Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Question Answers - Carbon and its compounds
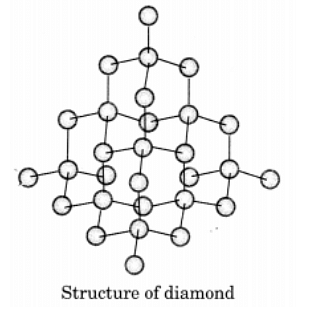
Q1. Why does graphite conduct electricity, but not a diamond?
Ans: 
Graphite is a crystalline form of carbon that conducts electricity due to its unique structure. Key points include:
- Each carbon atom in graphite is bonded to three other carbon atoms through strong bonds.
- The fourth electron of each carbon atom is free to move, which facilitates electrical conductivity.
- In contrast, diamonds have a tetrahedral bonding arrangement where all four electrons are involved in bonds.
- This means diamonds lack free electrons, making them poor conductors of electricity.
The differences in atomic structure between graphite and diamonds explain their contrasting electrical properties.
Q2. Write three important uses of ethanol.
Ans:
- Solvent: Ethanol effectively dissolves varnishes, medicines, and various organic compounds.
- Beverage: It is a popular ingredient in alcoholic drinks such as brandy and whisky.
- Industrial Use: Ethanol is commonly used in denatured spirit for industrial applications.
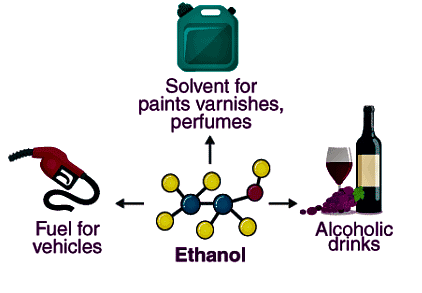 Uses of Ethanol
Uses of Ethanol
Q3. State what you will observe when sugar crystals are heated strongly.
Ans:
When sugar crystals are heated strongly, you will observe the following:
- The sugar will melt initially.
- As heating continues, it will turn brown and begin to swell.
- A large amount of steam will be released.
- Finally, a black, porous residue of carbon, known as charred sugar, will remain.
This process is a chemical change and can be summarised by the equation:
C12H22O11 + heat → 12 C + 11 H2O + other compounds.

Q4. How are the molecules of aldehyde and Ketone structurally different? [Old NCERT]
Ans:
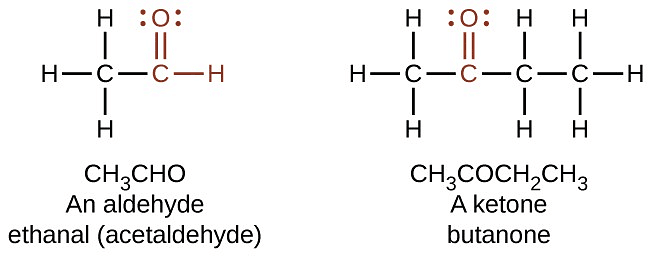
Aldehyde and ketone molecules differ structurally in the following ways:
- Aldehyde: The carbon atom in the carbonyl group is bonded to one alkyl group (R) and one hydrogen atom.
- Ketone: The carbonyl group is attached to two alkyl groups.
- Aldehydes are terminal functional groups, while ketones are non-terminal, located in the middle of the carbon chain.
Q5. A hydrocarbon molecule contains 4 hydrogen atoms. Give its molecular formula, if it is an:
(i) Alkane
(ii) alkene
(iii) alkyne.
Ans:
(i) An alkane with 4 hydrogen atoms is methane, CH4.
(ii) An alkene with 4 hydrogen atoms is ethene, C2H4.
(iii) An alkyne with 4 hydrogen atoms is propyne, C3H4.
Q6. Why is common salt added in soap making?
Ans:Common salt is added to soap making for several reasons:
- It helps the soap to separate from the solution.
- While most soap naturally separates, some remains dissolved.
- Soap is less soluble in salt water than in pure water.
- Adding salt causes soap molecules to group together, forming solid clumps.
- This process is known as salting out.
The chemical reaction involved in soap making is:
Fat + NaOH → Soap + Glycerol
This illustrates a saponification reaction, where fat or oil reacts with a base to produce soap and glycerol.
