoting the available fundraising instruments and structures on the SSE among social enterprises and NPOs.
2022-23 & Beyond
The year 2022-23, until December, had a mix of results, but it did better than many other countries, including the USA. Here are the main points:
The market where new securities are issued (primary market) did well, even with global financial uncertainty. More companies got listed on stock exchanges, a 37% increase compared to the previous year.
The standout event was LIC's listing in May 2022, the largest Initial Public Offering (IPO) in India's history and the fifth-largest globally.
In the primary market, where companies issue debt, there was a 10% increase in activity, but the total money raised went down by 27%.
The prices of things like crude oil, metals, and food shot up suddenly due to conflicts like the one between Russia and Ukraine.
Despite some troubles in global markets, the Indian stock market showed strength. A key index, Nifty-50, saw a 3.7% return, and even when measured in US dollars, it stood at 4.7%. The Sensex, another important index, closed 3.9% higher by December 2022 compared to its level on March 31, 2022.
 NASDAQ Index as of September 2021
NASDAQ Index as of September 2021During the same period, the US stock market, as measured by the S&P 500 Average Index, declined by 15.3%, and the NASDAQ Composite, focused on technology companies, dropped significantly by 26.4%. India performed better than other major emerging market economies from April to December 2022.
|
108 videos|425 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on Ramesh Singh Summary: Security Market in India- 3 - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs)? |  |
| 2. What regulatory measures have been implemented amid COVID-19? |  |
| 3. What is the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC)? |  |
| 4. What is the Financial Stability Assessment Programme (FSAP)? |  |
| 5. What is the role of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF)? |  |
















