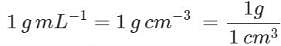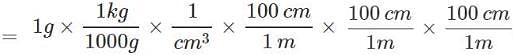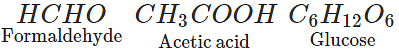Q.1. When do zeros present in a number become insignificant?
Ans. The zeros written to the left of the first non-zero digit in a number are insignificant. For example, in the number 0.014, both the zeros are insignificant.
Q.2. Is velocity a basic or derived quantity according to S.I. system?
Ans. Velocity is a derived quantity and it depends upon two basic quantities i.e. distance and time. The SI units of velocity are: Velocity = Distance/Time = ms−1
Q.3. Which is the more precise measurement of the length of a thread
(i) 10.0 cm (ii) 10.00 cm?
Ans. The measurement 10.0 cm represents a length between 9.9 cm and 10.1 cm while the measurement 10.00 cm is between 9.99 cm and 10.010 cm. This means that the measurement of 10.00 cm is the most precise representation.
Q.4. Why do we regard the gaseous state of water as vapours while that of ammonia as gas?
Ans. Only the gaseous states of those substances are regarded as vapours which are liquid at room temperature. Since water is a liquid, its gaseous state is called vapours. However, the gaseous state of ammonia is called gas because it is not a liquid at room temperature.
Q.5. Why is distilled water a compound while tap water a mixture?
Ans. Distilled water contains only H2O molecules since it is free from impurities. It is, therefore, a compound. Since some impurities such as dust particles etc. are normally mixed with tap water, it is, therefore, a mixture.
Q.6. Mixture of salt and water is a solution while that of oil and water is not. Explain.
Ans. The solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more components. The mixture of salt and water is generally homogeneous. Therefore, it is a solution. Oil and water on the other hand, form a heterogeneous or immiscible mixture. Therefore, it is not a solution.
 Mixture of Oil and Water
Mixture of Oil and Water
Q.7. When is the law of definite proportions not obeyed?
Ans. The law of definite proportions is not obeyed when the element exists in isotopic forms. For example, in HCl the elements H and Cl may be in the ratio of 1: 35 and 1: 37 by mass in case 35Cl and 37Cl isotopes are considered.
Q.8. Which law co-relates the mass and volume of a gas?
Ans. It is the Avogadro's Law and states that equal volumes of all gases under similar conditions of temperature and pressure contain equal number of moles (or molecules).
Q.9. Atomic mass of oxygen is 16 u. What does its indicate?
Ans. It indicates that the mass of an oxygen atom is 16 times more than 1/12th of the mass of carbon atom (C-12).
Q.10. An element has fractional atomic mass. What does it indicate?
Ans. It indicates that the element exists in the form of isotopes and its atomic mass is an average atomic mass.
Q.11. What is the difference between the mass of a molecule and molecular mass?
Ans. Mass of a molecule is that of a single molecule also known as its actual mass. But molecular mass is the mass of Avogadro's number (6.022 × 1023) of molecules.
Q.12. Where do we use the words mole and mol?
Ans. In the text part, we use the word mole while as a unit, we call it mol.
Q.13. Does one gram mole of a gas occupy 22.4 L under all conditions of temperature and pressure?
Ans. No, one gram mole of a gas occupies 22.4 L only under N.T.P. or S.T.P. conditions, i.e. at 273 K temperature and under 760 mm pressure. If these conditions are not used, then the volume is not 22.4 L.
Q.14. What is the basic difference between empirical and molecular formulae?
Ans. Empirical formula gives the simplest ratio of the atoms of different elements in the molecule of a substance but the molecular formula gives their actual ratio.
Q.15. The percentages of all the elements present in a compound are 92. What does it indicate?
Ans. This indicates that the compound contains in it oxygen also and its percentage is (100 - 92) = 8.
Q.16. Why is it necessary to balance a chemical equation?
Ans. A chemical equation has to be balanced in order to satisfy the law of conservation of mass. According to the law, there is no change in mass when the reactants change into the products. Therefore, the chemical equation has to be balanced.
Q.17. In the combustion of methane, why is methane regarded as the limiting reactant?
Ans. Methane (CH4) is regarded as the limiting reactant because air or oxygen is always present in excess. The amounts of CO2 and H2O formed in the reaction depend upon the amount of methane only. Therefore, it is regarded as the limiting reactant.
Q.18. What is the difference between molarity and molality?
Ans. By definition, molarity (M) of a solution is the number of moles of the solute dissolved per litre of the solution and molality (m) is the number of moles of the solute dissolved per kilogram of the solvent. Therefore, in molarity, volume of the solution is considered while in molality, mass of the solvent is taken into consideration.