Q7. What is meant by denatured alcohol? What is the need to denature alcohol? [Old NCERT]
Ans:Denatured alcohol is ethanol that has been made undrinkable by adding poisonous substances, such as:
- Methanol
- Pyridine
- Copper sulphate
Denaturing alcohol serves several purposes:
- It prevents misuse for drinking.
- It allows ethanol to be used in industrial applications with lower excise duty.
Overall, denaturing is essential to ensure that alcohol is used safely and legally in industrial contexts.
Q8. What is meant by the term “functional group”?
Ans:A functional group in an organic compound refers to a specific atom or a group of atoms that are bonded together in a distinctive way. This configuration typically serves as the site of chemical reactivity within the organic molecule. 
Q9. Draw the structural formula of ethyne. [Old NCERT]
Ans:
Ethyne is the simplest alkyne with the chemical formula C2H2. It features:
- A triple bond between the two carbon atoms.
- A single bond with one hydrogen atom on each carbon.
The structural formula of ethyne is:
H – C ≡ C – H
Q10. Why are detergents better cleansing agents than soaps? Explain. [Old NCERT]
Ans:
Detergents and soaps are both cleaning agents, but they have different properties:
- Detergents are sodium salts of long-chain benzene sulfonic acids.
- They work effectively in hard water and acidic solutions.
- Soaps are sodium and potassium salts of long-chain fatty acids.
- Soaps can form scum in hard water and break down in acidic environments.
- This limits the effectiveness of soaps compared to detergents.
Overall, detergents provide superior cleaning efficiency under various water conditions, making them more suitable for everyday use.
Q11. Name the functional groups present in the following compounds
(a ) CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3
(b ) CH3CH2CH2COOH
(c ) CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO
(d ) CH3CH2OH
Ans:
(a) A ketone functional group is present in the compound CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3.
(b) A carboxylic acid functional group is present in the compound CH3CH2CH2COOH.
(c) An aldehyde functional group is present in the compound CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO.
(d) An alcohol functional group is present in the compound CH3CH2OH.
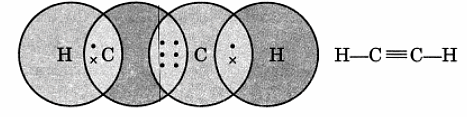
Q12. Draw the electron dot structure of ethyne and also draw its structural formula.
Ans:
Ethyne, or C2H2, has a simple electron dot structure and structural formula.
The electron dot structure shows the sharing of electrons between atoms:
- Each carbon (C) atom shares three electrons with the other carbon.
- Each carbon also shares one electron with a hydrogen (H) atom.
This can be represented as:
H - C ≡ C - H
The structural formula of ethyne visually represents the arrangement of atoms:
- It consists of two carbon atoms connected by a triple bond.
- Each carbon atom is bonded to one hydrogen atom.
Overall, ethyne is represented as:
H - C ≡ C - H
Q13. Draw the structures of diamond and graphite.
Ans:In diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms, creating a rigid three-dimensional structure. 
In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms in the same plane, forming a hexagonal array. One of these bonds is a double bond.
Q14. Catenation is the ability of an atom to form bonds with other atoms of the same element. Both carbon and silicon exhibit it. Compare the ability of catenation of the two elements. Give reasons. [Old NCERT]
Ans:Catenation is the ability of an atom to bond with other atoms of the same element. Both carbon and silicon demonstrate this property, but there are key differences in their abilities:
- Reactivity: Silicon compounds tend to be more reactive compared to those of carbon.
- Stability: Carbon forms very strong bonds, making its organic compounds more stable than silicon compounds.
- Catenation Strength: Overall, carbon exhibits better catenation due to its ability to form stable, long chains.
In summary, while both elements can catenate, carbon's stronger bonds lead to greater stability in its compounds.
Q15. Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain multiple bonds between the two C-atoms and show addition reactions. Give the test to distinguish ethane from ethene.
Ans:
The bromine water test is effective for distinguishing between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
- Saturated hydrocarbons, like ethane, do not react with bromine water.
- No change occurs in the reaction mixture, and the colour remains the same.
On the other hand:
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons, such as ethene, will react with bromine water.
- This reaction causes the bromine water to decolourise.
In summary:
- Saturated hydrocarbon + Br₂: No Reaction (No Colour Change)
- Unsaturated hydrocarbon + Br₂: Reaction occurs (Decolourisation)
Q16.A salt X is formed, and gas is evolved when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate. Name the salt X and the gas evolved. Describe an activity and draw a diagram of the apparatus to prove that the evolved gas is the one you have named. Also, write a chemical equation of the reaction involved. [Old NCERT]
Ans: The salt X is sodium ethanoate (CH3COONa), and the evolved gas is carbon dioxide (CO2).
To demonstrate that the evolved gas is carbon dioxide, follow these steps:
- Take a test tube and add ethanoic acid (CH3COOH).
- Add sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) to the acid.
- Seal the test tube with a cork and attach a delivery tube.
- Place lime water (Ca(OH)2) in another test tube and connect it to the delivery tube.
- Observe that the lime water turns milky, indicating the presence of carbon dioxide.
The equation for the reaction is:
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2 (g)
The milkiness in the lime water is due to the formation of calcium carbonate (CaCO3):
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
Q17. (a ) What are hydrocarbons? Give examples. (b ) What is a functional group? Give examples of four different functional groups.
Ans: Hydrocarbons are organic compounds consisting solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- Methane (CH₄)
- Ethane (C₂H₆)
A functional group is a specific group of atoms within a molecule that determines its chemical behaviour. These atoms are connected by covalent bonds.
- Hydroxyl group (-OH)
- Carboxyl group (-COOH)
- Amino group (-NH₂)
- Carbonyl group (C=O)
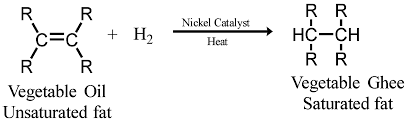
Q18. Name the reaction which is commonly used in the conversion of vegetable oils to fats. Explain the reaction involved in detail. [Old NCERT]
Ans: Vegetable oils typically contain long chains of unsaturated carbon atoms, whereas animal fats primarily consist of long chains of saturated carbon atoms. The process used to convert vegetable oils into fats is called hydrogenation.
This addition reaction involves the following key steps:
- Hydrogen gas is added to the oil.
- This reaction requires a catalyst, usually nickel (Ni).
- The unsaturated carbons in the oil bond with hydrogen, converting them into saturated carbons.
The result is a solid or semi-solid fat, which has a higher melting point than the original oil.
Q19. (a ) Write the formula and draw the electron dot structure of carbon tetrachloride. (b ) What is saponification? Write the reaction involved in this process. [Old NCERT]
Ans:
(a) The formula of carbon tetrachloride is CCl4.
Its electron dot structure shows carbon at the centre with four chlorine atoms surrounding it, each bonded to the carbon atom.
(b) Saponification is a method for making soap by hydrolysing fats or oils with a base, such as sodium hydroxide.
The reaction involved in this process is:
- CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH → CH3COONa + C2H5OH

Q20. A compound C (molecular formula, C2H4O2) reacts with Na – metal to form a compound R and evolves into a gas that burns with a pop sound. Compound C, on treatment with alcohol A in the presence of an acid, forms a sweet-smelling compound S (molecular formula, C3H6O2). In addition to NaOH to C, it also gives R and water. S on treatment with NaOH solution gives back R and A. Identify C, R, A, and S and write down the reactions involved. [Old NCERT]
Ans:
Compound Identifications:
- C: Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH)
- R: Sodium ethanoate (CH3COONa)
- A: Ethanol (C2H5OH)
- S: Ethyl ethanoate (CH3COOC2H5)
Reactions involved:
- Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium metal:
2 CH3COOH + 2 Na → 2 CH3COONa + H2- Ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of acid:
CH3COOH + C2H5OH → CH3COOC2H5 + H2O- Ethanoic acid reacts with NaOH:
CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O- Ethyl ethanoate reacts with NaOH:
CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH → CH3COONa + C2H5OH
Thus, compound C is ethanoic acid.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Question Answers - Carbon and its compounds
| 1. What are the main properties of carbon that make it unique among elements? |  |
| 2. What are the different allotropes of carbon, and how do they differ? |  |
| 3. How do carbon compounds differ from inorganic compounds? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of carbon in organic chemistry? |  |
| 5. What are some common uses of carbon compounds in everyday life? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|