Q.19. Classify the following substances into elements, compounds and mixtures : (i) Milk (ii) 22-carat gold (iii) Iodized table salt (iv) Diamond (v) Smoke (vi) Steel (vii) Brass (viii) Dry ice (ix) Mercury (x) Air (xi) Aerated drinks (xii) Glucose (xiii) Petrol/Diesel/Kerosene oil (xiv) Steam (xv) Cloud.
Ans. Elements - (iv), (ix) Compounds - (viii), (xii), (xiv), (xv) Mixtures - (i), (ii), (iii), (v), (vi), (vii), (x), (xi), (xiii).
Q.20. Why is air sometimes considered as a heterogeneous mixture?
Ans. This is due to the presence of dust particles which form a separate phase.
Q.21. What physical quantities are represented by the following units and what are their most common names?
(i) kgms−2
(ii) kgm2s−2
(iii) dm3
Ans.
(i) Force (newton)
(ii) Work (joule)
(iii) Volume (no special name).
Q.22. Rewrite the following after necessary corrections:
(i) The length of a rod is 10 cms.
(ii) The work done by a system is 10 Joules.
Ans.
(i) The length of a rod is 10 cm (s is not used).
(ii) The work done by a system is 10 joules (small letter is used in place of capital letter).
Q.23. Given that density of water is 1gmL−1. What is its density in kgm−3?
Ans.


= 1000 kg m-3
Q.24. What is the difference between the following?
(i) 2⋅5 × 103 g and 2⋅50 × 103g
(ii) 160 cm and 160.0 cm.
Ans.
(i) 2⋅5 × 103g has two significant figures while 2⋅50 × 103g has three significant figures. Hence, 2⋅50×103g represents greater accuracy than 2⋅5×103.
(ii) 160 has three significant figures while 160.0 has four significant figures. Hence, 160.0 represents greater accuracy.
Q.25. Why Law of conservation of mass should better be called as Law of conservation of mass and energy?
Ans. In nuclear reactions, it is observed that the mass of the products is less than the mass of the reactants. The difference of mass, called the mass defect, is converted into energy according to Einstein equation, E = Δmc2. Hence, we better call it as a law of conservation of mass and energy.
Q.26. Is the law of constant composition true for all types of compounds? Explain why or why not.
Ans. No, law of constant composition is not true for all types of compounds. It is true only for the compounds obtained from one isotope. For example, carbon exists in two common isotopes, 12C and 14C. When it forms CO2 from 12C, the ratio of masses is 12 : 32 = 3 : 8 but from 14C, the ratio will be 14 : 32 = 7 : 16 which is not same as in the first case.
Q.27. 1 L of a gas at S.T.P. weighs 1.97 g. What is the vapour density of the gas?
Ans. 22.4 L of the gas at S.T.P. will weigh = 1.97 × 22.4g = 44.1 g , i.e., molecular mass = 44.1. Hence, vapour density = 44.1/2 = 22.05.
Q.28. What is the difference in the molar volume of a gas if S.T.P. conditions are
(i) 1 atm,0∘C
(ii)1 bar,0∘C?
Ans.
(i) If S.T.P. conditions are 1 atm, 0∘C molar volume = 22400 cm3
(ii) If S.T.P. conditions are 1 bar, 0∘C, molar volume = 22700 cm3
Q.29. Why atomic masses are the average values?
Ans. Most of the elements exist in different isotopes, i.e., atoms with different masses,
Example: Cl has two isotopes with mass numbers 35 and 37 existing in die ratio 3 : 1. Hence, average value is taken.
Q.30. Why are the atomic masses of most of the elements fractional?
Ans. This is because atomic masses are the relative masses of atoms as compared with an atom of C-12 isotope taken as 12.
Q.31. What is die difference between the mass of a molecule and gram molecular mass?
Ans. Mass of a molecule is the actual mass of a single molecule expressed in grams whereas gram molecular mass is the mass in gram of Avogadro's number of molecules.
Q.32. Why molality is preferred over molarity in expressing the concentration of a solution?
Ans. Molality is the number of moles of the solute present in 1 kg of the solvent whereas molarity is the number of moles of the solute present per litre of the solution. Thus, molality involves only masses which do not change with temperature whereas molarity involves volume which changes with temperature. Hence, molality is preferred over molarity.
Q.33. Write the formulae and names of three compounds containing same percentage composition of C, H and O.
Ans. Compounds with the same percentage composition of C, H and O will have the same empirical formula. The compounds with the empirical formula CH2O can be 
Q.34. Determine the equivalent weight of each of the following compounds assuming the formula weights of these compounds are x, y and z respectively.
(i) Na2SO4
(ii) Na3PO4.12H2O
(iii) Ca3(PO4)2
Ans.
Eq wt = Mol. wt/Total positive valency of metal atoms
(i) x/2
(ii) y/3
(iii) z/6
 Mixture of Oil and Water
Mixture of Oil and Water